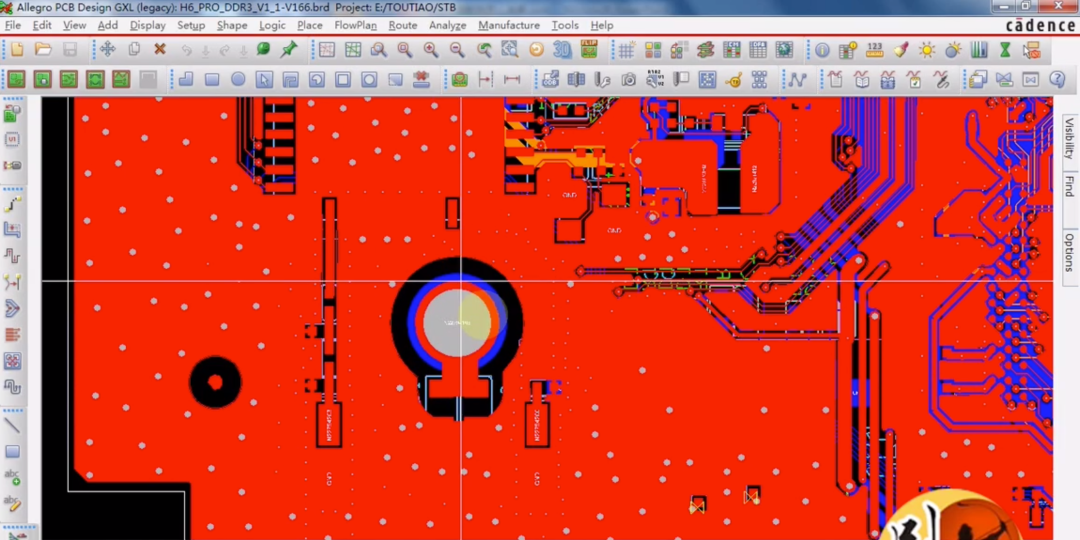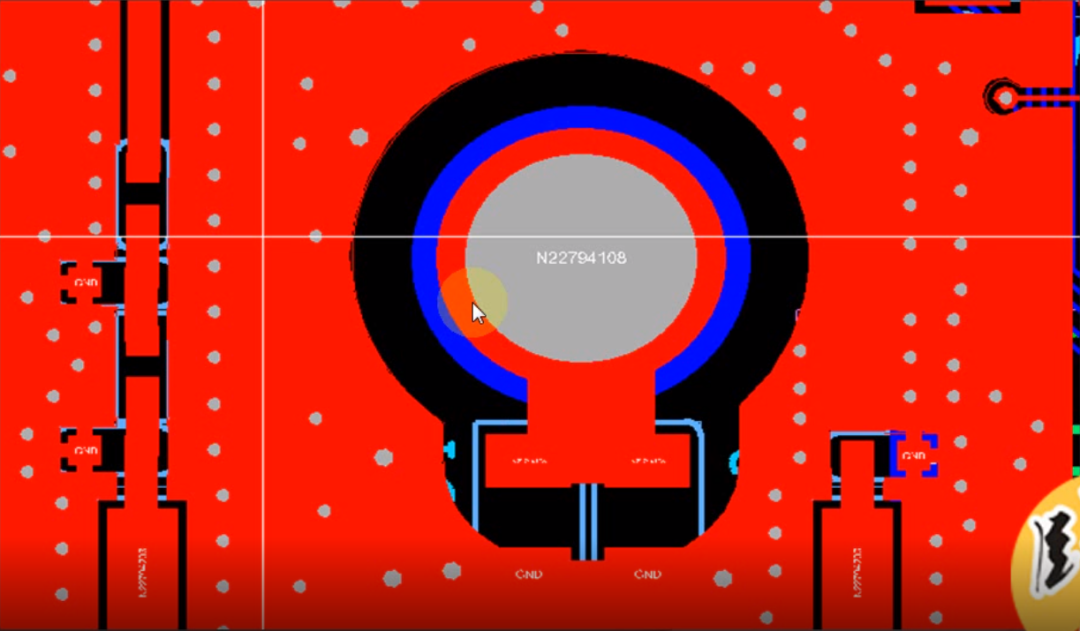
The chassis is made of metal, and there is a screw hole in the middle, which connects to the ground. Here, a 1M ohm resistor is connected in parallel with a 0.1uF capacitor to the ground of the circuit board. What are the benefits of this setup?
-
If the chassis ground is unstable or has static electricity, directly connecting it to the circuit board ground can damage the circuit board chips. By adding a capacitor, low-frequency high voltage and static electricity can be isolated, thus protecting the circuit board. High-frequency interference from the circuit will be directly connected to the chassis through the capacitor, serving to isolate direct current from alternating current.
-
So why add a 1M ohm resistor? This is because, without this resistor, when there is static electricity on the circuit board, the 0.1uF capacitor connected to the ground will interrupt the connection to the chassis ground, effectively leaving it floating. If these charges accumulate to a certain level, problems will arise; it is essential to connect to the ground. Therefore, the resistor is used for discharging.
-
A 1M ohm resistor is quite large, and if there is static electricity or high voltage from the outside, it can effectively reduce the current, preventing damage to the chips inside the circuit.