Enterprise-grade SSD hot-swapping is a fundamental feature. Whether installed in servers or supported RAID storage devices, when the system reports a disk failure, it is necessary to remove the faulty drive without shutting down the system and then insert a replacement drive to trigger the system for subsequent data reconstruction processes.
This article is accompanied by a short video that quickly demonstrates how to use the UK-based Quarch company’s PCIe Gen5 U.2 hot-swap module, while also connecting to Quarch’s Gen5 Power Analysis Module (PAM) to achieve real-time monitoring and problem analysis during the hot-swap process.
Note: The PAM is not mandatory during the automated hot-swap testing process, but it is very helpful for analyzing hot-swap failures. Engineers unfamiliar with Quarch can contact Saniffer for the latest white paper on PCIe5&6.0, CXL, NVMe, NAND, DDR5, UFS4 testing technologies and tools, version 10.1, with the following contact information:
Below are some explanations and descriptions of the basic concepts regarding hot-swapping:
Quarch’s hot-swap test suite is used not only by UNH IOL laboratories but also by mainstream companies in the SSD testing industry, from SAS/SATA SSD to PCIe Gen 3/4 NVMe SSD, which are all using this hot-swap suite for testing.
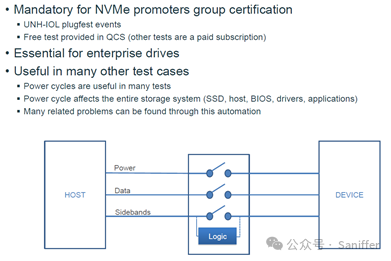
“Hot-swapping” is only applicable to enterprise-grade SSD trials, generally U.2/U.3/E1.S/E1.L/E3.S/E3.L or SAS and enterprise-grade SATA SSD, commonly referred to as Drive Control Module (disk control module).
For M.2, AIC cards, we generally refer to this module as Card Control Module (card control module), which is mainly used to import physical layer and link layer issues to test the DUT’s ability to handle various errors and exceptions.
Hot-swapping is a mandatory test item for PCIe Gen 4/5/6 NVMe SSD as well as SAS/SATA HDD/SSD. Hot-swap testing and power-off testing are two completely different tests. Generally speaking, power-off testing is relatively simple and mainly used to accelerate the reproduction of some SSD or firmware issues. However, several key points of hot-swap testing cannot be simulated by simple power-off testing, as follows:
-
Hot-swapping has differences in the order of pin connections;
-
During the hot-swap process, there may be intermittent signal issues when the pins contact the slot, similar to poor contact situations;
-
During the hot-swap process and after the position is stabilized, signal glitches may occur.
Of course, an additional function brought by hot-swap testing is power-off testing. However, implementing power-off functionality through the hot-swap module requires selecting the appropriate model. For example, some signals can remove signal glitch injection functionality, making those products more economical. Below is an example of the current most commonly tested NVMe SSD hot-swap; the SAS/SATA testing tools and methods are basically consistent, and will not be elaborated here.
The Quarch testing suite introduced below is not only used by UNH IOL laboratories but also by mainstream companies in the SSD testing industry for PCIe Gen 3/4/5 NVMe SSD and SAS/SATA SSD hot-swap testing.
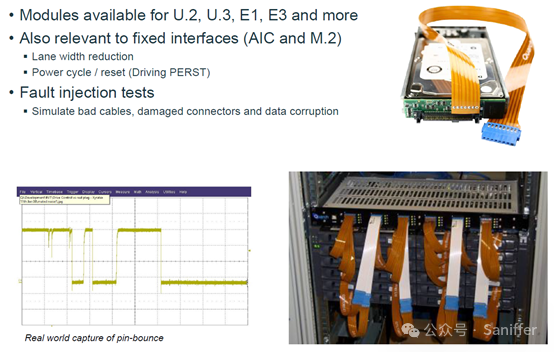
As mentioned above, the main function of the SSD hot-swap test suite is to test the hot-swapping of drives, especially U.2/U.3/EDSFF NVMe SSD. Generally, M.2 NVMe SSD or PCIe card-based SSDs do not undergo hot-swapping. However, through this suite, certain pins (including power) can be simulated to disconnect, have poor contact, or even break one direction of the differential signal line, or inject some signal glitches to simulate some fault scenarios to see if the SSD can still operate reliably and stably under these special conditions. Below are some tests that can be performed using these Quarch hot-swap modules.
-
Simulate SSD issues and faults during the hot-swap process
-
Simulate drive hot-swapping
-
Simulate pin bounce issues caused by hot-swapping
-
Simulate certain pins being disconnected
-
Simulate certain pins being stuck
-
Simulate signal glitches on certain pins
-
How many physical glitches? Inject a glitch once, or have continuous glitches? What is the interval time?
-
The height, density, and duration of glitches
-
Simulate very rapid on/off testing
Currently, these hot-swap suites provide various interface types, including Gen 4 U.2/U.3, M.2, PCIe Slot and EDSFF x4/x8. These hot-swap modules need to be connected between the SSD and the motherboard/backplane, and can be tested through Python scripts or graphical GUI interfaces.