As we all know, the main focus of Da Pang at work is to slack off. Last year, I was assigned a small RK3588S-PC host for a work project. Previously, I was busy customizing the system for the AIO-3588Q and had downloaded the official RK Linux SDK for source code compilation. However, there was an issue with the kernel driver compilation for the Ubuntu 20.04 version provided by RK; the module parameters added directly in the kernel’s config file do not take effect. Instead, you need to find the corresponding configuration file in RK’s device tree file to make modifications. Generally, the modification of Linux kernel module parameters is done in the rockchip_linux_defconfig file. Additionally, there is also a firefly-linux.config that is related to the kernel. Some parameters added in the rockchip_linux_defconfig file do not take effect during the system kernel compilation, which I suspect is due to filtering in RK’s compilation script. I won’t elaborate on the issues here; I will break them down later when I have time. To get to the point, the star of this issue is Waydroid. The official description is: a container-based method for launching a complete Android system on a regular GNU/Linux system running a Wayland-based desktop environment. In simple terms, it runs an Android system using LXC on a Linux system. To put it more plainly: Waydroid is an Android emulator based on container technology that can smoothly run Android applications in a Linux desktop environment (you can really open Android applications directly in the Linux desktop  ).
). Waydroid requires a Wayland desktop environment, which means you need to have Ubuntu version 22.04 or higher. In version 22.04, you need to manually modify the /etc/gdm3/custom.conf configuration file to set WaylandEnable=true, and then restart the gdm3 service. I recommend going straight to Ubuntu 24.04, as the system defaults to a Wayland desktop environment, and the kernel version is also updated. Currently, the latest official firmware is still the Ubuntu 22.04 version, so I recommend downloading the Ubuntu 24.04 firmware directly from the Ubuntu Rockchip community. Community address: https://joshua-riek.github.io/ubuntu-rockchip-download/, and mainstream Rockchip development boards all have firmware available.Installing Waydroid is quite simple; you can do it with just three commands:
Waydroid requires a Wayland desktop environment, which means you need to have Ubuntu version 22.04 or higher. In version 22.04, you need to manually modify the /etc/gdm3/custom.conf configuration file to set WaylandEnable=true, and then restart the gdm3 service. I recommend going straight to Ubuntu 24.04, as the system defaults to a Wayland desktop environment, and the kernel version is also updated. Currently, the latest official firmware is still the Ubuntu 22.04 version, so I recommend downloading the Ubuntu 24.04 firmware directly from the Ubuntu Rockchip community. Community address: https://joshua-riek.github.io/ubuntu-rockchip-download/, and mainstream Rockchip development boards all have firmware available.Installing Waydroid is quite simple; you can do it with just three commands:
sudo apt install curl ca-certificates -y # Install curl and CA certificatescurl -s https://repo.waydro.id | sudo bash # Add Waydroid software repositorysudo apt install waydroid -y # Install WaydroidAfter installing Waydroid, there will be a Waydroid application in the desktop applications. Clicking on the application will start Waydroid. However, on the RK3588S-PC, there is an issue: before starting Waydroid, you need to modify the Waydroid configuration file because Waydroid does not support the Mali-G610 graphics driver of RK3588 and needs to use software rendering mode. Modify the following two properties in the /var/lib/waydroid/waydroid.cfg configuration file:
ro.hardware.gralloc=defaultro.hardware.egl=swiftshaderAfter modification, you can start Waydroid. The first time you start it, it will download the official Android image, which defaults to lineage-18.1 version (Android 11). The latest official version has released lineage-20.0 version (Android 13), which needs to be manually downloaded from SourceForge. Download link: https://sourceforge.net/projects/waydroid/. Thanks to RK3588 being an ARM platform, it can natively support Android applications, allowing apps like WeChat and Douyin to be installed and run normally. Waydroid also supports multi-window mode, which needs to be manually enabled with the command:
waydroid prop set persist.waydroid.multi_windows trueAfter enabling multi-window mode, you can run apps installed in Waydroid simultaneously in the foreground, allowing you to browse Bilibili in Linux  . However, due to the limitations of the graphics driver in software rendering mode, it cannot run games well. Currently, Waydroid only supports ADM and Intel graphics; other graphics cards need to use software rendering mode. Additionally, Waydroid can also be installed and run on x86 platforms, and third-party translation libraries can be installed to support running ARM architecture apps.
. However, due to the limitations of the graphics driver in software rendering mode, it cannot run games well. Currently, Waydroid only supports ADM and Intel graphics; other graphics cards need to use software rendering mode. Additionally, Waydroid can also be installed and run on x86 platforms, and third-party translation libraries can be installed to support running ARM architecture apps.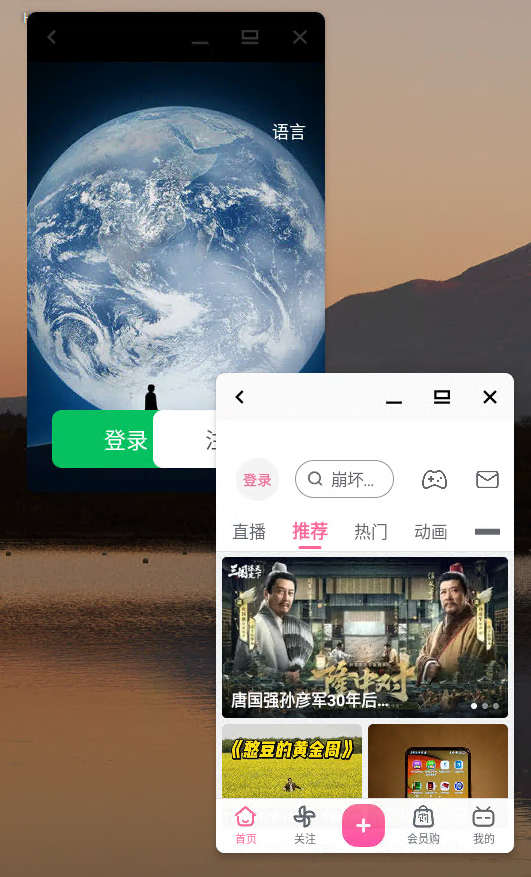 If anyone is interested, you can give it a try. For those using Linux for work, having Waydroid makes a big difference in usability. Finally, thanks to everyone for your support, Da Pang is going to slack off now
If anyone is interested, you can give it a try. For those using Linux for work, having Waydroid makes a big difference in usability. Finally, thanks to everyone for your support, Da Pang is going to slack off now 