
This article is from the WeChat public account:Pinwan (ID: pinwancool), Author: lzh, Cover image from: Visual China
At the end of 2021, the five major Android application stores in China jointly announced that they would promote support for 64-bit applications in the domestic Android ecosystem. According to the joint initiative released by these five manufacturers, any APP uploaded or updated on OPPO, vivo, Xiaomi, Tencent Application Assistant, or Baidu Mobile Assistant must be in 64-bit format by the end of December 2021, and 32-bit APKs will no longer be accepted. Furthermore, starting in 2023, 32-bit applications will not be able to run on systems that support 64-bit.
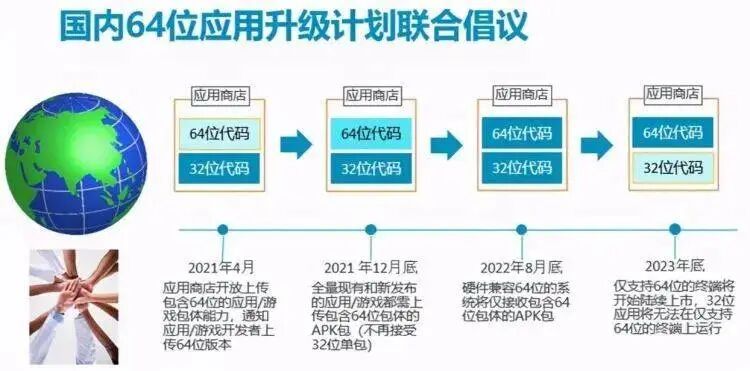
Huawei has also notified all developers through the Huawei Developer Alliance email that it will phase out 32-bit applications and fully promote 64-bit versions:
Starting February 1, 2022, new games and applications listed/updated in the Huawei App Market must include a 64-bit version, and the Huawei App Market will no longer accept applications that only contain a 32-bit version; starting September 1, 2022, the Huawei App Market will no longer accept applications that contain a 32-bit version.
The main reason for the urgent promotion of 64-bit applications by mobile terminal manufacturers comes from pressure from the upstream supply chain. For example, ARM announced that starting in 2022, it will no longer support 32-bit in its Cortex big core CPU products, which is pushing downstream manufacturers to fully support 64-bit applications.
The Road to 64-bit Android Has Not Been Smooth
Users who pay attention to mobile hardware should know that support for 64-bit applications was already available when the Android 5.0 system was released, with the Qualcomm Snapdragon 410 processor being the first 64-bit processor from Qualcomm, released in 2013. However, it was not until 2022 that 64-bit support was “forced” into implementation, which is three years later than Google’s requirement in 2019 for developers to submit 64-bit applications to the Google Play Store.
Although Google had already integrated the latest development tools in Android Studio to default to 64-bit so files for apps, this “mandatory” new regulation did not seem to attract enough attention, as developers could still modify the configuration files in Android Studio to package so files in 32-bit to “bypass” the requirement. The international environment is such, but the domestic Android ecosystem is different.
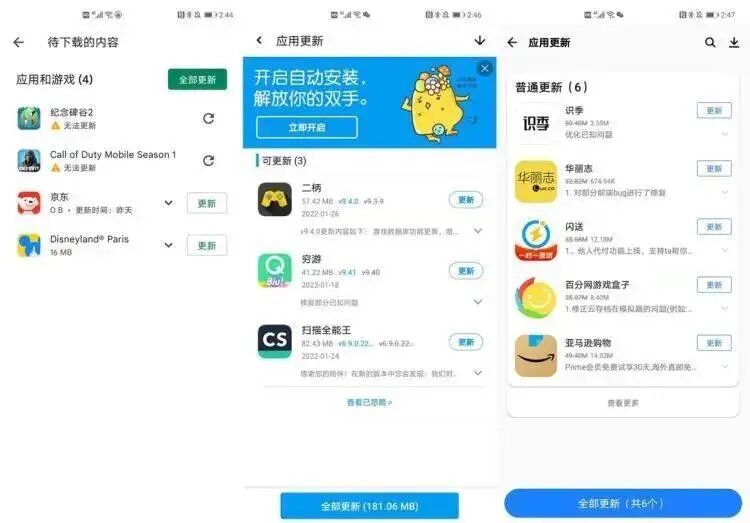
Apps updated in the Play Store and App Store differ
Not only do mobile manufacturers have their own official software stores, but there are also third-party markets like Baidu Software Manager, CoolAPK, and Tencent Mobile Assistant. If a phone has installed a non-official version from the official market, it may frequently switch between versions from multiple stores, making 64-bit adaptation even more challenging. Installing a clean official application is not an easy task.
In summary, the confusion of official, unofficial, and firmware versions is a common problem in the software installation ecosystem.
By 2021, before the release of Qualcomm’s 8 Gen 1 and MediaTek’s 9000 processors, there was a lack of an effective way to fundamentally solve this problem.
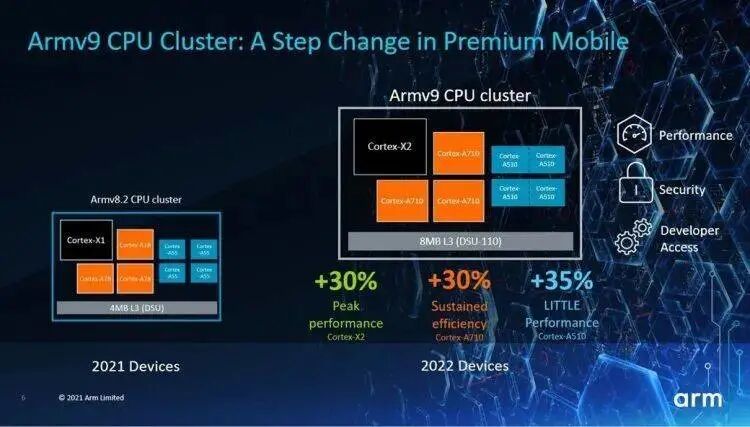
The only solution left is to eliminate this situation from the “bottom up” by controlling the hardware ecosystem. For example, Qualcomm and MediaTek released the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 and Dimensity 9000 at the end of last year, which not only feature significant performance improvements that the public can “perceive”—the entire framework has been upgraded to ARM’s latest generation of Cortex-X2 super big core, Cortex-A710 big core, and Cortex-A510 small core architecture—but the most significant change is the more fundamental “upgrade,” which is that the instruction set adopts ARM V9.
ARM V9, like the previous generation V8, is a pure 64-bit instruction set, with the Cortex-X2 super big core and Cortex-A510 small core only supporting (backward compatibility with V8) 64-bit, while only the “middle core” Cortex-A710 big core is compatible with the 32-bit V7 instruction set.

In other words, if this software is still 32-bit, then running on new architecture processors like Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 and Dimensity 9000 with the V9 instruction set can only be locked to run on the A710 core, meaning that regardless of whether the phone is locked or running in “performance mode,” the application will always be running on the A710 core, which is less powerful than the super big core and not energy-efficient compared to the small core.
What Are the Improvements of 64-bit?
The most direct advantage is that it can be seen directly in numbers, that is, 64-bit processors have stronger performance. Vivo once stated, “Supporting 64-bit devices is the only way for Android applications to utilize more than 4GB of RAM address space, leverage wider registers and higher precision in data processing, and obtain enhanced security features.”
At the same frequency, a 64-bit processor can handle 8-byte data, while a 32-bit processor can only handle 4-byte data, allowing for faster data processing. Additionally, there is a significant difference in addressing space; for example, the 32-bit addressing space is 2 to the power of 32, supporting about 4GB, while 64-bit is an exponential increase, being 2 to the power of 64, and supports dynamic memory allocation.
In summary, the collaboration of 64-bit processors, 64-bit application systems, and 64-bit applications is essential for improving operational efficiency.
Since 64-bit applications can bring performance improvements, why is their adoption so difficult?
In addition to the previously mentioned confusion of software versions and download channels, a major reason is that Android has very good compatibility with “old devices”. For example, although Google has implemented various measures to encourage developers to release 64-bit applications, it still retains compatibility with 32-bit applications, even providing a 32-bit option on its own Chrome browser download page.
Moreover, for developers, the maintenance and operational costs are also a stumbling block to the widespread adoption of 64-bit. For instance, if a developer only creates a 32-bit application, it can run perfectly on a 64-bit processor, albeit not in optimal conditions.
However, if they only develop 64-bit applications, some older devices will not be able to run them, leading to a risk of losing users. Additionally, developing and testing for both 32-bit and 64-bit requires separate processes, which adds to the maintenance burden.
Another important point is that developers do not solely use pure Java for Android application development; they utilize the Android NDK to combine Java with C++, and C++ development is typically a team effort, which poses maintenance and security challenges for small development teams.
How Are Android’s 64-bit Devices and Apps Developing in 2022?
Now that the joint initiative has been announced, how are Android phone manufacturers implementing it?
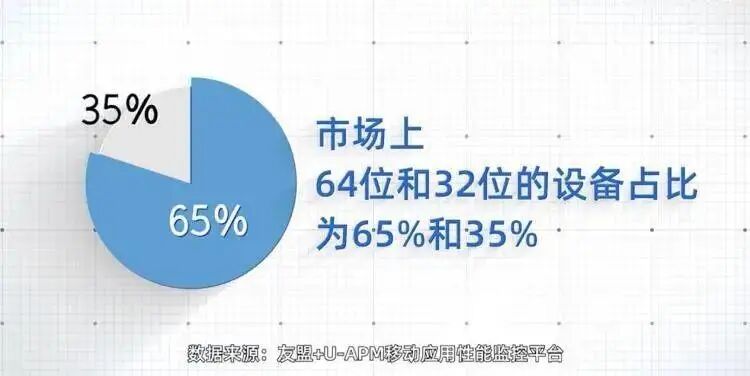
According to data from Umeng+ U-APM, as of December 2021, the market share of 64-bit and 32-bit devices was 65% and 35%, respectively. Furthermore, according to Umeng+ U-APM’s mobile application performance monitoring platform, the application crash rate for 32-bit devices is 4.8 times that of 64-bit devices, indicating that 64-bit applications are the trend in terms of both device share and stability.
Currently, whether in the built-in official application stores of mobile terminal devices or in third-party application markets, neither Huawei nor OPPO’s application stores directly indicate whether upgraded applications are 64-bit; only Xiaomi clearly marks which software is upgraded to 64-bit in its application store.
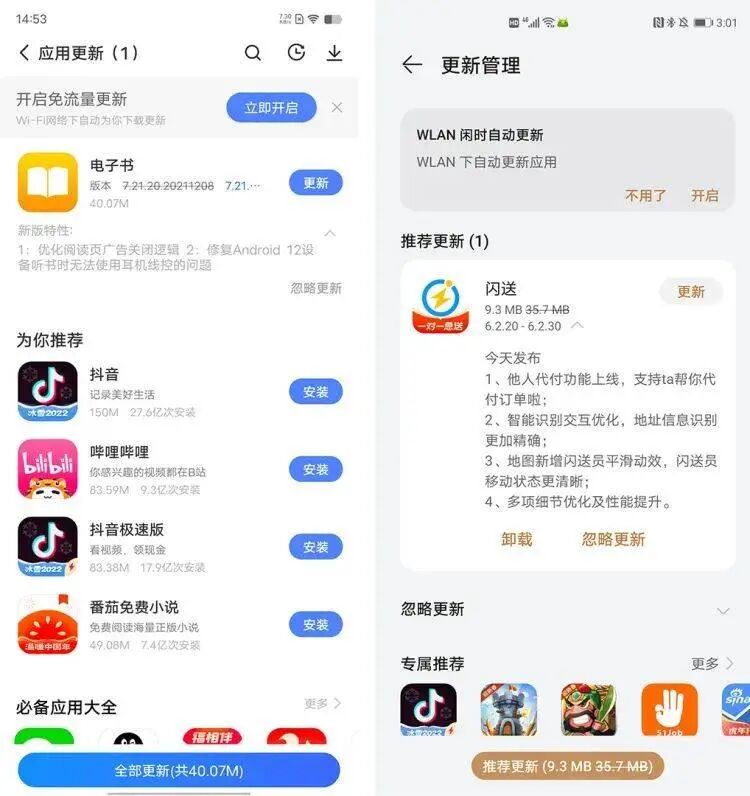
The left side shows the Vivo application store, while the right side shows the Huawei application store, neither of which labels 64-bit apps.
For example, on my Huawei phone, I need to use a third-party program called LibChecker to check the applications on my device. Currently, there are 312 applications, with about 66% being 64-bit and 29% being 32-bit.
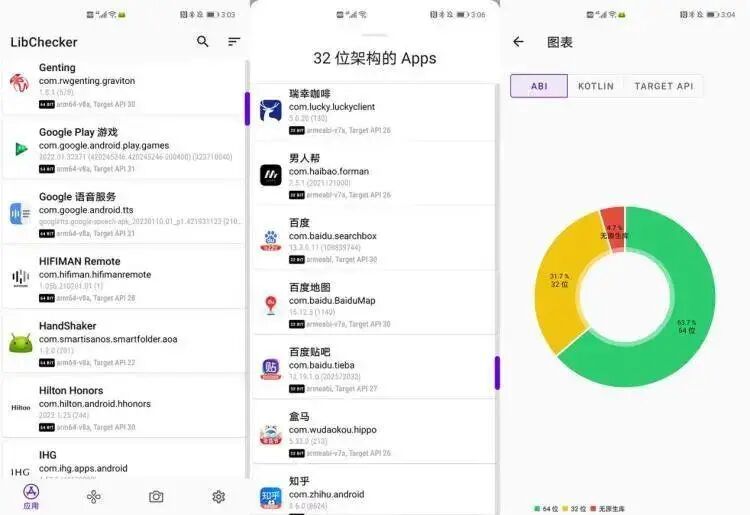
LibChecker shows that the 64-bit software is mostly from Google and international apps, while the 32-bit ones are predominantly domestic software. The phone is a Mate 40 Pro with EMUI 11 version.
However, upgrading Android applications to 64-bit does not necessarily mean they will be better than 32-bit. For instance, a user on Zhihu named Shijinshuijiu reported that the QQ app in the Play Store is a 64-bit version but has serious bugs and cannot be used, and it lacks a night mode and a simplified mode.
Moreover, the old version of QQ Music in the Play Store is 64-bit, while the new version has reverted to 32-bit.
The left side shows the Xiaomi 12 Pro with Baidu Maps as a 64-bit app, while the right side shows a 32-bit app, with no noticeable difference in loading speed.
The open software ecosystem of Android directly leads to fragmentation in the software sector, making unification a challenging task.
Additionally, looking at current Android software, the installation package sizes are increasing, which directly leads to higher memory consumption during installation, increased system resource usage during operation, and higher performance requirements for the system. Adopting a 64-bit system allows single-threaded processing to exceed 4GB of RAM, which can better utilize the internal hardware of the phone for handling large games and high-bitrate video files.
This explains why smartphone RAM is increasing, often reaching 12 or 16GB, and processor frequencies are also rising. All of this is to ensure that 64-bit software can run smoothly, but it also brings some negative factors, such as power consumption issues and heat generated by super big cores running large software.
In summary, 2022 may become the “year of large-scale adoption of 64-bit applications” for Android, with hardware driving software upgrades becoming the norm. However, ultimately, effective and non-blanket measures are needed to ensure the healthy development of the Android ecosystem.
This article is from the WeChat public account:Pinwan (ID: pinwancool), Author: lzh
The content represents the author’s independent views and does not reflect the position of Huxiu. Unauthorized reproduction is prohibited. For authorization matters, please contact [email protected]. If you have any objections or complaints regarding this article, please contact [email protected].
End
Want to gain knowledge? Follow Huxiu’s video account!