 [Yangtze Alliance Reading 365 Day 267]
[Yangtze Alliance Reading 365 Day 267]
“Bibliometric Insights into Breast Cancer Organoid Chips: Trends & Emerging Areas“ published in “Int J Surg“Breast cancer is a highly prevalent malignant tumor among women worldwide, and its treatment faces challenges due to the diversity of genetic mutations and individual patient differences. Organoid chip technology provides new tools for studying the pathological mechanisms of breast cancer, drug screening, and personalized treatment by simulating the tumor microenvironment. This study employs bibliometric methods to analyze the research hotspots, development trends, and future directions in the field of breast cancer organoid chips, revealing academic dynamics and potential opportunities in this area.

Main Content
1. Research Background and Objectives
Breast cancer is a highly prevalent malignant tumor among women worldwide, and its treatment faces challenges due to the diversity of genetic mutations and individual patient differences. Organoid chip technology provides new tools for studying the pathological mechanisms of breast cancer, drug screening, and personalized treatment by simulating the tumor microenvironment. This study employs bibliometric methods to analyze the research hotspots, development trends, and future directions in the field of breast cancer organoid chips, revealing academic dynamics and potential opportunities in this area.
2. Research Methods
Data Source: Through the Web of Science Core Collection database, keywords such as “organoid chip” and “breast cancer” were used for retrieval, ultimately including 151 English publications (as of April 2025).
Figure 1: Detailed process of literature selection and retrieval strategy.
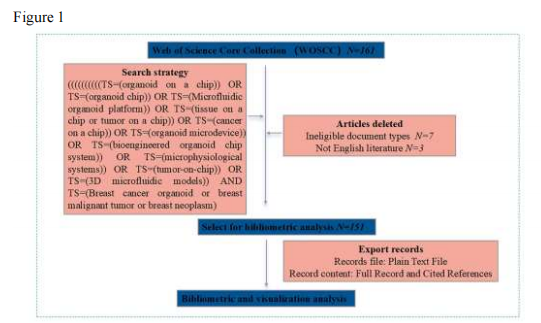
Figure 2: Annual publication volume statistics for breast cancer organoid chip research from 2008 to 2025.
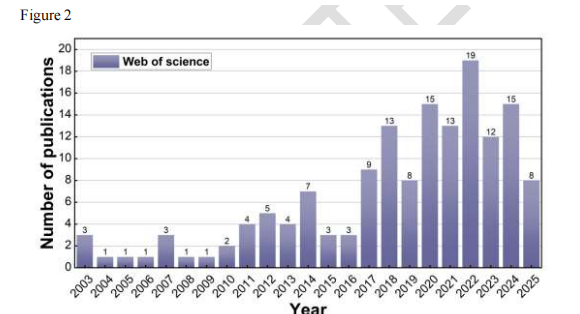
Figure 3: Literature coupling analysis of countries/regions and institutions, including the distribution of 31 countries/regions and 47 institutions.
Analysis Tools: Visualization analysis was conducted using CiteSpace and VOSviewer, covering dimensions such as publication volume, country/institution collaboration, keyword co-occurrence, and journal and author impact.
Figure 4: Keyword visualization analysis, including co-occurrence networks, word clouds, and country-keyword co-occurrence relationships.
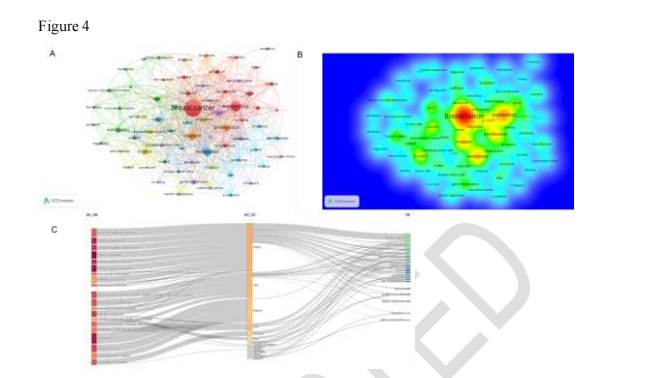
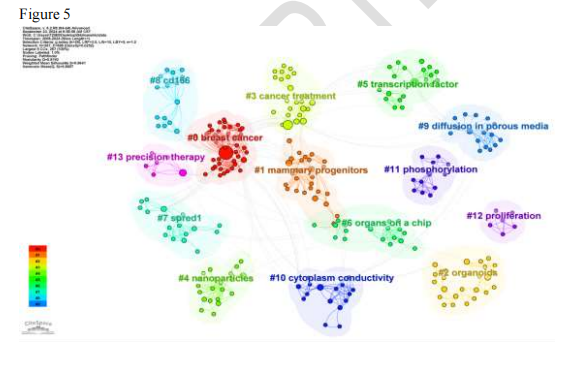
Figure 5: Keyword clustering visualization, dividing into 13 research direction clusters.
3. Core Research Results
Publication Trends
Since 2013, related research has gradually emerged, initially focusing on normal breast epithelial organoid models, with a rapid increase in publication volume over the past decade, peaking in 2022.
Country and Institution Contributions
China: 74 publications (ranked first globally), with 1667 citations, indicating high research quality; the United States published 38 papers, with a total link strength of 3071 (ranked first globally), indicating a denser international collaboration network.
Institutions: Fudan University, Sun Yat-sen University, and China Medical University each published 5 papers, while Nanyang Technological University (total link strength 1022) and MIT play a core role in international collaboration.
Research Hotspots and Keywords
High-frequency keywords: breast cancer, invasion, metastasis, microfluidics, tumor microenvironment, etc., reflecting the research focus on the biological behavior of cancer cells and the application of chip technology.
Evolution of Research Stages:
2008-2010: Establishment of organoid culture methods;
2010-2015: Mechanisms of tumor stem cell migration and metastasis;
2015-2020: Tumor microenvironment and angiogenesis;
Post-2020: Clinical translation (e.g., drug sensitivity screening).
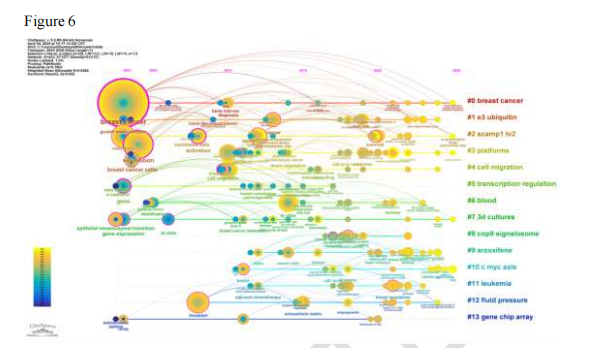
Figure 6: Timeline of keywords in breast cancer organoid chip research, showcasing the evolution of research hotspots at each stage.
Journal and Author Impact
Highly cited journals: “Cancer Research” (304 citations), “Lab on a Chip” (253 citations), “Cell” (229 citations), all of which are Q1 journals.
Figure 7: Analysis of the burst intensity of highly cited keywords, marking active periods of hotspot keywords.

Figure 8: Visualization of journal co-citation networks, reflecting the thematic correlation strength between journals.
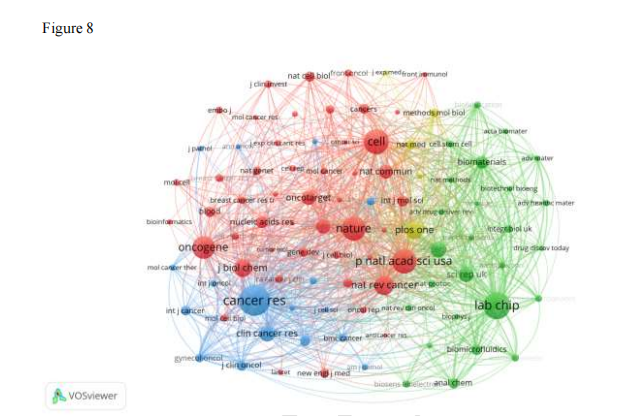
Figure 9: Burst analysis of highly cited references, filtering key literature.
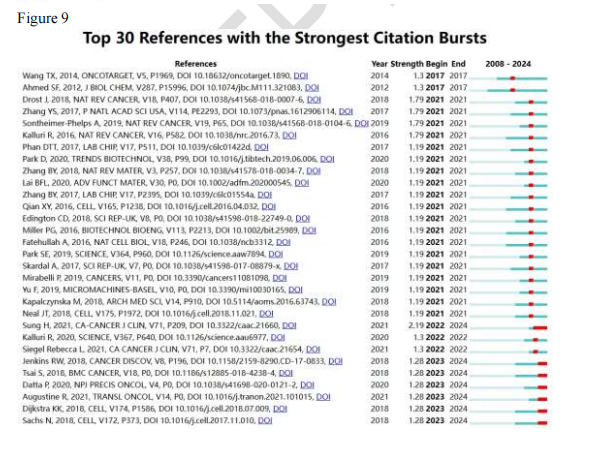
Core Authors: Dongeun Huh (in the field of bioengineering and organ-on-chip), Douglas Hanahan (tumor mechanism research), etc., with total link strengths of 795 and 740, respectively.
Figure 10: Author co-citation network analysis, presenting core scholars and their collaboration relationships.
4. Future Research Directions
Model Optimization: Enhance the pathological representativeness of organoids for breast cancer tissues, simulating vascularization and immune cell infiltration.
Drug Screening and Personalized Treatment: Utilize organoid chips for high-throughput drug testing, developing treatment plans based on patient genetic characteristics.
Technology Integration: Combine CRISPR gene editing, microfluidic chips, and artificial intelligence to optimize culture conditions and analyze cell behavior.
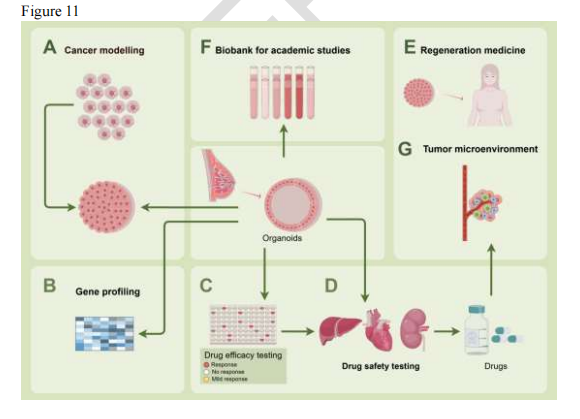
Figure 11: Current hotspot areas in breast cancer organoid chip research, including disease modeling, drug screening, and 7 other directions.
5. Challenges and Ethical Issues
Technical Barriers: Incomplete organoid tissue structure, batch heterogeneity, difficulties in integrating multiple cell types, and cost issues in large-scale production.
Ethical Considerations: Informed consent from patient samples, protection of genetic data privacy, and patent disputes in commercial applications.
6. Research Significance
This study systematically reveals the development trajectory of the breast cancer organoid chip field through bibliometric analysis, providing data support for researchers to grasp hotspot directions (such as tumor microenvironment simulation and personalized treatment), and points out the dual demand for technological breakthroughs and ethical norms, which is significant for promoting the translation of basic research into clinical applications.
Reasons for Recommendation
First systematic bibliometric analysis: This study comprehensively analyzes the breast cancer organoid chip field through bibliometric methods, using CiteSpace and VOSviewer visualization techniques to reveal the evolution trajectory of research hotspots and international collaboration networks, providing a macro academic map for subsequent research.
Multidimensional interdisciplinary perspective: Integrating biomedicine, engineering, and informatics, it not only analyzes basic research (such as optimizing organoid culture models) but also focuses on interdisciplinary applications like microfluidic chip technology and artificial intelligence integration, highlighting the potential for technological translation.
Forward-looking predictions of future directions: Based on keyword clustering and timeline analysis, it clearly proposes a three-stage research path from tumor microenvironment simulation to “enhancing model pathological representativeness – drug screening – personalized treatment,” providing clear guidance for the development of the field.
Breakthroughs in dual dimensions of technology and ethics: This study simultaneously explores technical bottlenecks (such as functional deficiencies and heterogeneity) and ethical challenges (sample privacy and patent disputes), providing risk warnings and compliance references for research standardization and clinical translation.
References: Tian, Y., Chang, H., Cheng, M., Jin, J., Ye, X., & Zhao, X. (2025). Bibliometric insights into breast cancer organoid chips: Trends & emerging areas. International Journal of Surgery, ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.1097/JS9.0000000000002560
When we discuss breast cancer research, we often focus on clinical data or single technological breakthroughs, but this article provides a unique perspective through bibliometrics, like a panoramic map, clearly outlining the development trajectory and future direction of this field over the past decade.
A set of data in the article is particularly impressive: China ranks first globally with 74 publications and 1667 citations in related research, with institutions like Fudan University making significant contributions. This not only reflects research strength but also indicates that Chinese scholars have gained a voice in this cutting-edge field. However, what truly captivates me is the interdisciplinary charm revealed by the research, from the initial optimization of organoid culture models to the deep integration with microfluidic chips and artificial intelligence, the collision of basic medicine and engineering technology is opening new paths for breast cancer research.
For clinical doctors, the article’s mention of the “from laboratory to clinical” translation direction is highly enlightening. Organoid chips can accurately simulate the tumor microenvironment of patients, providing possibilities for personalized drug screening, and in the future, it may achieve precise treatment with “one chip per person.” For readers without a medical background, it is worth paying attention to the ethical considerations behind the technology: when we use patient tissues to construct organoids, how do we balance research progress with sample privacy? These discussions give a humanistic warmth to cold technology.
The value of this article lies in its ability to not only summarize research achievements but also serve as a compass, guiding future research key nodes, whether it is enhancing the pathological representativeness of organoids or overcoming technical bottlenecks in multicellular integration culture, each direction could become the next breakthrough point. For basic researchers, it provides a macro research perspective; for clinical practitioners, it showcases the potential of translational medicine; and for the public, it unveils the mysteries of cutting-edge medical research, showing how the scientific power against breast cancer is gradually accumulating. Research is never an island; when different fields focus on this, perhaps the dawn of a cure is not far away.
(Du Jiaqi, Eight-Year Graduate Student at Shanghai Changhai Hospital)
Editor: XU, LYYReview: Zhang Jian, Li HengyuLiterature Delivery: If you need the full text, please leave your email in the background.


 Remember to like, comment, and check in~
Remember to like, comment, and check in~