RS232: Asynchronous transmission standard interface. Typically, the RS-232 interface appears in the form of 9 pins (DB-9) or 25 pins (DB-25).
Using a DB-9 9-pin connector, transmission employs shielded twisted pair cables, utilizing only three wires for sending data, receiving data, and signal ground.
RS485: A standard that defines the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers in balanced digital multipoint systems. Digital communication networks using this standard can effectively transmit signals over long distances and in environments with high electronic noise.
Currently, a two-wire connection method is commonly used, which adopts a bus topology, allowing up to 32 nodes to be connected on the same bus. In RS485 communication networks, a master-slave communication method is generally employed, where one master controls multiple slaves.
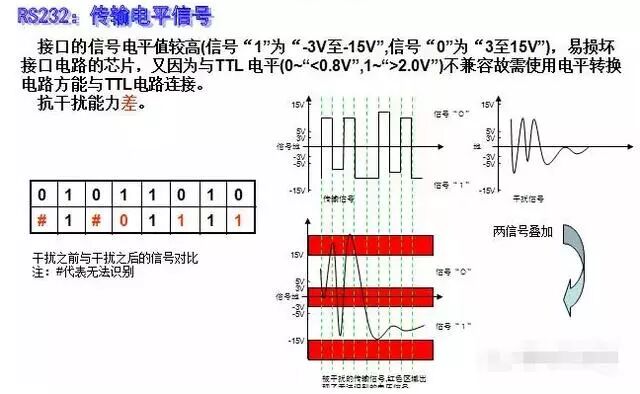
Electrical Characteristics of the Interface
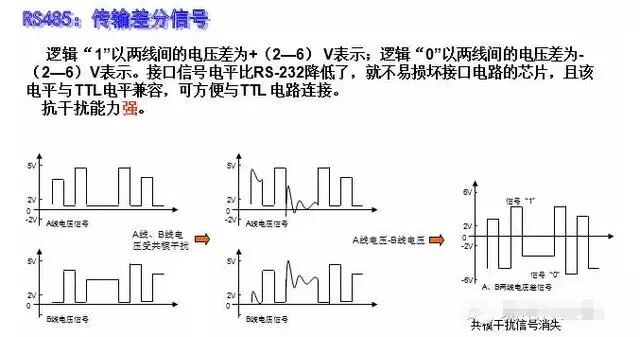
Electrical Characteristics of the Interface

Differences in Transmission Distance
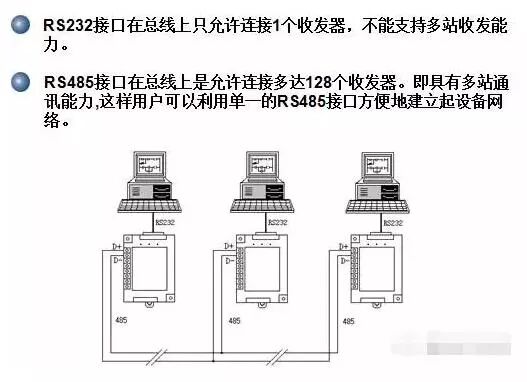
Differences in Multipoint Communication

Differences in Transmission Cables

Differences in Baud Rate