Using Phyphox and ESP32 Bluetooth to Plot Power Supply Voltage vs. External Resistance
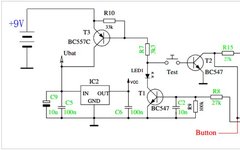
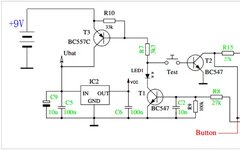
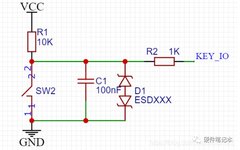
1 Introduction After conducting the experiment “Plotting the P-R Characteristic Curve of the Power Supply,” using the existing circuit and making a few modifications to the experimental source code, the microcontroller successfully performed the experiment “Plotting the Relationship Curve between Power Supply Output Voltage and External Resistance.” 2 Circuit Setup for the Experiment Connect a … Read more