
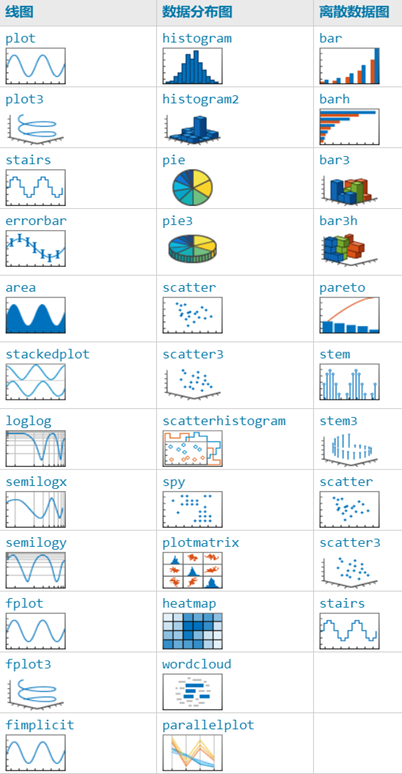
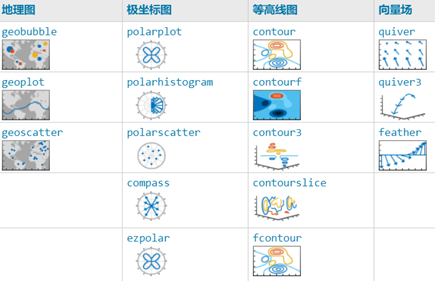
As we all know, MATLAB is not only adept at handling numerical computations related to matrices, but it also has a deep foundation in scientific visualization. The many feature-rich functions it provides can very well meet our diverse needs for displaying numerical information graphically.
MATLAB has the capability to represent graphics in two dimensions, three dimensions, and even four dimensions. It can express data characteristics through aspects such as line style, boundary color, color, rendering, lighting, and perspective.
The visualization capabilities of MATLAB are built on a set of graphic objects. At the core of graphic objects is the operation of graphic handles (Graphics Handle).
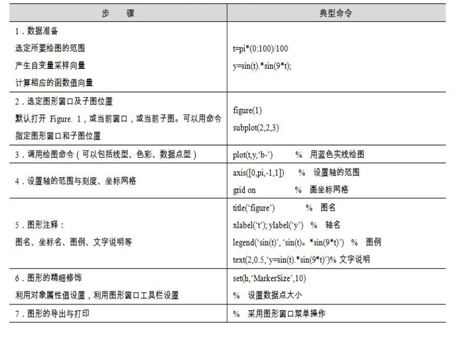
Some commonly used low-level commands are as follows:
gcf: Returns the handle of the current window object (Get Current Figure)
gca: Returns the handle of the current axes object (Get Current Axes)
gco: Returns the handle of the current graphic object (Get Current Object)
get: Obtains the properties of the handle graphic object and returns certain object handle values
set: Changes the properties of the graphic object
This article mainly introduces some high-level plotting commands related functions:

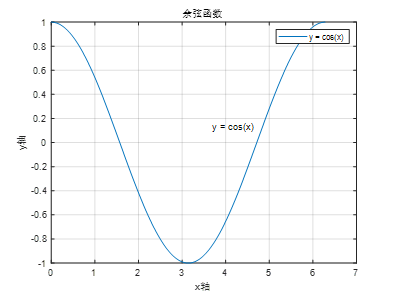
x=0:0.01:2*pi;
y=cos(x);
plot(x,y);
xlabel(‘x-axis’); % x-axis annotation
ylabel(‘y-axis’); % y-axis annotation
title(‘Cosine Function’); % Graph title
legend(‘y = cos(x)’); % Graph annotation
gtext(‘y = cos(x)’); % Graph annotation, use mouse to position annotation
grid on; % Show grid lines
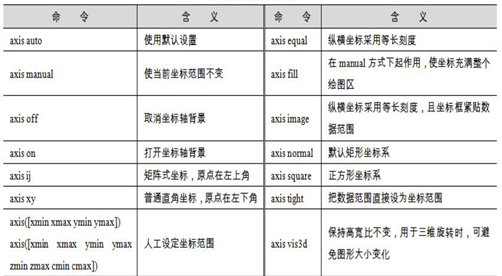
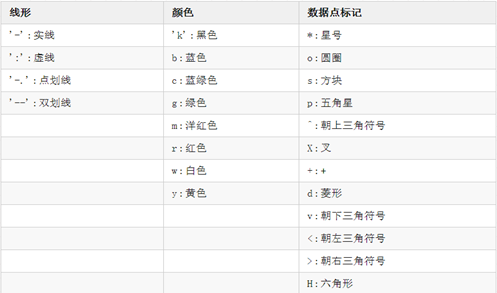
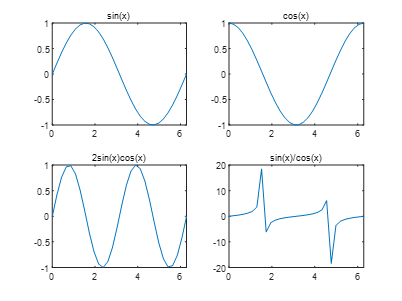
Create several coordinate systems on the same screen using the subplot(m,n,p) command;
Divide one screen into m×n graphic areas, where p represents the current area number, and draw a graph in each area.
x=linspace(0,2*pi,30);y=sin(x); z=cos(x);
u=2*sin(x).*cos(x);v=sin(x)./cos(x);
subplot(2,2,1),plot(x,y),axis([0 2*pi -1 1]),title(‘sin(x)’)
subplot(2,2,2),plot(x,z),axis([0 2*pi -1 1]),title(‘cos(x)’)
subplot(2,2,3),plot(x,u),axis([0 2*pi -1 1]),title(‘2sin(x)cos(x)’)
subplot(2,2,4),plot(x,v),axis([0 2*pi -20 20]),title(‘sin(x)/cos(x)’)
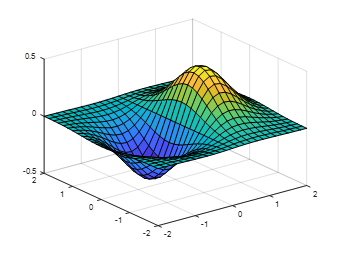
For 3D plotting in MATLAB, the most commonly used functions are surf and mesh, along with their derived functions.
x=linspace(-2,2, 25); % Take 25 points on the x-axis y=linspace(-2, 2, 25); % Take 25 points on the y-axis [xx,yy]=meshgrid(x, y); % xx and yy are both 21×21 matrices zz=xx.*exp(-xx.^2-yy.^2); % Calculate function values, zz is also a 21×21 matrix surf(xx, yy, zz); % Draw the 3D surface plot
Using the peaks function as an example, plot in various ways 1. meshz can add a skirt to the surface: [x,y,z]=peaks;meshz(x,y,z);axis([-inf inf -inf inf -inf inf]);
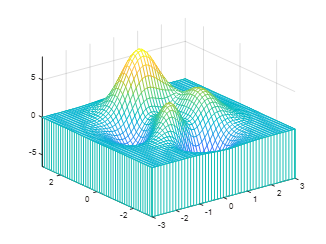
2. waterfall can create a water flow effect in the x or y direction:[x,y,z]=peaks;waterfall(x,y,z);axis([-inf inf -inf inf -inf inf]);
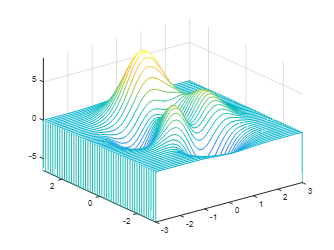
3. Water flow effect in the y direction:[x,y,z]=peaks;waterfall(x’,y’,z’);axis([-inf inf -inf inf -inf inf]);
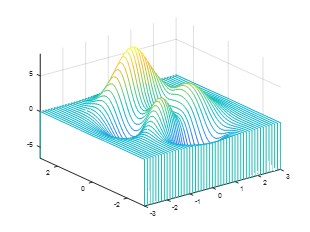
4. meshc can simultaneously draw a mesh graph and contour lines: [x,y,z]=peaks;meshc(x,y,z);axis([-inf inf -inf inf -inf inf]);
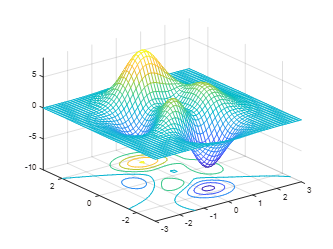
5. surfc can simultaneously draw a surface plot and contour lines:[x,y,z]=peaks;surfc(x,y,z);axis([-inf inf -inf inf -inf inf]);
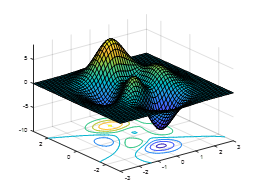
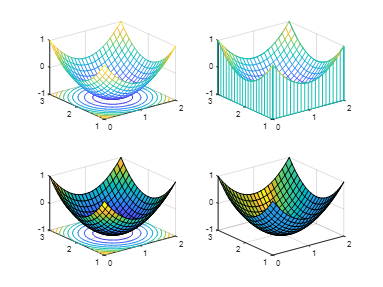
6. Comparing the functions meshc, meshz, surfc, and surfl
[x,y]=meshgrid(0:0.1:2,1:0.1:3)
z=(x-1).^2+(y-2).^2-1
subplot(2,2,1);meshc(x,y,z)
subplot(2,2,2);meshz(x,y,z)
subplot(2,2,3);surfc(x,y,z)
subplot(2,2,4);surfl(x,y,z)
For example, using the same color map, draw a cone using different coloring methods.
[x,y,z] =cylinder(pi:-pi/5:0,10)
colormap(lines)
subplot(1,3,1)
surf(x,y,z);
shading flat
subplot(1,3,2)
surf(x,y,z);
shading interp
subplot(1,3,3)
surf(x,y,z)

Author: Senior Zhang from Extreme Value Academy
Previous Recommendations
1. How to register for the Mathematical Contest in Modeling?
2. What kind of team should you form? Will couples break up if they team up?
3. How should you choose a topic for modeling in the Mathematical Contest in Modeling? Why is Problem F a language modeling problem?
4. Why participate in the Mathematical Contest in Modeling? Why do HR value this competition?
5. What preparations should you make before the end of the semester for the Mathematical Contest in Modeling?
6. What preparations should you make after the end of the semester for the Mathematical Contest in Modeling?
7. Why should there be dual leaders? What should each be responsible for?
8. What two violations should you pay attention to when participating in the Mathematical Contest in Modeling?
9. Competition Skills: How to maintain a reasonable schedule? How to adjust your mindset?
10. Competition Skills: Why should there be no communication during problem analysis?
11. Competition Skills: Your paper was evaluated in 10 minutes?
12. Competition Skills: How can you win the O award and F award?
13. Paper Structure: If the model assumptions are well written, the paper won’t be bad!
14. Paper Structure: How to write the main body of the paper for the Mathematical Contest in Modeling?
15. Paper Writing: How to write the key abstract?
16. Mathematical modeling textbook PDF written by expert Frank Giordano
17. Public Course 1: Common Heuristic Algorithms – Artificial Application Network
18. 2021 Mathematical Contest in Modeling C Problem Data Released Early, How to Analyze and Process with Python?

