
1 Fault Types of Electronic Control Units
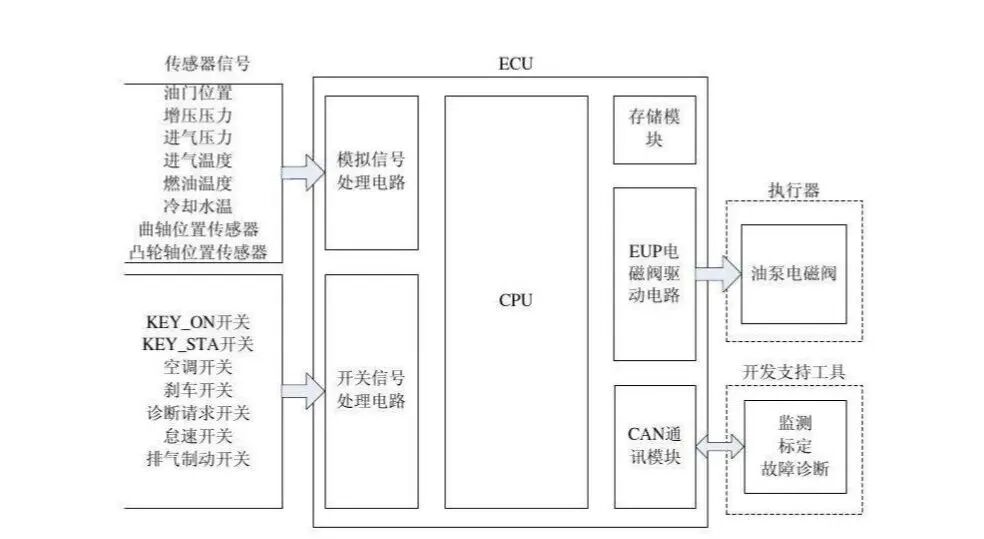 Based on the location of the faults in the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), they can be divided into: ECU peripheral circuit faults and ECU internal faults.The ECU peripheral circuits include the power circuit, sensor signal circuit, and actuator drive circuit. ECU peripheral circuit faults mainly refer to faults in the ECU power circuit; once the power circuit malfunctions, the ECU cannot operate normally.ECU internal faults can be further divided into: power circuit faults, output power module faults, memory faults, and water ingress or moisture faults in the ECU.01 Power Circuit FaultsDue to the presence of surge voltage, many components are prone to failure, with the most common being the failure of surface-mounted capacitors, resistors, diodes, and even peripheral protection circuits of certain critical chips, along with the copper traces on the printed circuit board burning out. This situation is the most common ECU fault.02 Output Power Module FaultsDue to the large drive current on the output power module, it is easy to cause the power board to overheat, making this the most failure-prone part of the ECU; certain automotive fuel injectors may fail to inject fuel and suddenly stall, often due to breakdowns in the power drive circuit.03 Memory FaultsDue to the impact of surge voltage during operation, certain bytes may be lost in the program memory, leading to abnormal operation of the engine or other controlled objects; or after an accident, the contents of the EEPROM may be rewritten to an abnormal state, causing temporary system failure.If programmable memory (EPROM or EEPROM) has issues, it can be replaced. During replacement, a programmer (also known as a burner) is used to read the program from a good chip with the program and then write it to a blank chip of the same model, finally installing the copied chip into the ECU.Note that some automotive manufacturers specify the number of times a chip can be copied (3-7 times); exceeding this limit may render the chip unusable, and some manufacturers use encryption methods to prevent chip copying.2 Causes of ECU Faults
Based on the location of the faults in the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), they can be divided into: ECU peripheral circuit faults and ECU internal faults.The ECU peripheral circuits include the power circuit, sensor signal circuit, and actuator drive circuit. ECU peripheral circuit faults mainly refer to faults in the ECU power circuit; once the power circuit malfunctions, the ECU cannot operate normally.ECU internal faults can be further divided into: power circuit faults, output power module faults, memory faults, and water ingress or moisture faults in the ECU.01 Power Circuit FaultsDue to the presence of surge voltage, many components are prone to failure, with the most common being the failure of surface-mounted capacitors, resistors, diodes, and even peripheral protection circuits of certain critical chips, along with the copper traces on the printed circuit board burning out. This situation is the most common ECU fault.02 Output Power Module FaultsDue to the large drive current on the output power module, it is easy to cause the power board to overheat, making this the most failure-prone part of the ECU; certain automotive fuel injectors may fail to inject fuel and suddenly stall, often due to breakdowns in the power drive circuit.03 Memory FaultsDue to the impact of surge voltage during operation, certain bytes may be lost in the program memory, leading to abnormal operation of the engine or other controlled objects; or after an accident, the contents of the EEPROM may be rewritten to an abnormal state, causing temporary system failure.If programmable memory (EPROM or EEPROM) has issues, it can be replaced. During replacement, a programmer (also known as a burner) is used to read the program from a good chip with the program and then write it to a blank chip of the same model, finally installing the copied chip into the ECU.Note that some automotive manufacturers specify the number of times a chip can be copied (3-7 times); exceeding this limit may render the chip unusable, and some manufacturers use encryption methods to prevent chip copying.2 Causes of ECU Faults
The main causes of damage to the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) are environmental factors, voltage overload, and improper operation.
01 Environmental FactorsSince the ECU is installed in vehicles, it is frequently affected by heat, humidity, vibration, water exposure, surge voltage, and other environmental factors, which can easily lead to ECU faults.In particular, sudden temperature changes can cause condensation, and the water from condensation can corrode the circuit board;additionally, water ingress into the ECU can cause short circuits and irreversible corrosion.02 Voltage OverloadThis is usually caused by short circuits in the solenoid or actuator circuits.If a shorted solenoid or actuator is not detected and repaired before replacing the ECU, the resulting overload voltage may also damage the newly replaced ECU.Therefore, it is essential to thoroughly investigate the cause of the original ECU damage before replacing it.03 Improper OperationFor example, failing to take electrostatic protection measures during disassembly, not disconnecting the battery power before installing the ECU, or measuring its terminals with a low-resistance multimeter can all easily cause ECU damage.3 ECU Fault Detection Procedures
When the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is not functioning properly, the first step is to check whether the ECU’s peripheral circuits are normal, followed by static and dynamic detection procedures.
01 Peripheral Circuit InspectionBefore suspecting a fault in the ECU itself, the peripheral circuits, especially the power circuit, should be checked and confirmed to be normal.Power circuit detection method:The terminal connected to the battery positive through a fuse is called the ECU’s constant power supply, while the terminal connected to the battery positive through the ignition switch or relay is the ECU’s conditional power supply. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at these terminals, which should be equal to the battery voltage.Additionally, check that the ECU’s ground terminal is well grounded.02 Static DetectionStatic detection refers to using a diagnostic tool to test the communication function of the control system.If the communication connection is normal, it indicates that the ECU’s power supply, ground wire, chip set, and basic functions are normal;if the communication connection fails or cannot communicate, a multimeter should be used to check the ECU’s power voltage, reference voltage (+5V), and ground wire.If the power voltage and ground wire are normal but the reference voltage is too low, it indicates a fault in the ECU’s power circuit or a short circuit in the external reference power line;if the reference voltage is too high, it also indicates a fault in the ECU’s power circuit or an open circuit in the power ground wire.If everything is normal in static detection, proceed to dynamic data stream detection.03 Dynamic DetectionDynamic detection refers to using a diagnostic tool to read data streams while the system is in operation to observe whether the sensor signals are correct.If a signal is lost, the sensor can be disconnected, and a signal simulator (signal generator) can be used to simulate and send the signal based on its nature (preferably sending the signal to the ECU input) for further testing.If the test result is normal, it indicates a fault in the external wiring or the sensor itself;if no data is displayed, check the soldering of the interface circuit.If the soldering is good, then the ECU has a fault in the input signal processing circuit.However, if the input data stream detection is normal but the output function is poor, the static detection of component functions should be performed one by one to test the output function, while using a multimeter and test light to monitor the test results (the multimeter connected before the drive circuit, and the test light connected after the drive circuit).If the multimeter monitoring result is correct but the test light does not operate, it indicates a fault in the ECU drive circuit (which can be replaced with the same or similar components);if the multimeter monitoring result is incorrect, it indicates a fault in the ECU output signal processing circuit.04 Internal Inspection of ECUAfter confirming that the ECU is basically functioning normally through static and dynamic detection, the next step is to analyze the signal of various parameters. If the parameters differ significantly or the input signal and output circuit are normal but the ECU is not functioning properly, the ECU should be checked or replaced.The method for internal inspection of the ECU will be introduced in a separate article.4 Repairing the ECU
In principle, the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) can only be replaced, not repaired. For chip and program faults, it is best to replace it with the same model ECU. However, some ECU faults can be repaired by replacing components, mainly including the following situations.
01 Power FaultsThere are two types of ECU power faults:one is the main power fault, and the other is the reference voltage fault (5V).① Main Power Fault: One is a shorted protection diode (caused by reversing the battery connection), which can be resolved by removing it or replacing it with a diode of the same specification.The other is an open circuit in the main ground wire (burnt out).This fault can be resolved by soldering and connecting wires.② Reference Voltage Fault: If the reference voltage is too low, disconnect the related external circuits; if the voltage can be restored to (5±0.1)V, it indicates that the external circuit sensor load is too high, and it is necessary to check and eliminate it one by one;if the reference voltage cannot reach (5±0.1)V, the voltage regulator module should be replaced;if the reference voltage is too high (greater than 5V), check the ground wire of the power module and the ground wire of the circuit board (ground wire), and after finding the specific fault point, repair the ground wire or replace the module.02 Output Power Module FaultsThe corresponding power module can be found to test its input and output signal voltages. After confirming the module is damaged, it can be replaced with a module of the same or similar parameters, such as ignition modules, air conditioning control modules, fuel control modules, and fan control modules.03 Capacitor and Resistor DamageSome capacitors are electrolytic capacitors, which can easily fail after prolonged use of the ECU; at this time, they can be replaced with capacitors of the same capacity rated for 16-25V.The same principle applies to replacing resistors.04 Water Ingress and Moisture FaultsAfter water ingress or moisture, the ECU can be dried. The drying method is to first rinse with anhydrous ethanol (industrial alcohol), then place the ECU in a large sealed bag and use a vacuum machine (an air conditioning vacuum machine can also be used) to vacuum for 24 hours before reinstalling it for testing.Vehicles that have been submerged will have corrosion on the circuit board, causing component pins to break, stick together, or components to be damaged, which can be checked and repaired or replaced one by one.For example, a repair shop received a faulty vehicle with the following symptoms:When the engine is running normally, turning on/off the headlights or other electrical devices causes backfiring in the exhaust pipe, and in severe cases, it can rupture the exhaust pipe.After checking, the peripheral circuit was normal with no faults, and it was suspected that there was a fault inside the ECU. Upon opening the ECU box for careful inspection, it was found that a ground wire had broken due to corrosion. This ground wire was the signal shielding line for the oxygen sensor passing through the ECU’s internal grounding position. The breakage caused the shielding function to fail, leading to interference of the oxygen sensor signal by other electrical signals. After soldering it back together, the fault was eliminated, and the vehicle returned to normal operation.
(Image and text source from the internet)
Click the mini-program below to see more repair cases
