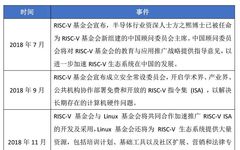
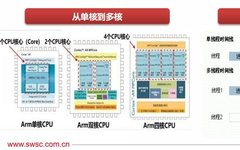
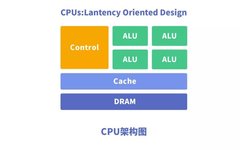
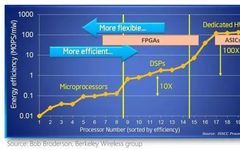
Innovations in RISC-V: Standing on the Shoulders of Giants
RISC-V is also known as “the Linux of CPUs.” For some, this title feels like a legacy and an innovation at the same time, especially if you are a staunch believer in open source. However, I am a true pragmatist, and the excessive marketing of RISC-V has made me lose interest in the term. It … Read more