Following the introduction of the Gigabit Industrial Ethernet technology EtherCAT G by Beckhoff at the SPS fair in Nuremberg last year, the ETG (EtherCAT Technology Group) technical committee officially accepted this technology as an important supplement to the EtherCAT standard in September this year.

This means that the EtherCAT G technology, which can extend EtherCAT to Gigabit and 10 Gigabit levels, will be supported and promoted by ETG in the future.
So, how should we view the evolution of EtherCAT technology to the G era?
In this issue, we will briefly discuss EtherCAT G technology, combining some publicly available information.
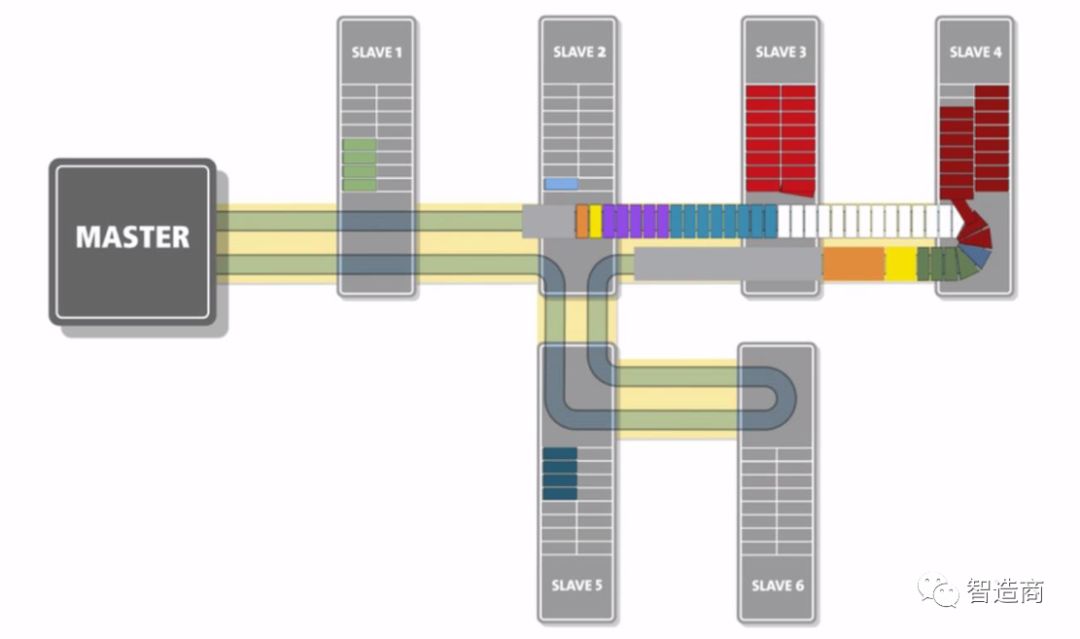
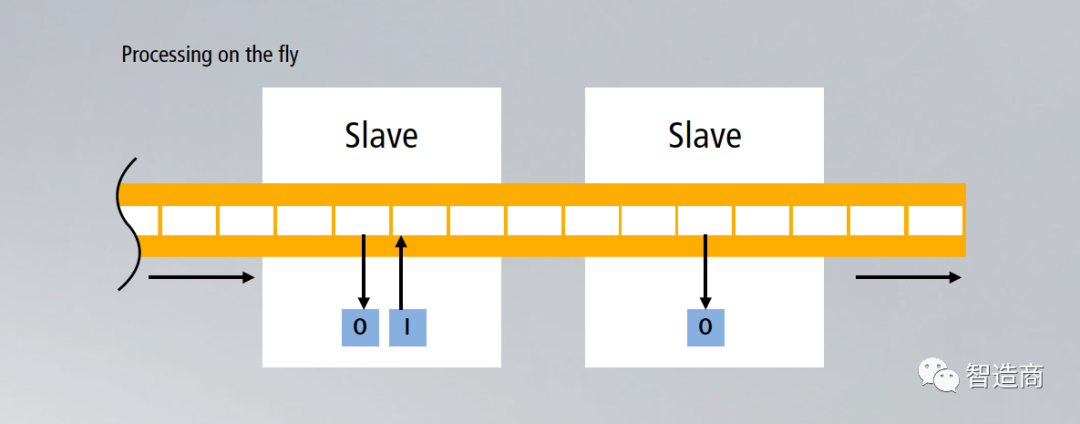
We know that EtherCAT was launched by Beckhoff in 2003 and has since been supported and promoted by ETG. Its unique operating mechanism – the processing-on-the-fly, commonly known as the “data train”, enables it to achieve extremely high communication rates and is considered the fastest industrial Ethernet bus currently available. Therefore, EtherCAT is very suitable for automation applications that have many system nodes and require short cycle response times.

However, due to the existing EtherCAT communication bandwidth being at the hundred megabit level, it shows certain limitations in coping with the increasing volume of data transmission and processing tasks in current manufacturing systems, such as:

-
In the measurement testing field, ultra-sampling applications that require extremely high sampling rates;
-
Large-scale complex applications with a huge number of devices in the system, requiring very short cycle times;
-
Visual applications that require real-time transmission and processing of video image data streams;
-
Complex motion control applications, such as planar transfer systems;
-
…
In this case, we need to use Gigabit or even 10 Gigabit Ethernet technology, EtherCAT G or EtherCAT G10, to expand the application areas of EtherCAT.

At the 2018 SPS fair in Nuremberg, Beckhoff officially launched EtherCAT G to the market and subsequently submitted this Gigabit Ethernet technology as an extension of EtherCAT to ETG. After a comprehensive review, ETG accepted EtherCAT G as a supplement and improvement to EtherCAT technology at its technical committee meeting on September 24 this year. Currently, ETG is working to add EtherCAT G to the relevant technical specifications.
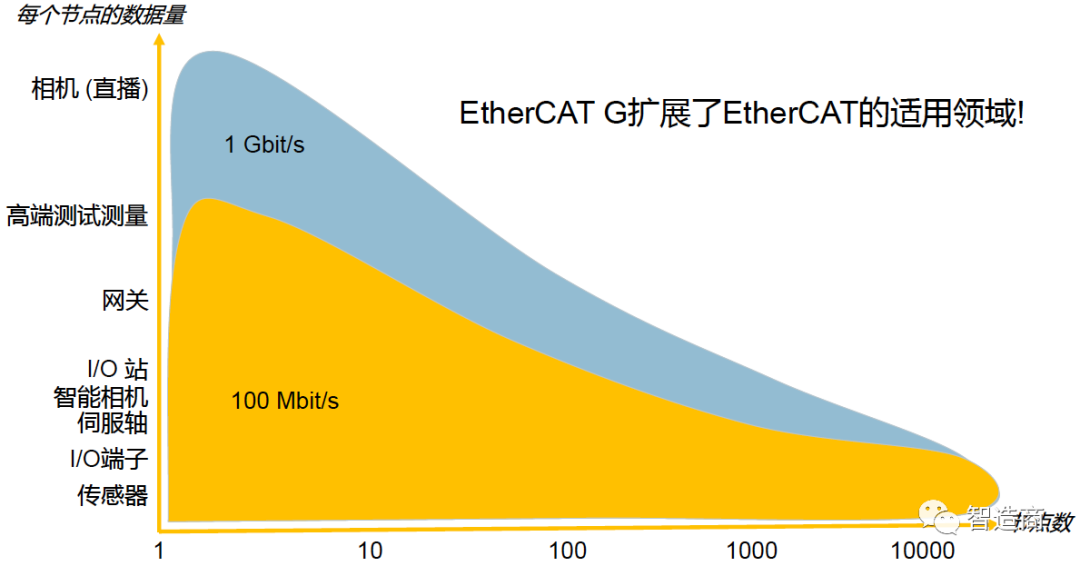
According to the official information, EtherCAT G and EtherCAT G10 have the following characteristics:
-
Still based on EtherCAT’s unique processing-on-the-fly operating mechanism;
-
Bandwidth will expand to 1Gb/s and 10Gb/s;
-
Fully compatible with EtherCAT;
-
Compliant with Ethernet standards (IEEE 802.3);
-
In standard mode, the master station does not require software adaptation;
ETG claims that EtherCAT G maintains the unique functional mechanisms and high-speed characteristics of EtherCAT, while helping users integrate and consolidate new large-volume data transmission and processing tasks based on the existing technology system, which will expand the application range of EtherCAT technology.
It is worth noting that ETG did not refer to EtherCAT G and EtherCAT G10 as new versions of EtherCAT in its official announcement, but defined them as an extension and expansion of EtherCAT technology, similar to the previous Safety over EtherCAT and EtherCAT P, and emphasized that EtherCAT G is fully compatible with the existing hundred megabit level EtherCAT.
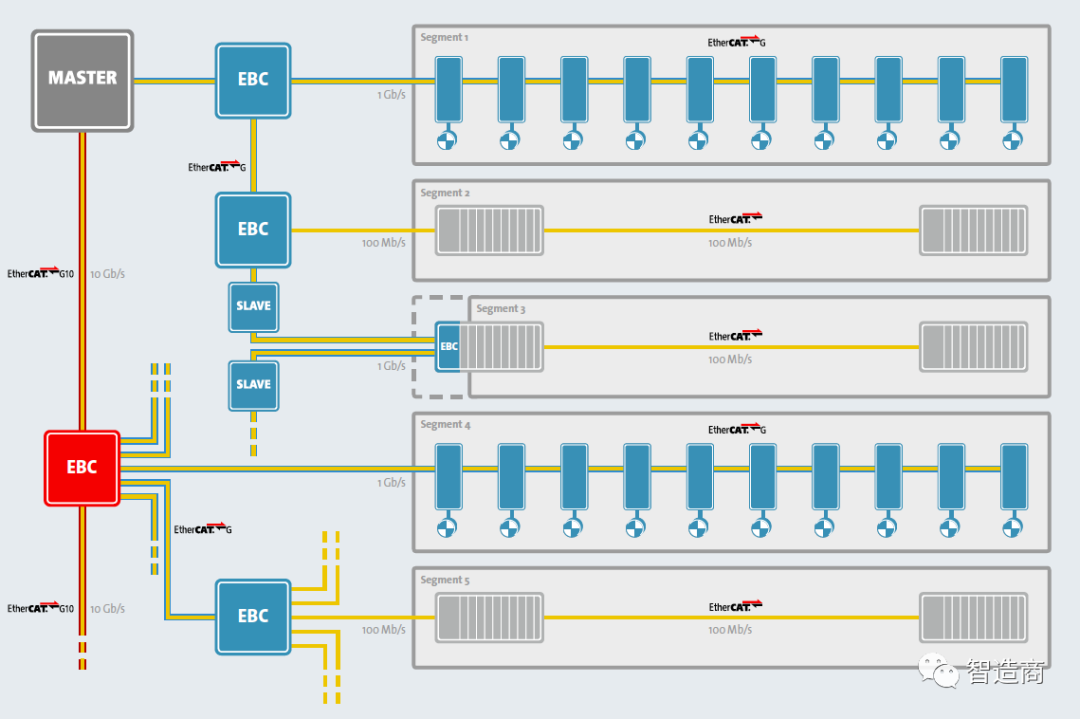
This means that EtherCAT G slave devices can operate in a hundred megabit EtherCAT network; conversely, hundred megabit EtherCAT devices can also be used in EtherCAT G systems, but in this case, the entire network will automatically switch to 100 Mb/s.
To effectively integrate hundred megabit EtherCAT devices and segments into Gigabit EtherCAT G systems, EtherCAT G supports branch management functions.

On one hand, users can use the EtherCAT Branch Controller (EBC) to separate hundred megabit EtherCAT from Gigabit EtherCAT G segments, allowing for parallel processing of data transmission, thus reducing and avoiding the speed reduction impact of hundred megabit EtherCAT devices on Gigabit EtherCAT G system performance; on the other hand, with the help of parallel data processing mechanisms, EBC can also help reduce the information transmission delay caused by too many device nodes in the Gigabit EtherCAT G system.
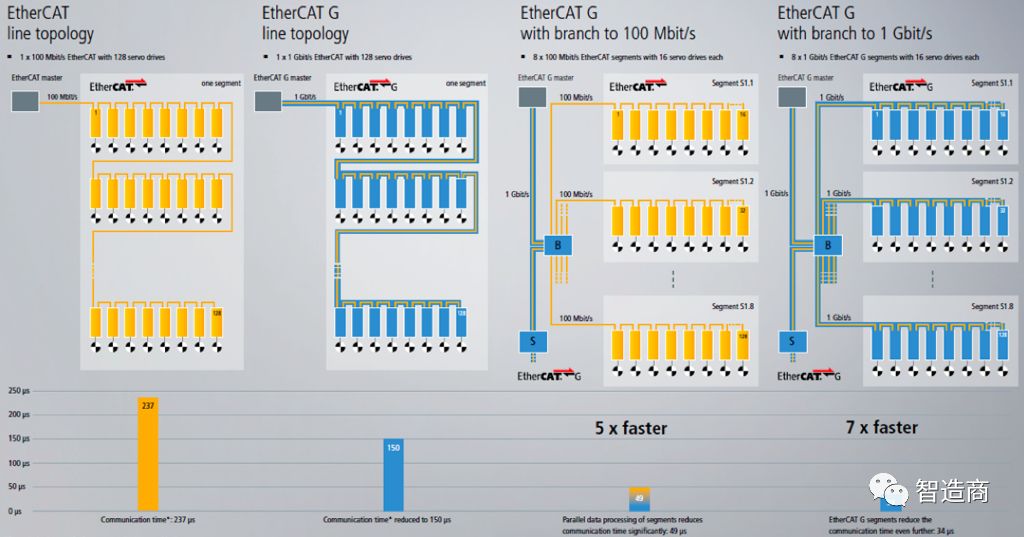
According to the official data, taking a large servo system with 128 axes as an example, assuming each servo drive contains 8 bytes of input / 8 bytes of output, with 1024 bytes of input/output data per cycle:
-
If they are connected in a single EtherCAT segment, the communication cycle time will be 237 μs;
-
If all devices in the segment, including the master station and each servo drive, use EtherCAT G, the communication time will drop to 150 μs;
-
However, if EBC is used to divide the 128 servo axes into 16 segments, even if only the master station uses EtherCAT G while all slaves still use EtherCAT, the communication time will significantly reduce to 49 μs;
-
And if all master and slave devices are changed to EtherCAT G on this basis, the communication time will further decrease to 37 μs.
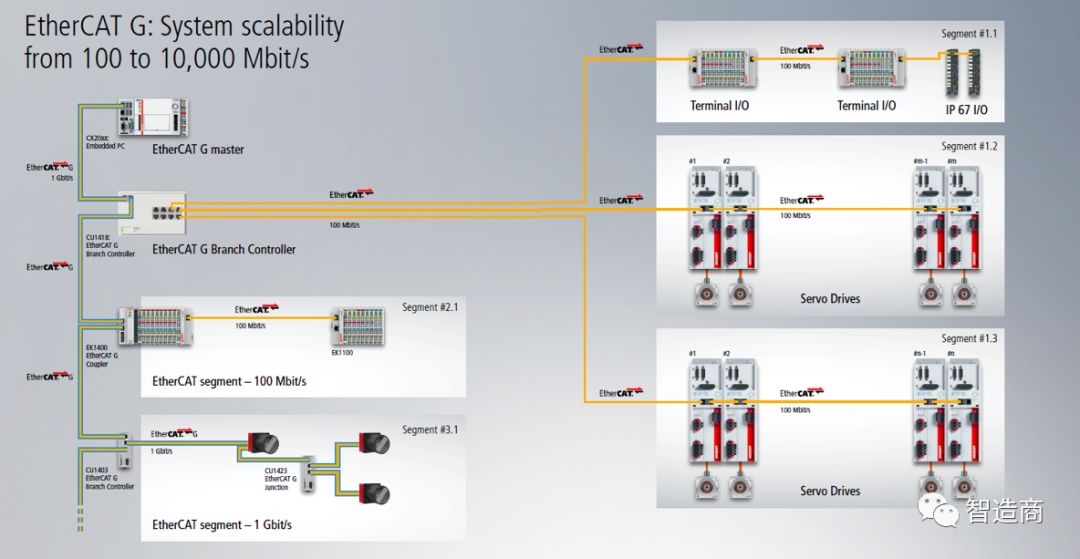
From this, we can see that systems already equipped with EtherCAT technology can significantly reduce communication time to one-fifth of the original by simply introducing EBC segment controllers to separate the original EtherCAT segments and changing the master station to EtherCAT G devices without replacing existing EtherCAT devices. This means that in addition to helping integrate data processing applications, EtherCAT G also provides a new solution for enhancing system communication rates; moreover, users can protect their existing device assets while expanding applications through EtherCAT G.
Currently, Beckhoff has launched corresponding segment controller products.
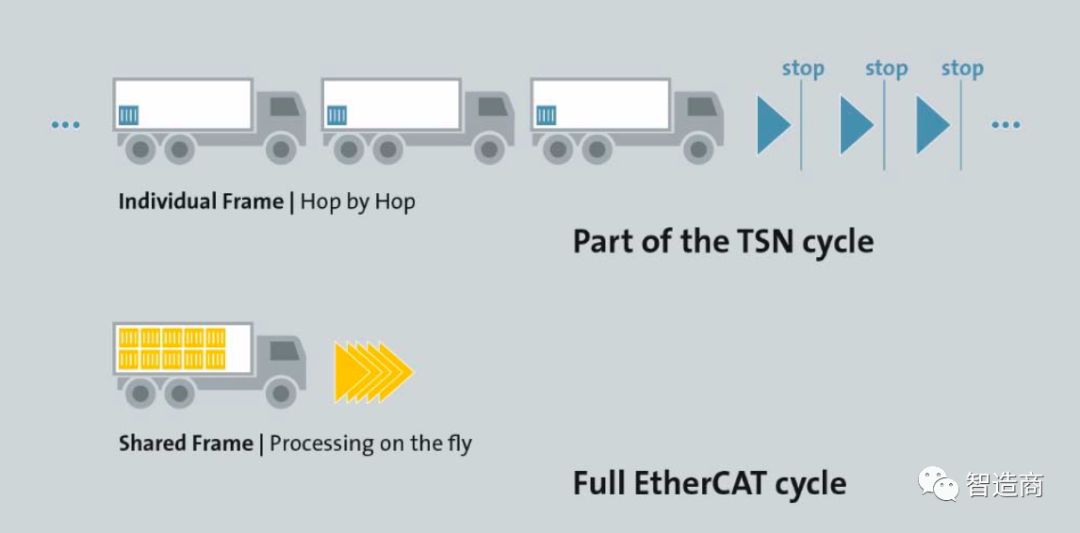
Regarding the currently popular TSN technology, ETG positively recognizes its advantages in constructing heterogeneous networks, etc.; however, considering that the TSN standard has not yet been officially released, it believes that there is still some uncertainty at present (to be discussed later).
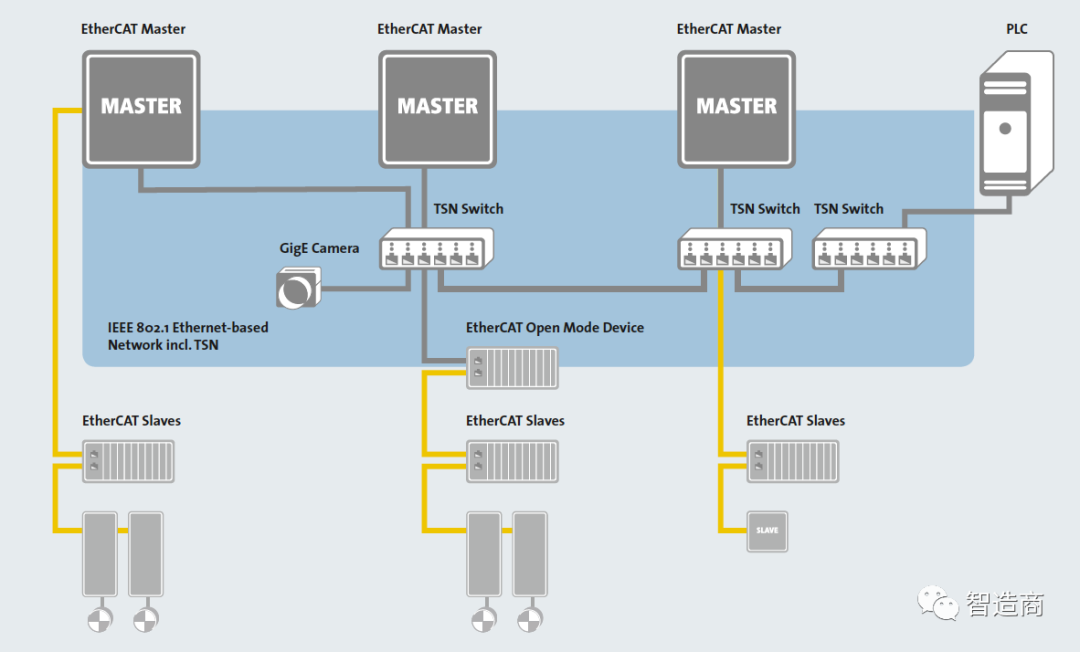
At the same time, EtherCAT will appropriately use TSN technology, for example: launching the EtherCAT – TSN device profile to help users integrate EtherCAT devices and segments into TSN heterogeneous networks.
However, TSN will not change EtherCAT, and there will be no new version related to TSN integration.

In summary, the emergence of EtherCAT G continues to confirm the trend we previously discussed, which is the evolution of industrial communication buses to Gigabit levels, aimed at meeting the increasing data application needs in the industrial field. However, it adopts a relatively unique problem-solving approach, namely: extending and expanding based on existing mature technologies while being fully backward compatible, allowing users to expand functions based on the current system without worrying that the original EtherCAT will be replaced, and without having to wait for EtherCAT G.
Because the application areas of EtherCAT and EtherCAT G are different, the two coexist rather than replace each other.
The above content is purely the author’s personal opinion, and any similarities are purely coincidental.
Related information and images are referenced from:
beckhoff.com
ethercat.org
