★
Embedded AI Series – Converting YOLOv3 Model Using RKNN Toolkit
”
1 Introduction
- Since my development work is primarily focused on AI applications in machine vision, the commonly used model is the YOLO model. Therefore, I will demonstrate the conversion of the YOLOv3 model using the example code from the RKNN toolkit in the darknet directory.
- The YOLOv3 model is quite old, and it is no longer used in current projects. The reason for using YOLOv3 in this section is to minimize changes to the original example code of the RKNN toolkit, ignoring some parameter details in the original code, and focusing on demonstrating the model conversion process of the RKNN toolkit.
2 Introduction to RKNN Toolkit Model Conversion
2.1 Why Convert Models
Various deep learning frameworks, such as TensorFlow and PyTorch, export AI models that cannot be directly inferred on Rockchip’s NPU chips. They need to be converted into the RKNN format that the RK NPU can process.
2.2 RKNN Toolkit Model Conversion Process
The basic workflow for model conversion using the RKNN toolkit is as follows:
- Start
- -> Create an RKNN object to initialize the RKNN SDK environment
- -> Call the config interface to set parameters such as model preprocessing and quantization methods
- -> Call load_caffe, load_darknet, load_keras, load_mxnet, load_onnx, load_pytorch, load_tensorflow, load_tflite interfaces to import the original Caffe, Darknet, Keras, MXNet, ONNX, PyTorch, TensorFlow, and TensorFlow Lite models
- -> Call the build interface to construct the RKNN model
- -> Call the export_rknn interface to export the RKNN model
- -> Call the release interface to free the RKNN object
- End
2.3 Model Quantization
- During the model conversion process, model quantization is required. A simple explanation of model quantization is to reduce the size of the model, making the model file smaller, consuming less memory during loading and execution, and running faster, which is especially important for embedded environments, but it may result in a loss of accuracy or performance.
- Model quantization is a highly specialized task, and we will temporarily ignore it and use the default settings.
3 Writing Python Code for Model Conversion
3.1 Preparing Example Code
In the previous article “Embedded AI Series – Installing RKNN Toolkit”, I downloaded v1.7.5.tar.gz. After extracting this archive, navigate to the directory rknn-toolkit-1.7.5:
# cd /work/rk/download/; tar xvzf v1.7.5.tar.gz -C ..# cd ../rknn-toolkit-1.7.5/3.2 Writing Python Code for YOLOv3 Model Conversion
Darknet is the deep learning framework that birthed the YOLO model. Although the PyTorch version of YOLO has become mainstream in modern practice, understanding the classic principles of YOLO still requires knowledge of Darknet.
In the rknn-toolkit-1.7.5 directory, under examples/darknet/yolov3/, there is a Python file: test.py, which has two main functions:
- Convert the YOLOv3 model to RKNN format;
- Use the exported RKNN model to infer and recognize an image.
This section will focus only on model conversion, so I have written convert.py based on the original test.py, which only performs the YOLOv3 model conversion.
This file should also be placed in the directory examples/darknet/yolov3/, and the content of convert.py is as follows:
# file: convert.pyimport platformimport sysimport numpy as npimport urllib.requestfrom rknn.api import RKNN
if __name__ == '__main__':
MODEL_PATH = './yolov3.cfg' WEIGHT_PATH = './yolov3.weights' RKNN_MODEL_PATH = './yolov3_416.rknn' DATASET = './dataset.txt' target = 'rv1126'
# Create and initialize RKNN object rknn = RKNN()
# Set model parameters rknn.config(reorder_channel='0 1 2', mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]], std_values=[[255, 255, 255]], target_platform=[target])
# Load Darknet model print('--> Loading model') ret = rknn.load_darknet(model=MODEL_PATH, weight=WEIGHT_PATH) if ret != 0: print('Load darknet model failed!') rknn.release() exit(ret) print('done')
# Build corresponding RKNN model based on the loaded model structure and weight data. print('--> Building model') ret = rknn.build(do_quantization=True, dataset='./dataset.txt') if ret != 0: print('Build model failed.') rknn.release() exit(ret) print('done')
# Save RKNN model to the specified file (with .rknn suffix) print('--> Export RKNN model') ret = rknn.export_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_PATH) if ret != 0: print('Export RKNN model failed.') rknn.release() exit(ret) print('done')
# Release RKNN object rknn.release()3.3 Introduction to Main Functions of convert.py
- RKNN(): When using all API interfaces of the RKNN Toolkit, you must first call the RKNN() method to initialize the RKNN object. This function has two optional parameters: verbose and verbose_file. The verbose parameter specifies whether to print detailed log information on the screen; if the verbose_file parameter is set and the verbose parameter is True, the log information will also be written to the file specified by this parameter.
- config(): Before constructing the RKNN model, you need to configure parameters such as channel mean, channel order, and quantization type. These operations can be configured through the config interface. The parameters of this function will not be explored in depth for now.
- load_* series functions: The RKNN Toolkit currently supports loading and converting models from Caffe, Darknet, Keras, MXNet, ONNX, PyTorch, TensorFlow, and TensorFlow Lite. When converting different models, you need to call the corresponding interface for loading. In this section, we use load_darknet().
- build(): Construct the corresponding RKNN model based on the loaded model structure and weight data.
- export_rknn(): Save the RKNN model to the specified file (with .rknn suffix).
- release(): Release the RKNN object after use.
4 Converting YOLOv3 Model to RKNN Format
4.1 Introduction to Core Files of YOLOv3
The convert.py file uses two core files of YOLOv3: yolov3.cfg and yolov3.weights.
- yolov3.cfg is the configuration file for the model, defining the architecture of the YOLOv3 model and detailing the neural network structure of YOLOv3. However, it is just a shell and cannot perform effective object recognition.
- yolov3.weights is the weight file for the model, containing all the parameter values learned by the model after training. In simple terms, it is the “knowledge” that the model has learned, and with this “knowledge,” it can recognize objects.
When the configuration file yolov3.cfg and the weight file yolov3.weights are loaded together, a trained YOLO model is obtained.
4.2 Manually Downloading yolov3.weights
The yolov3.cfg file is already present in examples/darknet/yolov3/, but yolov3.weights is missing and needs to be downloaded separately. The link for yolov3.weights in the original example code test.py is no longer valid, so I found another link online, which needs to be manually downloaded from the web. The file size is approximately 248MB, and the URL is:
https://sourceforge.net/projects/yolov3.mirror/files/v8/yolov3.weights/, After downloading, place it in the examples/darknet/yolov3/ directory.
4.3 Checking the Integrity of yolov3.weights
Since yolov3.weights is large, it may not download completely due to network issues. You can check the integrity of the file by calculating its MD5 value. Using the following command will yield the MD5 value of yolov3.weights:
# md5sum yolov3.weights // Correct value: c84e5b99d0e52cd466ae710cadf6d84c4.4 Model Conversion
Use convert.py to convert the YOLOv3 model to RKNN format by executing the following command:
# python3 convert.pyDuring the conversion process, there will be warnings about deprecated functions, which can be ignored. Finally, we successfully exported the required RKNN model yolov3_416.rknn, with a model size of 60MB, which meets expectations:
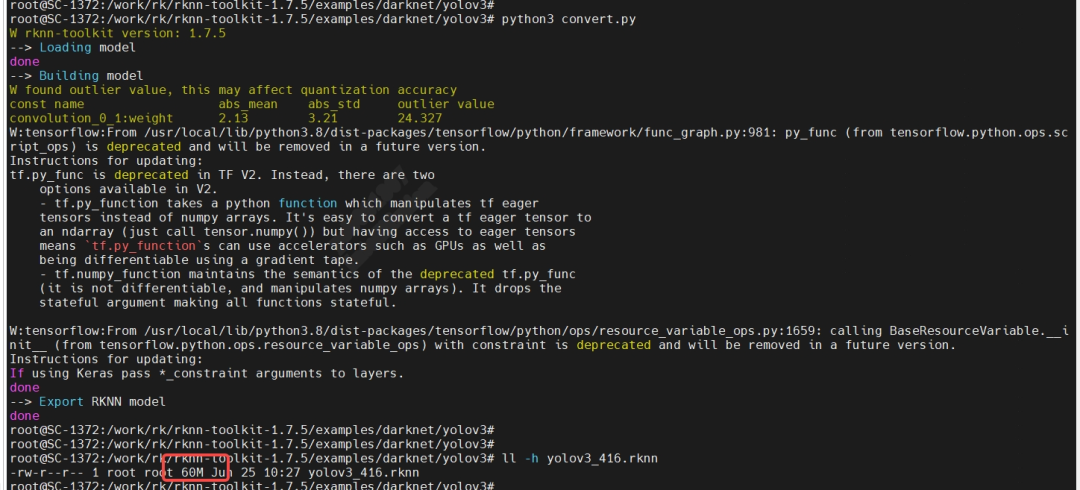
4.5 Verifying the Converted RKNN Model
If there is a development board connected to the environment where the RKNN toolkit is located, you can use the example code test.py provided by the RKNN toolkit to perform object recognition on an image to verify the RKNN model. However, I do not have a development board, only a factory product with the RV1126 chip as the hardware platform for development experiments. In the future, I will write C++ code to run the converted RKNN model directly in the factory product to verify its functionality.