

When it comes to great inventions in human history, there are countless examples. The steam locomotive, for instance, was the main mode of transportation in the 19th century, representing fashion and progress. Wherever the steam locomotive went, it was equivalent to the advancement of human industrial civilization! However, in the 20th century, steam locomotives were gradually replaced by diesel locomotives, and now electric locomotives have taken over from diesel engines!
The invention we will discuss today is similar to the steam locomotive of its time; it was an important invention during a certain period, widely used but now replaced by more advanced products. It is the mechanical calculator, the predecessor of the electronic calculator!

As we all know, the first electronic computer in human history was successfully produced in the United States in 1946. This electronic computer used vacuum tubes, weighed 30 tons, consumed a lot of energy, and due to serious heat generation during operation, it needed to frequently shut down for rest!
Such electronic computers could only be afforded by wealthy countries like the United States! In fact, it wasn’t until the 1970s, after the advent of integrated circuits, that portable computers became truly popular among the public. So, the question arises: what did people, especially researchers or commercial accountants, use to perform complex calculations before that?
Some people might answer: the abacus!
Indeed, at that time, the abacus was mainly used in China!
However, the West had a much more advanced product that lasted for three centuries: the mechanical calculator!
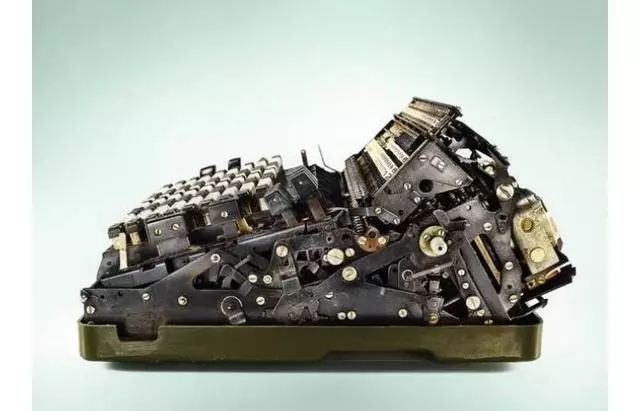

The two images above show the commonly used mechanical calculators after World War II, which are the last generation of mechanical calculators. These calculators are not much larger than a rectangular lunch box and can be considered portable!
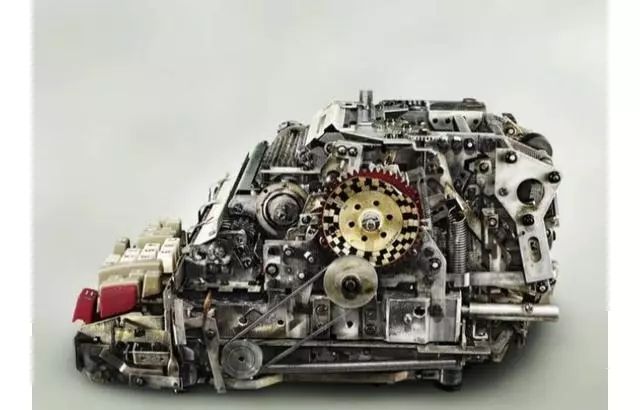
However, the earliest mechanical calculators invented by humans were vastly different from these later products!

The image above is the first true mechanical calculator in human history, known as the wheel-based adder, also called Pascal’s adder!
This machine was invented in 1642 by the French philosopher and mathematician Blaise Pascal!
Seeing the name Pascal, you, who have gone through nine years of compulsory education and excelled, might feel a bit familiar?
That’s right, this Pascal is the same as the unit of pressure we often encounter in physics: Pascal!
Speaking of Pascal, he can truly be regarded as a child prodigy! He was born in 1642 into a family of mathematicians in France. He lost his mother at the age of three and was raised by his father, who worked as a tax collector. From a young age, he showed great interest in scientific research!
Young Pascal had a deep affection for his father. He watched his elderly father struggle to calculate tax rates and wanted to help, but was afraid his father wouldn’t trust him. Thus, this future great scientist thought of making a machine to help his father calculate taxes. At the age of 19, he invented the first mechanical computer in human history!

The first epoch-making mechanical computer in human history was a gift from a devoted son to his elderly father!
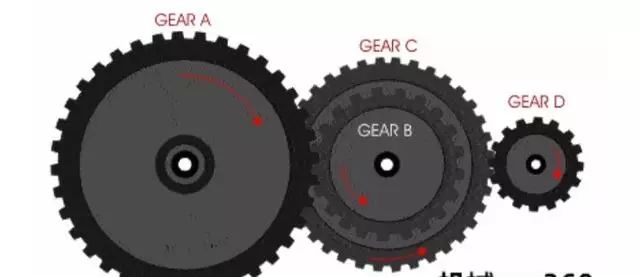
Pascal’s computer is a device made up of a series of gears, shaped like a rectangular box! It needs to be wound up like a children’s toy with a key before it can operate, and it can only perform addition and subtraction!
This is a decimal adder made using the principle of gear engagement. When the gears rotate one full turn, the longest tooth among the ten will engage with the higher-positioned gear to achieve carrying. The same principle applies in reverse for subtraction calculations.
Pascal was a true genius; he made contributions in many fields. He is described as a mathematician, physicist, philosopher, fluid dynamicist, and the founder of probability theory. Anyone who has studied physics knows the “Pascal’s law” about the properties of liquid pressure, which is his great discovery named after him!
He was also a writer, and his beautifully written essays were once very famous in France! Unfortunately, his long-term engagement in arduous research harmed his health, and he passed away at the young age of 39 in 1662!
Ten years after Pascal’s death, a greater figure in the history of science, the German Leibniz, improved Pascal’s adder and ultimately became the founder of mechanical calculators!
After going through nine years of compulsory education and excelling, doesn’t the name Leibniz sound familiar to you?
That’s right, this Leibniz is one of the greatest figures in the history of mathematics, as he and Newton independently invented calculus!
However, Leibniz is very different from Newton, as Newton was best at “daydreaming.” Although these daydreams were indeed great and advanced, he rarely invented or created physical objects!But Leibniz was very good at inventing and creating tangible objects; this mechanical calculator is one of his inventions!
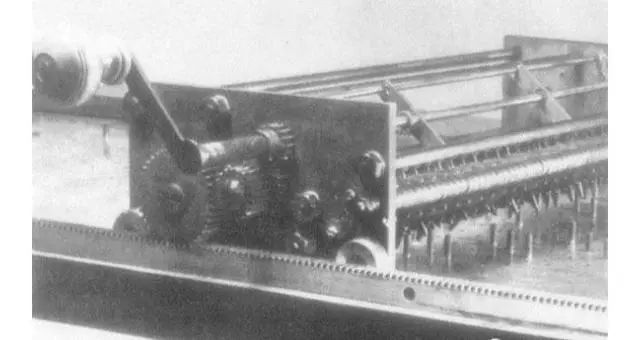
Leibniz’s improvements enabled the mechanical calculator to perform multiplication and division, and even square root calculations!

This calculator uses the number of revolutions of a handle to represent the multiplier, with different positions of the long axis corresponding to different gear teeth, allowing for multiplication calculations!
Another significant contribution of Leibniz to humanity was in 1700, inspired by a Chinese I Ching (Bagua) given to him by a friend, he grasped the essence of binary!
Although Leibniz’s multiplier still used decimal, it pioneered the design of computers and proposed the rules for binary operations, laying a solid theoretical foundation for the modern development of computers!
Although Leibniz’s mechanical calculator was useful, it was cumbersome due to the long axis, with some models weighing dozens of kilograms and measuring up to a meter in length! It took over a hundred years until 1874 when Baldwin and Odhner built upon previous work and used variable tooth gears to shorten the long calculation axis!
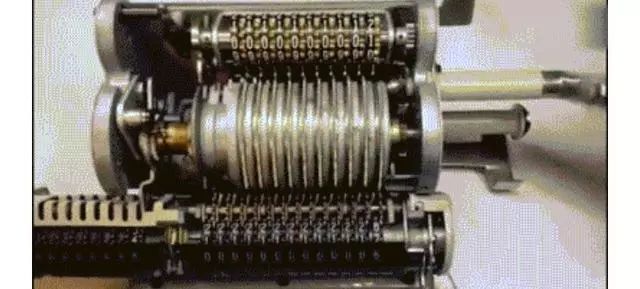
However, the calculators at this time were still quite troublesome, as their results needed to be manually recorded on paper!
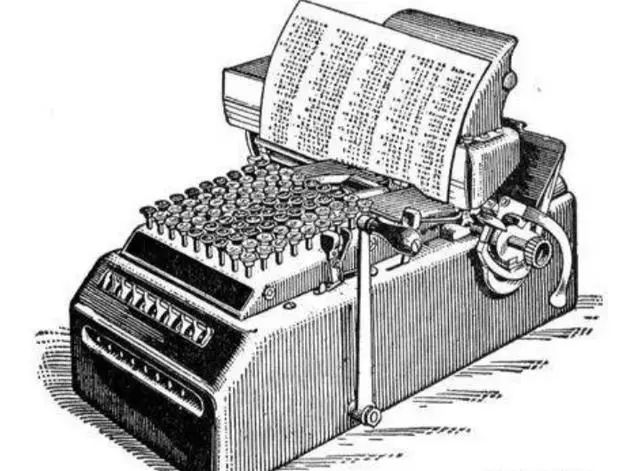
In less than ten years, another brilliant American inventor, Felt, emerged. He combined the calculator with the typewriter that had already appeared at the time, allowing the calculation results to be directly recorded on paper!
Later, someone improved Felt’s calculator by adding an electric motor, resulting in the electric calculator, while the earlier calculators were referred to as manual calculators!
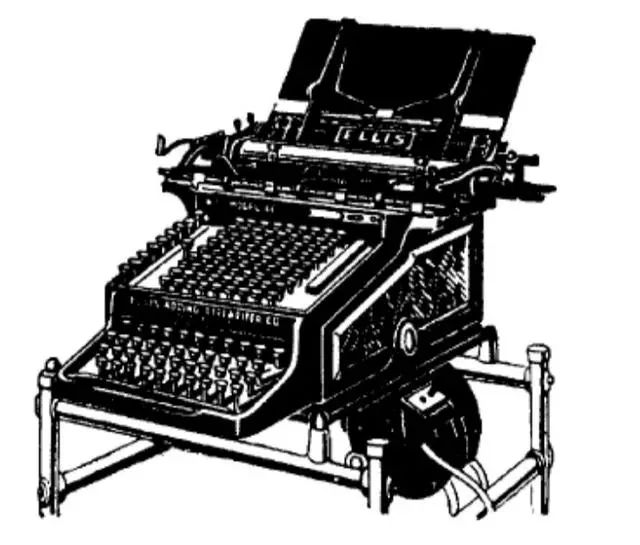

Later, the full keyboard was changed to a nine-key style!
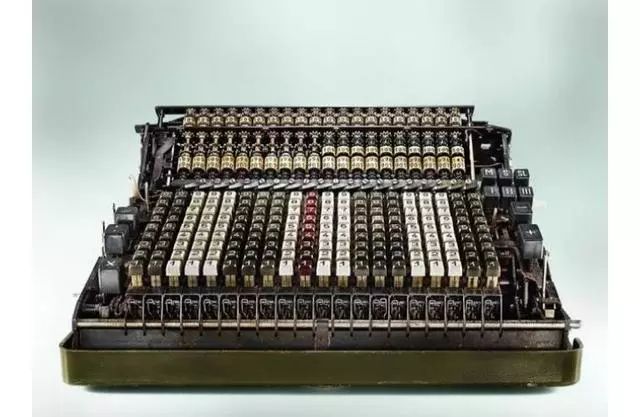

The image above shows the full keyboard, while the image below shows the nine-key style!
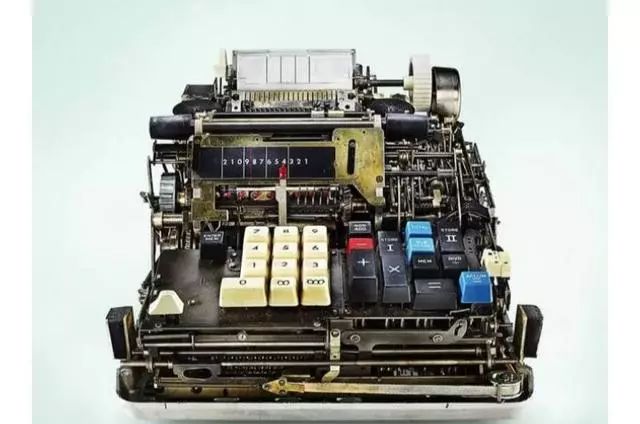

The mechanical calculator has finally reached perfection!
Mechanical computers reached their peak of application during World War II, serving as the basis for bomb sighting devices in bombers. Additionally, they were used to calculate the speed of aircraft after radar detection and to adjust the elevation angle of naval guns during combat!
Mechanical computers continued to be used for a while after the emergence of electronic computers, mainly because the electronic computers of that time were too expensive and bulky! However, the main components of electronic computers quickly evolved from vacuum tubes to transistors and finally to integrated circuits!
By the 1970s, handheld electronic computers using integrated circuits were introduced, which were very affordable and portable, leading to the gradual disappearance of mechanical computers, and by the 1980s, they were completely extinct!

Next, we will showcase some vintage mechanical calculators from the collection of photographer Kevin Twomey.
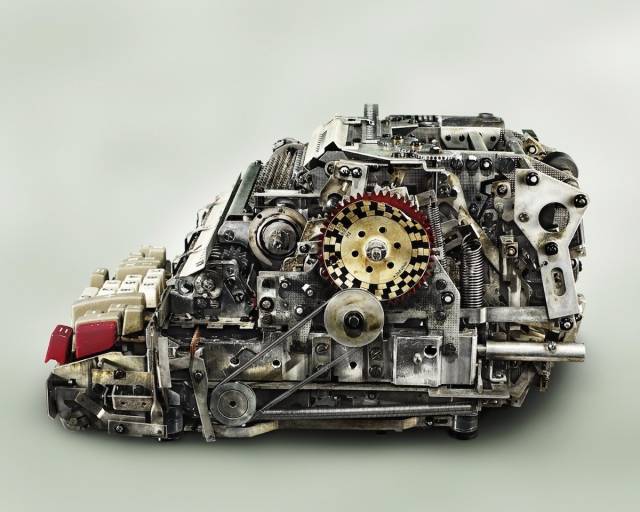

Harman 505 Calculator
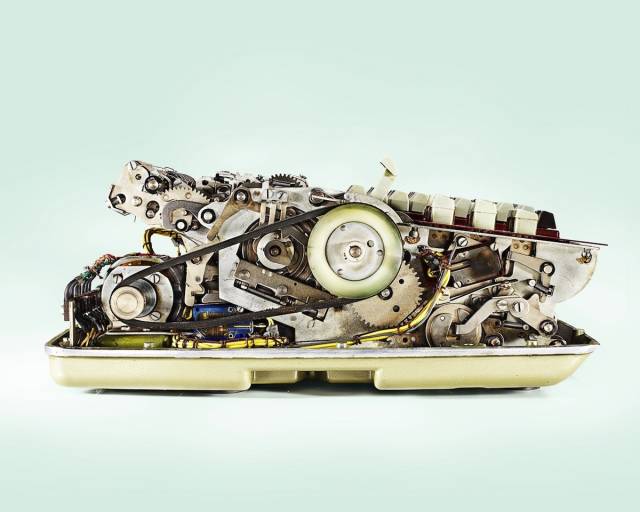 Bruns 11s Calculator
Bruns 11s Calculator
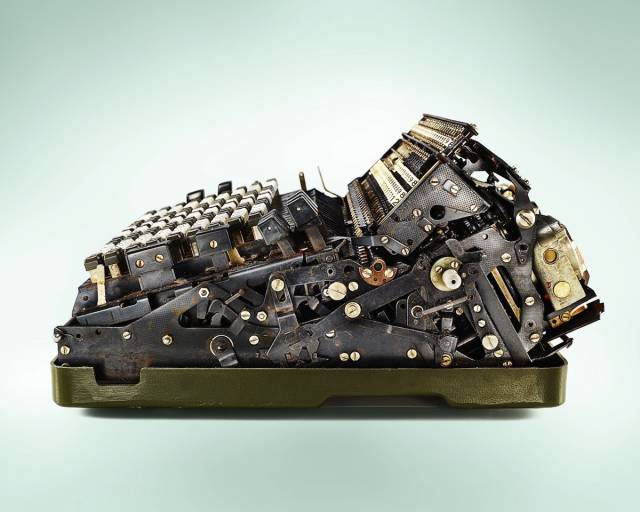

Cellatron R44SM Calculator
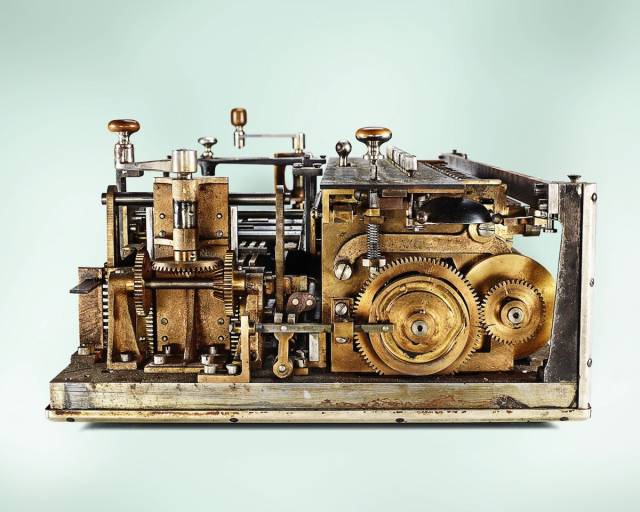
Millionaire Calculator
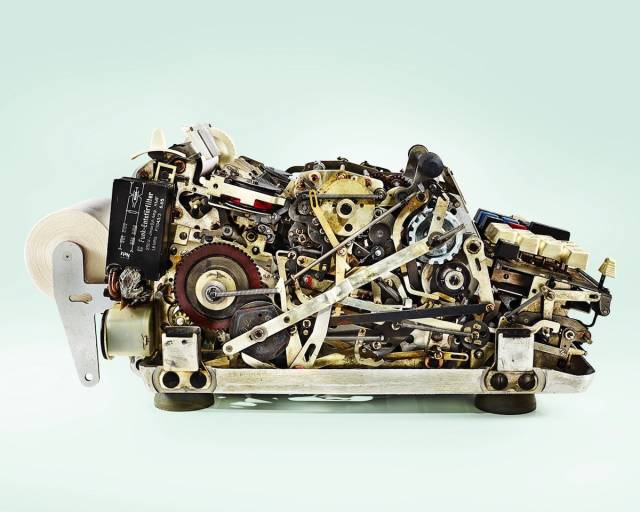
Harman 300 Calculator

Bruns 11s Calculator
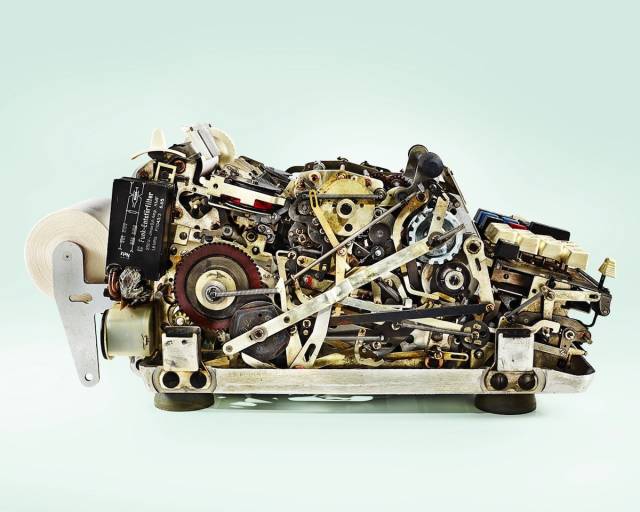
Diehl Transmatic Calculator
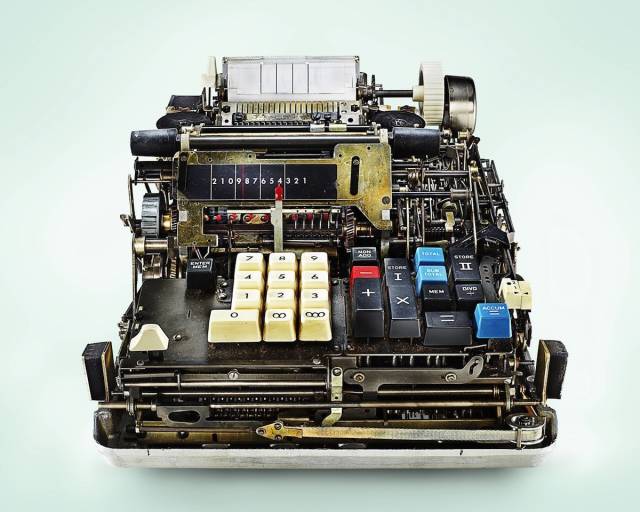

Diehl Transmatic Calculator
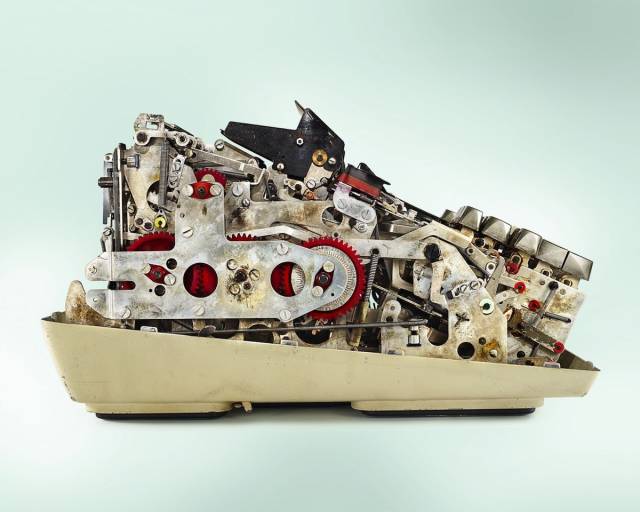

Friden 1217 Calculator
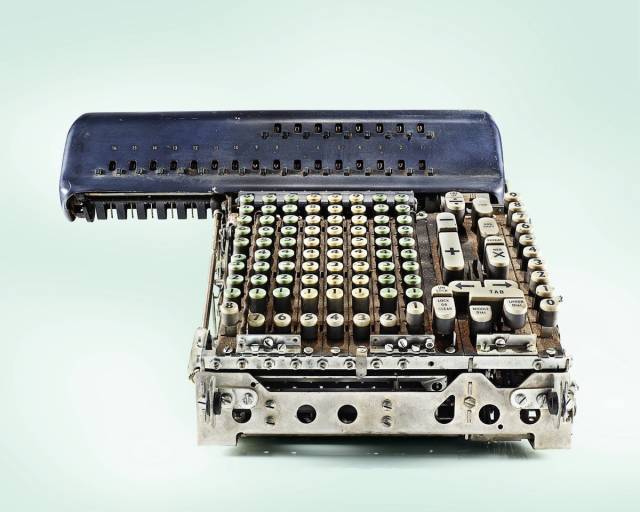

Marchant EFA Calculator
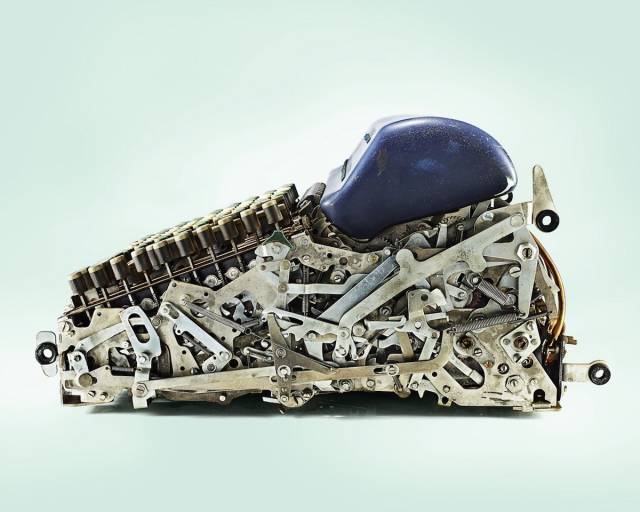

Marchant EFA Calculator
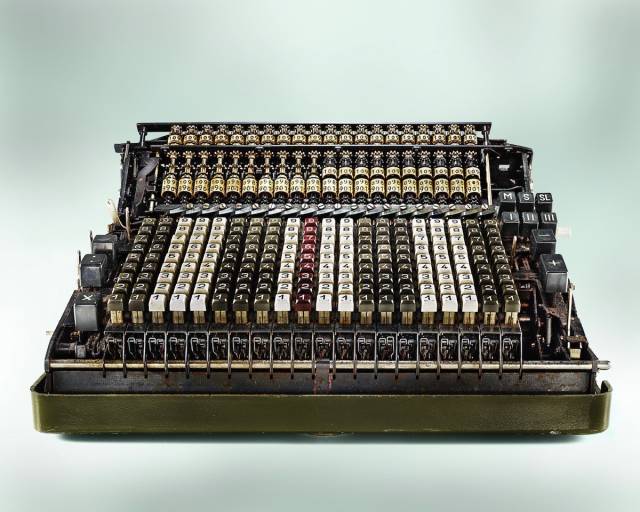

Cellatron R44SM Calculator
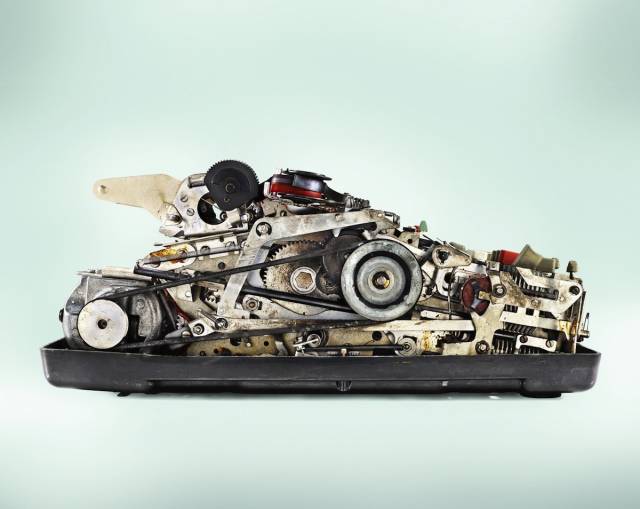

Monroe Mach 1.07 Calculator

Monroe Mach 1.07 Calculator
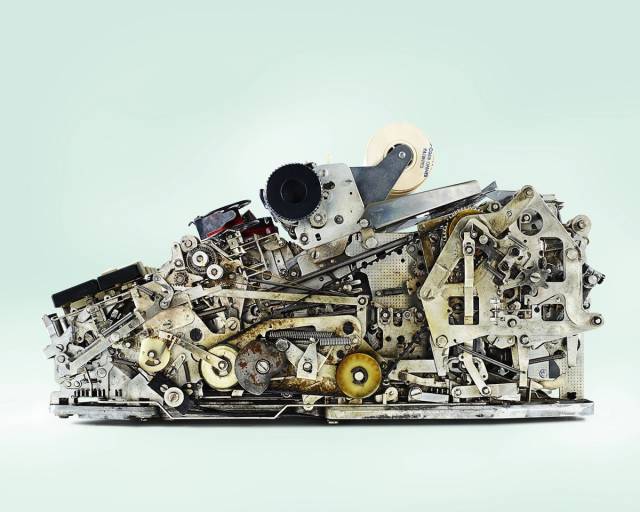

Monroe PC1421 Calculator
Mechanical calculators have complex structures, and once they malfunction, repairs are very troublesome. They require professional repair personnel to disassemble them completely, replace parts, reassemble them, and then test the entire calculator to ensure normal operation. Often, they would malfunction once or twice every few weeks. This is also one of the reasons mechanical computers were completely replaced!
Despite their many issues, mechanical calculators have a significant advantage: they are incredibly durable and can last for hundreds of years if properly maintained! This is incomparable to modern electronic computers!
Although mechanical calculators have completely exited the stage of human history, their intricate structure and complex operation embody the beauty of pure mechanical physical motion, making them absolute favorites in today’s industrial collectibles! Many rare models have entered national museums, becoming national treasures in many countries!
Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from the internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If there are any copyright issues, please contact us for removal. Thank you!
Complete Question Bank for 2023 Electrician Junior Exam (Includes Answers)
Three Essential Tools for Electricians, Easily Accessible via WeChat!
[Collection] The “Path” of a Ten-Year Veteran Electrician, Secrets to Earning Over Ten Thousand a Month!
Five Major Electrical Drawing Software (CAD, Eplan, CADe_simu…), Which One Do You Pick?
Latest Electrical Version of CAD Drawing Software, with Detailed Installation Tutorial!
Latest Electrical Drawing Software EPLAN, with Detailed Installation Tutorial!
Common Issues for Beginners Using S7-200 SMART Programming Software (Includes Download Links)
Super Comprehensive Electrical Calculation EXCEL Sheet, Automatically Generated! No Need to Rely on Others for Electrical Calculations!
Bluetooth Headphones, Free Books for Electricians/PLC? Come and Get Your Electrical Gifts!
Basic Skills for PLC Programming: Ladder Diagrams and Control Circuits (Includes 1164 Practical Cases for Mitsubishi PLC)
Still Can’t Understand Electrical Diagrams? Grab the Basics of Electrical Diagram Recognition and Simulation Software for Quick Hands-On Learning!
12 Free Electrician Video Courses, 10GB Software/E-Book Materials, and 30 Days of Free Live Electrician Classes!
