

Editor’s Note:
By chance, I learned that Raspberry Pi can also be related to PLCs in industrial applications, and there are some mature solutions. I found this quite interesting and thought it could be popularized. Thus, we have this series of articles today. Starting from today, we will successively publish three articles, explaining from the aspects of background and hardware, system software, and control software, hoping to help everyone broaden their ideas and practical projects.

Raspberry Pi is a credit card-sized computer designed for student computer programming education. Based on an open Linux system, it allows free development in programming languages such as C/C++, Python, and Javascript, providing an excellent learning and testing platform for many programming enthusiasts. With the help of open-source software and hardware resources, it has become possible for us to quickly realize IEC61131-3 standard edge computing PLC products.
Before formally introducing how to implement Raspberry Pi edge computing PLC, we first need to look at the background of the concept of edge computing PLC. In the era of Industry 4.0, the boundary between traditional control technology OT (Operation Technology) and information technology IT (Information Technology) is becoming increasingly blurred. Currently, in the field of industrial automation, if we need to integrate traditional PLC controllers with IT systems, a large number of gateway products are used, which may be a helpless move at this stage.
However, the complexity of the system architecture greatly increases the latency of industrial data and reduces the efficiency of big data collection, thereby restricting the accuracy of future industrial big data analysis. At the same time, all raw industrial data will be collected and analyzed by cloud platform servers. As factory applications become more complex, the computational power limits of cloud platforms and the bloated databases will pose great challenges to future industrial intelligence.
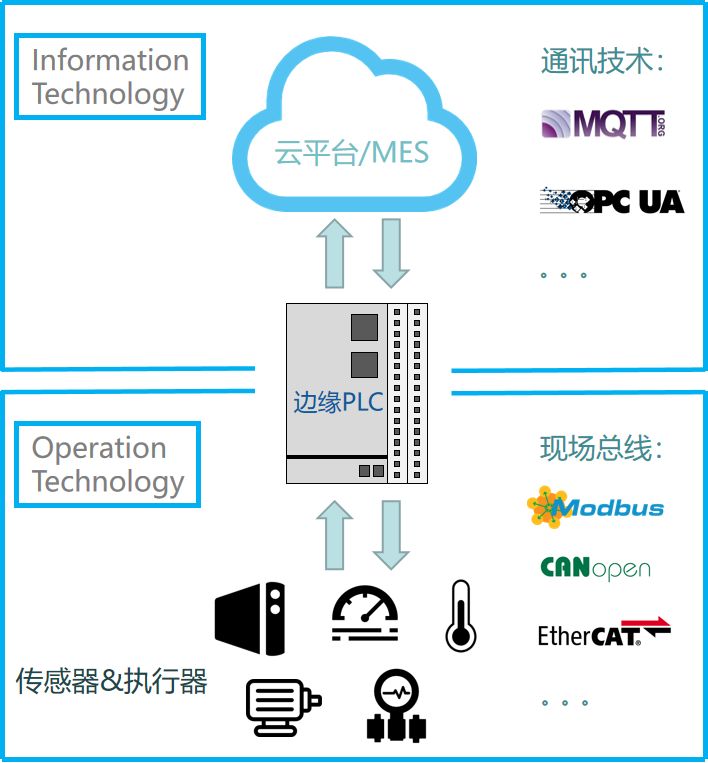
To achieve this goal, in addition to powerful data processing capabilities and large-capacity memory hardware support, the software needs to simultaneously support open OT and IT platforms, such as IEC61131-3 programming, PLCopen MC motion control, EtherCAT, CANopen, Modbus, and other traditional OT technologies, as well as open IoT programming platforms like Node-RED, local embedded databases, OPC-UA, MQTT, and other IT technologies.
Here we have also preliminarily sorted out the relevant technical parameters of the Raspberry Pi 3B+ Compute Module core board:
Processor: Broadcom BCM2837B0, Cortex-A53 (ARMv8) 64-bit SoC @ 1.2GHz
RAM Memory: 1GB LPDDR2 SDRAM
Flash Memory: 8GB/16GB/32GB eMMC Flash
Operating Temperature Range: -25℃ – 80℃
Hardware Certification:
Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC) 2014/30/EU
Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive 2011/65/EU
Maintenance End Date: January 2026
However, after a comprehensive analysis, we believe that the Raspberry Pi CM core board’s processor still has relatively few peripheral interfaces for industrial control applications. For example, the UART peripherals for implementing industrial controller RS232/RS485/RS422 interfaces only have 2, and there is no CAN bus interface. Ethernet must be expanded through a USB interface chip, which greatly limits the real-time performance of network interaction. This will pose significant challenges for some field buses that require high speed, such as EtherCAT, mainly limited by the bandwidth of the internal USB-to-Ethernet interface chip and the real-time processing of Ethernet packets by the USB chip.
Of course, we need to give the industrial controller products developed based on the Raspberry Pi CM core board an appropriate positioning to fully utilize its hardware features. Traditionally, industrial controllers use processors with lower clock frequencies and very limited memory space. Therefore, the Raspberry Pi CM industrial controller should leverage its high-performance computation and large storage capacity, allowing computations and data storage that traditionally needed to be done on the cloud to be delegated to the Raspberry Pi CM industrial controller as needed. This is the edge computing PLC concept we introduced earlier. At the same time, it can also communicate with other industrial controllers or sensors through industrial field buses and communication protocols, such as Modbus, CANopen, EtherCAT, OPC-UA, etc.
Regarding the hardware part, one last point to note: the processor of the Raspberry Pi CM core board generates significant heat, so proper heat dissipation design is required. Similarly, its power consumption is high and not suitable for some low-power or heat-sensitive application scenarios.
Next Article
We will focus on analyzing the issues and improvement solutions of the basic operating system Linux on Raspberry Pi in industrial scenarios, so stay tuned.

Author Bio
Bao Rui, CTO and co-founder of Yikong Technology, previously worked at KW-Software in Germany for 10 years engaged in IEC61131-3 software solution development, technical support, and marketing, with in-depth research and experience in IEC61131-3 standards and related industrial controller products, field bus development and applications, system architecture, and basic platform technologies.
Complete question bank for the beginner electrician exam in 2021 (including answers)
Is troubleshooting inverter faults difficult? Just one click!
Can you brush through all electrical exam questions with one click? Have you not owned this artifact yet?
Which of the five major electrical drawing software (CAD, Eplan, CADe_simu…) do you pick?
Latest electrical version CAD drawing software, with super detailed installation tutorial!
Latest electrical drawing software EPLAN, with super detailed installation tutorial!
Common issues for beginners using S7-200 SMART programming software (with software download)
Comprehensive electrical calculation EXCEL sheets, generated automatically! No need to ask for electrical calculations!
Bluetooth headsets, electrician/PLC introductory books given away? Come and claim your electrical gift!
Basic skills in PLC programming: ladder diagrams and control circuits (with 1164 practical cases of Mitsubishi PLC)
Still can’t understand electrical diagrams? Take away the basics of electrician diagram reading and simulation software, and quickly get started with theory and practice!
12 free electrician video courses, 10GB of software/e-books, and 30 days of free electrician live courses are given away!