
Click the blue text to follow us
Recently, scholars from the University of California, Berkeley published a paper titled “Why Do Multi-Agent LLM Systems Fail?”, analyzing and summarizing the failure modes of multi-agent systems. I have tried several popular multi-agent development frameworks, and while the demo examples can run successfully, there is still a distance to practical application in production.Multi-agent systems are the mainstream direction for future AI application development. Studying this paper provides valuable guidance for the development of multi-agent applications.
Below is a summary of the paper:
Definition
- Agent: An artificial entity based on LLM, capable of prompt specification (initial state), dialogue tracking (state), and interaction with the environment (e.g., using tools, actions).
- Multi-Agent System (MAS): A collection of agents designed to interact through orchestration to achieve collective intelligence. MAS is structured coordination work that implements task decomposition, performance parallelization, context isolation, dedicated model integration, and diverse reasoning discussions.
Failure Rates of Five Multi-Agent Frameworks
The failure rates of five popular multi-agent development frameworks (using GPT-4o and Claude-3 models) 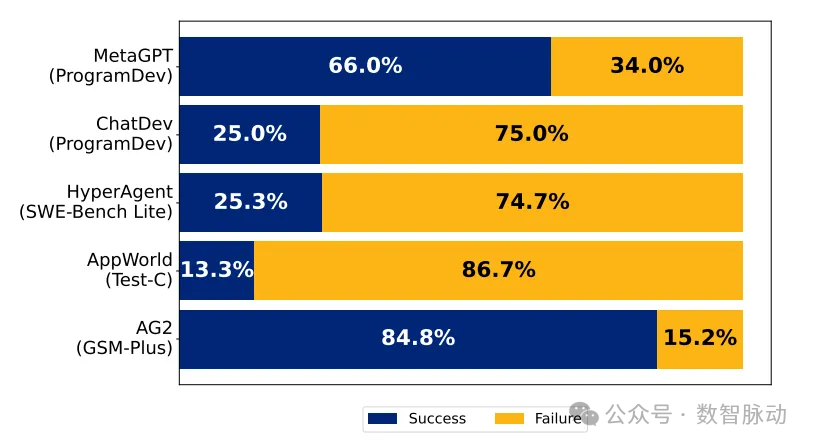
14 Failure Modes
Dialogue among agents is divided into three stages: Pre Execution, Execution, and Post Execution. If a failure mode spans multiple stages, it indicates that the problem may occur at different stages. The percentages represent the frequency of each failure mode and category appearing in the analyzed sample set:
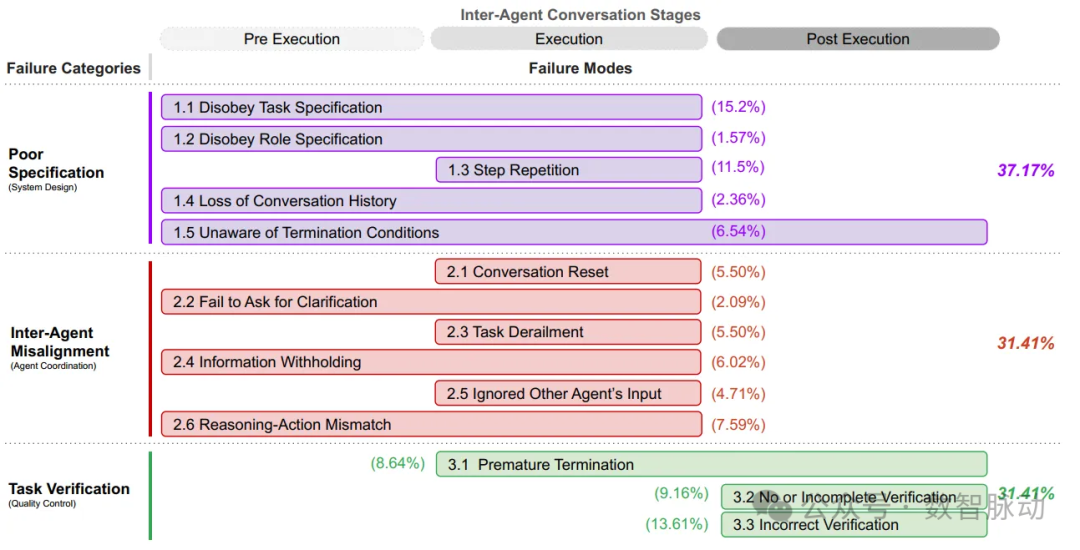
⚙️Specification and System Design Failures
Failures caused by system design defects, poor session management, unclear task specifications or constraint violations, and insufficient definition or adherence to agent roles and responsibilities.
- Violation of Task Instructions: Failure to adhere to the constraints or requirements of a given task, leading to suboptimal results.
- Non-compliance with Role Instructions: Failure to follow the responsibilities and constraints of assigned roles, which may lead to agents overstepping their bounds.
- Step Repetition: Unnecessarily repeating completed steps, which may cause task delays or errors.
- Loss of Dialogue History: Accidental truncation of context, ignoring recent interaction history, reverting to a previous dialogue state.
- Unawareness of Termination Conditions: Lack of awareness of the criteria that trigger the termination of agent interactions, which may lead to unnecessary continuations.
🤖Agent Misalignment
Poor communication, inadequate collaboration, and behavioral conflicts among agents gradually deviate from task objectives.
- Dialogue Reset: Accidentally or unnecessarily restarting a dialogue, which may result in lost progress.
- Failure to Request Clarification: Inability to request additional information when faced with unclear or incomplete data, which may lead to erroneous actions.
- Task Deviation: Straying from the given task’s objectives or focus, which may lead to irrelevant or unhelpful actions.
- Information Concealment: Failure to share or communicate important data possessed by agents, which may affect the decision-making of other agents.
- Ignoring Inputs from Other Agents: Neglecting or failing to adequately consider inputs or suggestions provided by other agents in the system, which may lead to suboptimal decisions.
- Reasoning-Action Mismatch: A discrepancy between the logical reasoning process of agents and the actions they actually take, which may lead to unexpected behaviors.
⚠️Task Validation and Termination Failures
Premature termination of execution without sufficient mechanisms to ensure accuracy, reliability of interactions, decisions, and outcomes.
- Premature Termination: Ending dialogue, interaction, or tasks before all necessary information exchanges or goals are achieved, which may lead to incomplete or erroneous results.
- No or Incomplete Validation: Omitting appropriate checks or confirmations of task results or system outputs, which may leave errors or inconsistencies undetected.
- Incorrect Validation: Failing to adequately validate key information or decisions during iterations, which may lead to errors or vulnerabilities in the system.
How to Improve the Performance and Reliability of Multi-Agent Systems
⚔️Tactical Strategies
- Improve prompts and clarify role task definitions: By providing clearer prompts and explicit role task definitions, agents can better understand and execute their tasks. For example, providing detailed background information and specific operational instructions for each agent can reduce misunderstandings and the likelihood of erroneous execution.
- Optimize agent organization and interaction: Adjust the organizational structure and interaction methods among agents to enhance collaboration efficiency. For instance, adopting a hierarchical structure or specific communication protocols can ensure smooth and effective information flow among agents.
- Self-validation and mutual validation: Incorporate self-validation and mutual validation steps during task execution. Agents can periodically check their work results or cross-validate with other agents to ensure the correctness and completeness of tasks. For example, requiring agents to review and confirm each other’s results before arriving at a final outcome.
🏗️Structural Strategies
- Strengthen validation processes: Establish more robust validation mechanisms to ensure the accuracy and reliability of task results. This includes introducing independent validation agents or adopting stricter validation standards to timely identify and correct errors.
- Standardize communication protocols: Develop unified communication standards and data formats to reduce misunderstandings and errors caused by unclear or inconsistent information transmission. By having clear communication protocols, agents can more accurately understand and process the information received.
- Incorporate probabilistic confidence measures in decision-making: Integrating probabilistic confidence measures into agent interactions can significantly enhance the reliability of decision-making and communication. Agents can be designed to take action only when confidence exceeds predefined thresholds.
- Memory state management: Effective memory and state management can help agents maintain an accurate understanding and tracking of context during task execution, avoiding failures due to information loss or confusion.
Welcome to follow me as we explore the journey of digital intelligence together!