Many high-end MicroSD (TF) cards claim to have read speeds exceeding 90MB/s, but in actual use, the speed is often found to be only half or even lower than the claimed value. So, who is affecting the performance of the storage card?

Understanding the Parameters of Storage Cards
With the popularity of smartphones and tablets, MicroSD (TF) standard storage cards have become ubiquitous. Therefore, the storage cards referred to in this article are these tiny MicroSD cards. The question arises: the packaging of commercially available storage cards prints many standards, such as Class2-10, UHS-I, SDHC, and SDXC. What do these terms mean?
SDHC and SDXC are standards used to distinguish capacity. In the world of storage cards, cards with a capacity of 2GB or less are collectively referred to as “SD” (disk format FAT16), cards with a capacity of 2GB to 32GB are called “SDHC” (disk format FAT32), while larger capacity cards are known as “SDXC” (disk format exFAT). Currently, the maximum capacity of SDXC cards has surpassed 200GB. Indeed, as 32GB cards have fallen below 50 yuan, SDHC has already exited the historical stage, and SDXC truly dominates the market.
Class and UHS represent the speed standards of storage cards (also known as video classes). Among them, Class has the longest history and includes several levels: Class0, Class2, Class4, Class6, and Class10. The number following Class represents the minimum sustained write speed of that class. For example, a Class2 card has a minimum write speed of 2.0MB/s, while Class10 means the write speed can reach at least 10MB/s.
With the emergence of features like 4K video recording, even Class10 has become insufficient. Therefore, the SD Card Association has introduced the “UHS-I” performance label, raising the write and read speeds to 50MB/s and 104MB/s, respectively. Currently, UHS-I is further divided into UHS-I U1 and UHS-I U3 standards (Figure 1), where UHS-I U1 means the minimum sustained write speed must reach 10MB/s (some high-end Class10 cards are also classified as UHS-I U1), while UHS-I U3 means that speed must exceed 30MB/s.
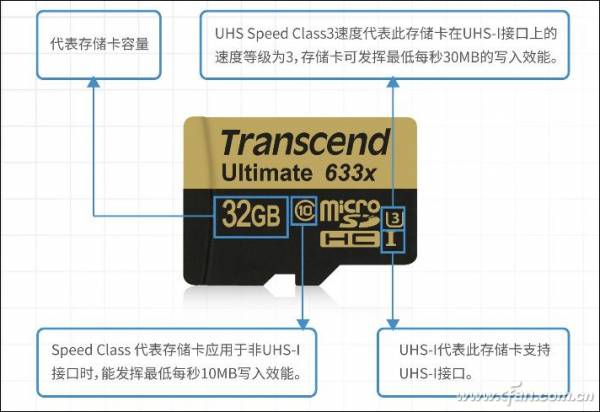
01
Regrettably, when we joyfully buy a UHS-I U3 high-speed storage card, in most cases, we cannot fully utilize its performance. Why is that?
Who Affects the Speed of Storage Cards
The Audi R8 supercar can reach a top speed of 330 Km/h, but this speed can only be achieved on a professional test track. In a busy urban area, even a high-end sports car must adhere to a speed limit of 80 Km/h, and if it encounters traffic jams, its actual speed may be less than that of a bicycle. The situation for storage cards is quite similar; their speed entirely depends on the host device.
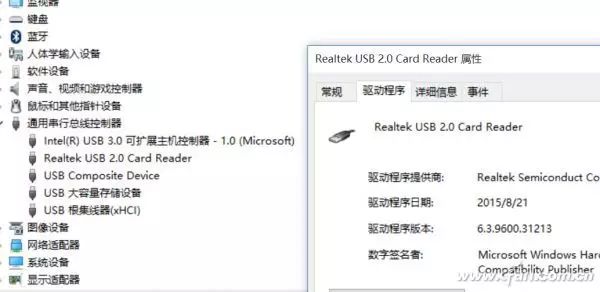
In simple terms, smartphones, tablets, laptops, and USB card readers all serve as hosts for storage cards, supporting them through physical slots and controller chips. The percentage of performance a storage card can achieve entirely depends on the card reader’s controller chip (Figure 2). The problem is that, for cost and positioning reasons, most manufacturers tend to cut corners in the selection of the card reader’s controller chip, thereby limiting the performance of the storage card.
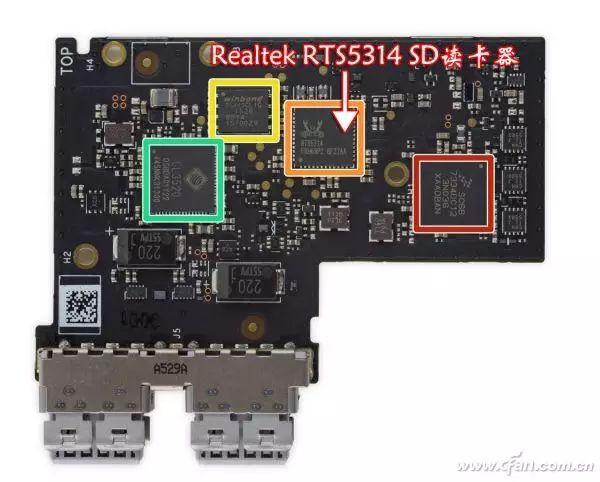
02 Microsoft Surface Book is equipped with a Realtek RTS5314 card reader controller chip.
The ThinkPad 8 is considered a high-end product among Windows tablets, and it was promoted as having a “built-in MicroSD card reader interface that significantly improves transfer speeds.” It seems that it should be able to fully unleash the potential of the storage card, right? Unfortunately, a user once tested a Lexar 64GB MicroSDXC UHS-1 card (rated 90MB/s read and 40MB/s write) and found that the read and write speeds when inserting the card into the ThinkPad 8 slot were around 24MB/s and 21MB/s, respectively (Figure 3). If this card is connected to a PC via a USB card reader, the read and write speeds can be increased to 92MB/s and 47MB/s (Figure 4). If the ThinkPad 8 performs like this, one can only imagine the performance of card readers in cheaper Windows tablets.
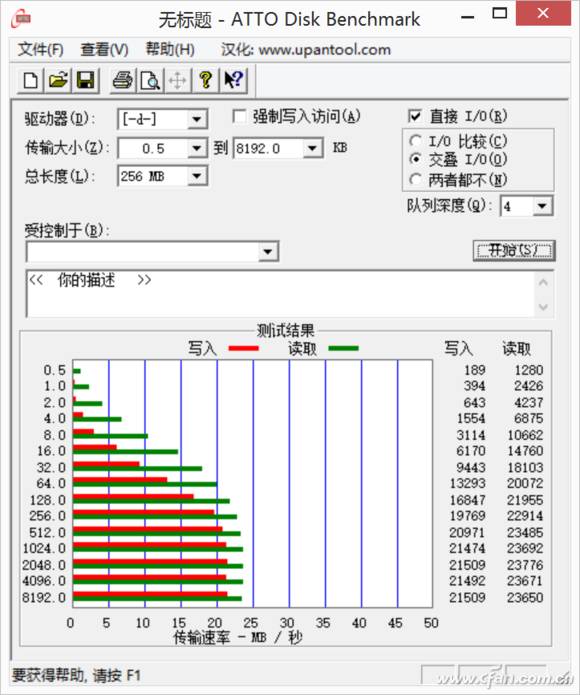
03
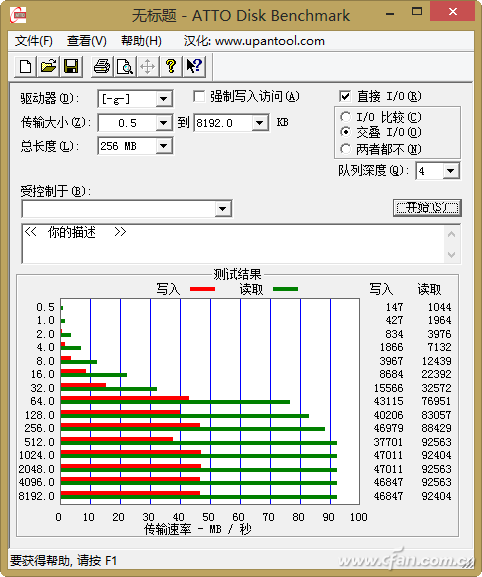
04
Laptops are no better than tablets; currently, most laptops still use USB2.0 bus for their card reader controller chips (Figure 5). Even the fastest storage cards cannot exceed the speed limit of USB2.0 when plugged into a laptop. In contrast, smartphones perform better than products that are several times their size.
05
Taking Samsung phones as an example, starting from last year’s Note4, they can perfectly unleash the performance of UHS-I standard storage cards (Figure 6). This is quite understandable, as mid-to-high-end smartphones now support 4K level video recording, and UHS-I was designed for high-definition video recording.
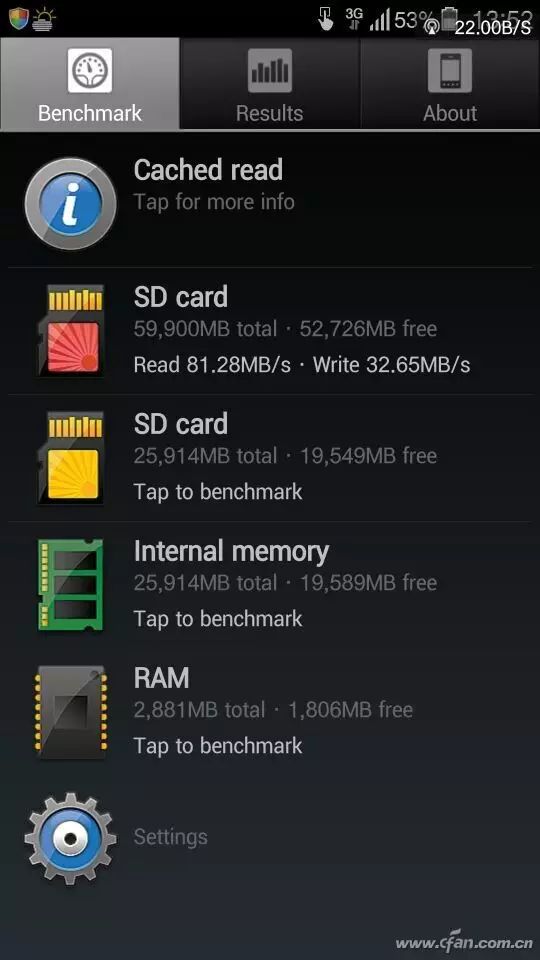
06 Toshiba EXCERIA storage card test screenshot using A1 SD Bench software.
Rationally Considering High-Speed Storage Cards
For cards of the same capacity, the price difference between UHS-I and UHS-I U3 standard storage cards can be several times (Figure 7). If you are not wealthy and do not have extremely demanding speed requirements such as 4K video recording, there is currently no need to choose a higher-speed storage card. When mobile devices fully support UHS-I U3 standard, UHS-I U3 storage cards will also drop to “bargain prices.”

07
In summary, when you find that the speed of a newly purchased storage card does not meet the claimed values, it may not be due to the manufacturer’s false advertising; the fundamental reason is that the card reader of the current device is inadequate. If you really want to tap into the performance of the storage card, using an external card reader with a USB3.0 interface and a high-quality controller chip is essential.
Further Reading: Is It Necessary to Buy a High-Speed SD Card Adapter?
To allow MicroSD cards to fit into laptop card readers (or DC, USB card readers), SD card adapters have emerged. However, the price of SD card adapters varies, and does choosing a high-priced SD card adapter enhance the performance of the storage card? In fact, the price difference of SD card adapters only reflects quality and lifespan and has no impact on speed whatsoever. Opening up an SD card adapter reveals that it is merely an extension of metal contacts, containing no chips or circuits.

