Many people have heard of touch screens in their daily lives, but what exactly is a touch screen? What are its principles and functions? Let’s explore it together.

Touch Screen
Function
For convenience, people use touch screens to replace mice or keyboards. A touch screen is an intelligent device that can display information and communicate with PLCs, and it also has memory and programming capabilities. We can use touch screens to display the operating status of PLCs, production line speed, and more.
Principle
When in operation, we must first touch the touch screen installed at the front of the display with our finger or another object. The system then locates the selected information input based on the icon or menu position touched by the finger.
The main types of touch screens
According to the working principle and the medium of information transmission, there are: resistive, infrared, surface acoustic wave, and capacitive.
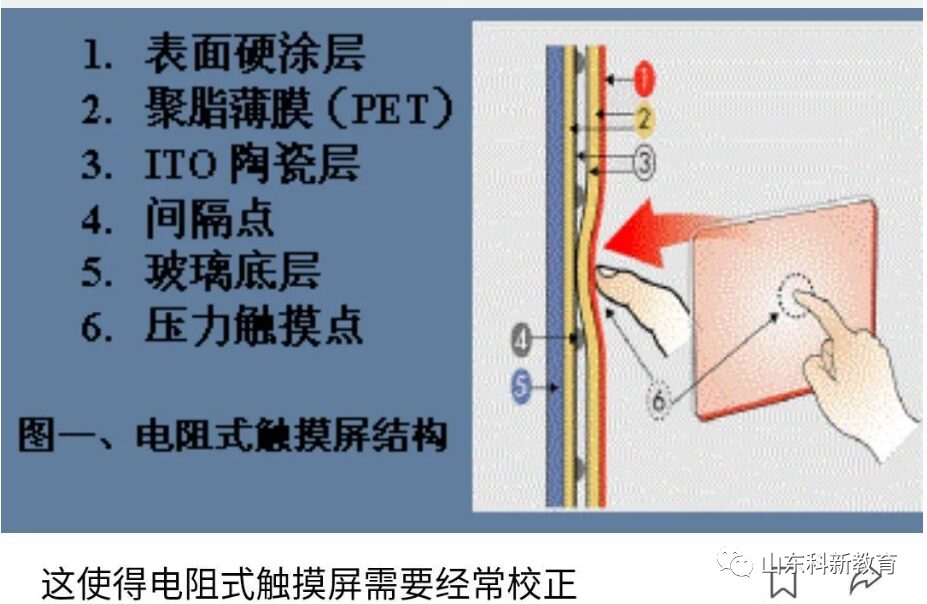
Resistive Touch Screen: The screen is made of a multi-layer composite film that matches the surface of the display, with a layer of glass or acrylic as the base, coated with a transparent conductive layer.
On top of this, there is a layer of hard, smooth, scratch-resistant plastic, which also has a transparent conductive layer on its inner surface. Between the two conductive layers, there are many tiny (less than one-thousandth of an inch) transparent isolation points that insulate them.
The key to resistive touch screens lies in material technology.
Types and Applications of Resistive Touch Screens
Resistive touch screens work in a completely isolated environment, resistant to dust and moisture. They can be touched by any object, making them suitable for industrial control and limited use in offices.
Types:
Resistive screens are classified into four-wire, five-wire, six-wire, and other multi-wire resistive touch screens.
Surface Acoustic Wave Touch Screen:
The touch part of a surface acoustic wave touch screen can be a flat, spherical, or cylindrical glass plate installed in front of CRT, LED, LCD, or other display screens. This glass plate is purely tempered glass, unlike other touch screen technologies, and has no film or overlay. The upper left and lower right corners are fixed with ultrasonic transmitting transducers, while the upper right corner has two corresponding ultrasonic receiving transducers.
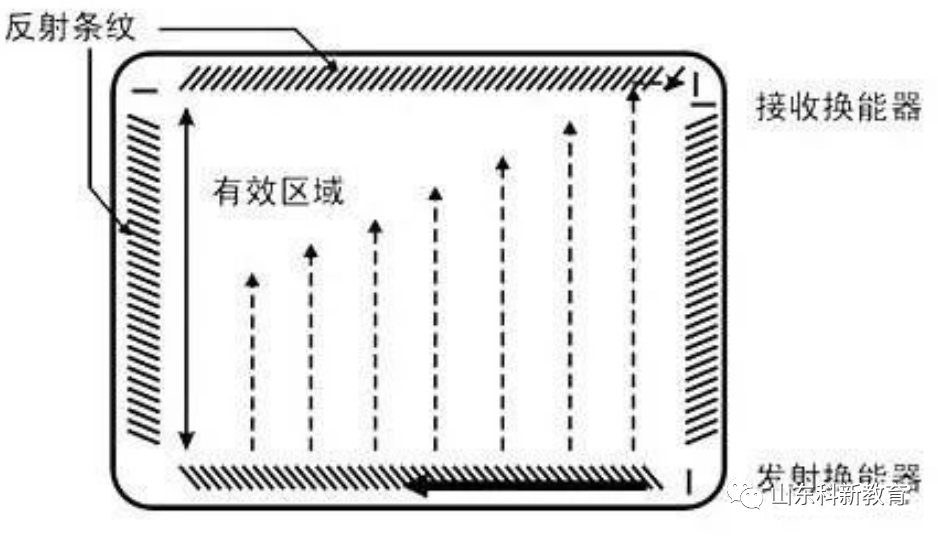
The four edges of the glass screen are engraved with precisely spaced reflective stripes at 45 degrees from sparse to dense.
Working Principle: The transmitting transducer converts the electrical signals from the controller via the touch screen cable into acoustic energy that travels to the left surface. This energy is then reflected by the precise reflective stripes at the bottom of the glass plate into a uniform surface, and the acoustic energy travels across the screen surface, directed by the upper reflective stripes to the receiving transducer on the X-axis, which converts the returning surface acoustic energy into electrical signals.
Advantages:
1. Surface acoustic wave touch screens are robust and suitable for public places.
2. They have a fast response speed, making them the fastest among all touch screens, providing a smooth user experience.
3. Their performance is stable because the principle of surface acoustic wave technology is consistent, and the controller measures the attenuation to calculate the touch position, ensuring high stability and accuracy.
4. The control card can differentiate between dust, water droplets, and fingers, as well as how many fingers are touching.
5. Surface acoustic wave touch screens have a third Z-axis, which responds to pressure. The greater the force applied to the screen, the wider and deeper the attenuation in the signal waveform.
Disadvantages
The disadvantage of surface acoustic wave touch screens is that dust and water droplets on the surface can block the transmission of surface waves. Although the intelligent control card can discern this, if dust accumulates to a certain extent, the signal will attenuate significantly, causing the surface acoustic wave touch screen to become sluggish or even non-functional. Therefore, dustproof touch screens have been introduced, and it is recommended to clean the touch screen regularly.
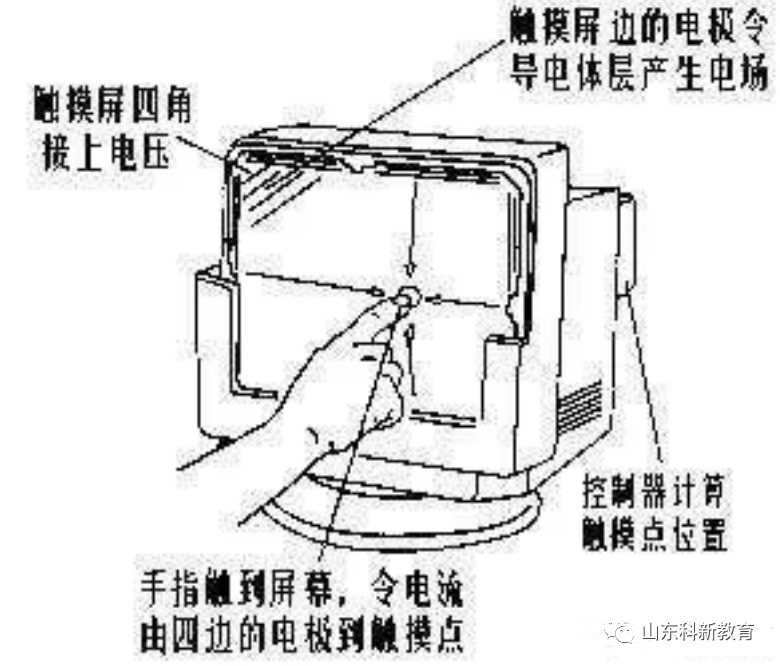
Capacitive Touch Screen
The structure of a capacitive touch screen mainly consists of a layer of transparent film deposited on the glass screen, followed by a protective glass layer over the conductor layer. The double glass design thoroughly protects the conductor layer and sensors. Additionally, elongated electrodes are deposited along the edges of the touch screen, creating a low-voltage AC electric field within the conductor. When the user touches the screen, a coupling capacitance is formed between the human electric field, the finger, and the conductor layer. The current emitted by the edge electrodes flows toward the touch point, and its strength is proportional to the distance between the finger and the electrode. The controller behind the touch screen calculates the current ratio and strength to accurately determine the touch point location.
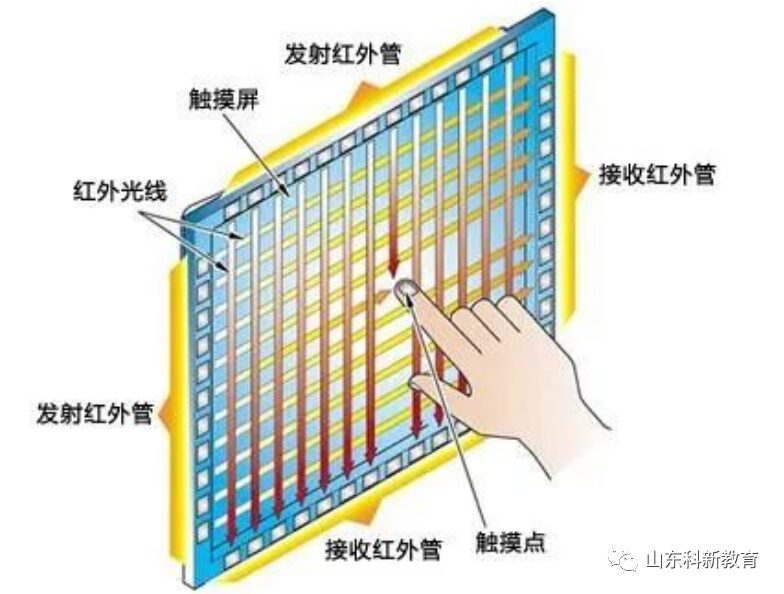
Infrared Touch Screen: They are inexpensive, easy to install, and can detect light touches and fast touches well. However, infrared touch screens rely on infrared sensing, and external light changes, such as sunlight and indoor lighting, can affect their accuracy. Additionally, infrared touch screens are not waterproof and are sensitive to dirt; any small foreign object can cause errors and affect performance, making them unsuitable for outdoor and public use.
“

”
Scan the QR code above
GetFree 【Siemens Data Collection】
Disclaimer: This article is reprinted from the internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If there are copyright issues, please contact us for deletion, thank you!