
With edge computing, various issues arising from the overly centralized data processing model of cloud computing in digital transformation are easily resolved.

Decentralized technologies such as edge computing and boundary-less communication will play a key role in the upgrading of digital transformation. Image/China News Network
Written by | Liu Honglun
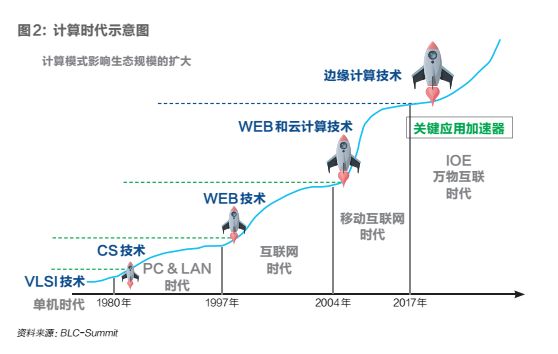
Since the birth of computers, we have experienced several different IT eras: single machines, PC & LAN, the Internet, and mobile Internet. In the near future, humanity will welcome the era of IOE (Internet of Everything), but we must realize that the evolution of computing models also affects the expansion of ecological scales.
Currently, China is at a critical period of digital transformation. Digital transformation essentially refers to the process of traditional economic models transitioning towards a digital economy, driven by digital technology to enhance productivity and transform production methods.
As new technologies develop and the efficiency of traditional industries declines, traditional industries urgently need to utilize the new generation of information technology to break down data barriers across different levels and industries, strengthen data-driven capabilities, improve overall operational efficiency, accelerate digital transformation and upgrades, and build a new digital economy system. So, which technologies will become the key drivers for the success of enterprise digital transformation? What relationships need to be managed effectively in digital transformation?
Academically, it is widely believed that the most significant change in this new round of industrial transformation is the inclusion of ‘things’ into intelligent interconnectivity, achieving deep collaboration and integration between OT (Operation Technology) and ICT. Ultimately, this is about leveraging data value and enhancing productivity based on the interconnectivity of all things.
In summary, digital transformation must effectively manage five relationships: the relationship between cloud and edge, i.e., the relationship between cloud computing and edge computing; the integration of OT and ICT; the match between technological innovation and industry applications; the relationship between people and things, as well as between things and things; ensuring broad connectivity while also guaranteeing the security of all connection points.
A report from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology shows that there is a significant disparity in the development level of the digital economy across various industries, exhibiting characteristics where the tertiary industry outperforms the secondary industry, which in turn outperforms the primary industry. Currently, the tertiary industry continues to lead, the secondary industry is steadily improving and making continuous efforts, while the primary industry is relatively lagging.
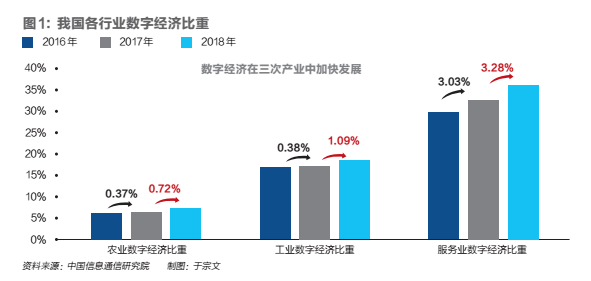
For an industry to transform, the fundamental reason is to better leverage its value chain and reorganize the collaboration between upstream and downstream in the value chain. Issues such as an excessively long value chain and low industry innovation capacity have led to the need for transformation and upgrading. In other words, when an industry cannot generate more profit or maintain profitability, it must consider transformation and upgrading.
Currently, impacted by technological advancements, rising labor costs, and frequent fluctuations in capital markets, traditional heavy asset manufacturing industries urgently need to transform and upgrade to increase competitiveness, innovation, and survival rates. It is foreseeable that the growth rate of the industrial digital economy will accelerate.
Technology is the cornerstone of business development. To achieve rapid growth in the industrial digital economy, the coordinated growth of different technologies becomes particularly important.
Different Eras, Different Key Technologies
In every computing model, we need foundational technologies, infrastructure, and most importantly, key application accelerators. In the standalone era, VLSI was the foundational technology, while high-level languages and operating systems were the key application accelerators; as we entered the PC & LAN era, we manufactured microprocessors, and DOS and Windows became the key application accelerators, bringing computers into the hands of everyone and allowing people to experience the power of computers firsthand.
As history progresses, the Internet era has become a time of heroes, where WWW and TCP/IP technologies, through HTML as a key accelerator, have enabled the rise of Google, Facebook, Baidu, Alibaba, and other internet giants. At this time, Nokia was still the king of mobile phones, occupying half of the entire mobile phone market, and no one would have thought that this giant would nearly vanish overnight in the tidal wave of mobile Internet. Android and iOS became the key application accelerators of the 4G and smartphone era.
Before long, we will usher in the era of the Internet of Everything, with more and more intelligent devices emerging. So what will be the key application accelerators of this era?
Undoubtedly, cloud computing has brought great convenience to our lives, allowing enterprises to use computing resources as easily as using water and electricity. However, the development of any phenomenon has two sides. Now, cloud computing has become the ruler of ‘things’, where the cloud can directly control all ‘things’, but users must obtain permission from the cloud to use their own ‘things’, and we are becoming more accustomed to this model.
It is estimated that by 2020, the number of smart devices owned per person globally will reach 6.58, totaling 46 billion devices, with the vast majority of smart devices located at the network edge. Currently, all edge devices and applications are vertically independent systems, each with its own boundaries, including system boundaries, network boundaries, application boundaries, manufacturer boundaries, and old and new products. How do we solve the instant interconnectivity across boundaries? How do we achieve free interoperability across boundaries? How do we ensure the free delivery of product services at the edge? The answer lies in leveraging edge computing and boundary-less communication to realize end-to-end service delivery.
In the industrial sector, to achieve cost reduction, quality improvement, innovation enhancement, and most importantly, safety assurance, the key is to realize interconnectivity, interoperability, and mutual services. This is a decentralized process that drives the manufacturing industry from ‘hardware thinking’ to ‘service-oriented thinking’, relying on emerging technologies to enhance the collaborative efficiency of the entire value chain, driving innovation and quality improvement at every stage of the value chain through ‘services’.
The Key Significance of Edge Computing
According to IDC predictions, data generated by IoT devices will grow from 0.1ZB in 2013 to 4.4ZB by 2020. Humanity has truly entered the era of massive data.
It is foreseeable that as digital transformation accelerates, the number of intelligent devices appearing in every link of traditional manufacturing will also increase. Compared to the smart devices in individuals’ hands, the data from intelligent devices on production lines has greater mining value.
From the perspective of enterprise managers, there are two main purposes for choosing industrial upgrades: first, to improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and provide a better customer experience; second, to reshuffle the value chain to discover new business models and provide new products and services.
From a strategic perspective, the objectives of industrial upgrades are to optimize digital business and to innovate and transform digital business.
The future will be a society where data generates value. How to effectively utilize and extract more data value will be one of the key points for enhancing enterprise value. Currently, the data stored in the cloud is just the tip of the iceberg; more data still resides in terminal devices. Moreover, data is increasing explosively, while the computing power of the cloud is becoming increasingly inadequate, with time efficiency nearing its peak.
Although the most popular model currently is the large platform industrial internet model, these platforms still operate independently, creating more data islands. Achieving interconnectivity and generating greater value from data across different platforms is incredibly challenging. This centralized model largely hinders the free flow of massive data. Therefore, the most important issue we need to solve is how to maximize the value generated by data across the entire value chain, addressing aspects such as computational efficiency, delivery capability, and security assurance at each link of the value chain.
The widespread application of edge computing can indeed enhance computational efficiency, reduce latency, and improve data security. Consequently, the various issues arising from the overly centralized data processing model of cloud computing in digital transformation are easily resolved.
Moreover, processing data at the edge in ‘micro-clouds’ not only improves efficiency but also promotes the transition of traditional manufacturing from ‘hardware thinking’ to ‘service thinking’. In the ‘edge computing + boundary-less communication’ model, each intelligent edge device can switch between service provider and client at any time.
Edge computing will be the key accelerator of digital transformation.
In the centralized era, massive data from digital transformation is aggregated to the cloud through a hierarchical network, where it is analyzed and processed. The efficiency of this data processing method will increasingly decline in the era of massive data generation.
However, in the era of edge computing, digital transformation will shift from a product-oriented approach to a service-oriented approach, with every edge-capable endpoint able to become a service provider, allowing all service providers to exist on the same plane. The application of edge computing in digital transformation will drive the transition from product-oriented to service operation across the entire lifecycle, triggering innovation in product services and business models, profoundly impacting the development of value chains, supply chains, and ecosystems, and promoting their high-quality development.
As more and more intelligent edge devices become increasingly sophisticated, the variety of services they can provide will also change dramatically, with personalized innovations emerging continuously. Products and services that were previously unimaginable under a purely cloud architecture will become possible.
In simple terms, empowering the edge is a resource push that harbors new creative pathways. Without breaking, there can be no establishment. The bold application of edge computing will provide greater opportunities to help enterprises accelerate digital transformation, thereby unlocking data value and potentially generating new business models.
When endpoints possess stronger processing capabilities, they can deliver real-time and continuous effects on-site, with data being analyzed and processed locally, enabling programs that previously needed to be transferred to the center for service to be directly delivered by the endpoint as a service source, moving towards a true IOS (Internet of Service).
In some IoT scenarios that require extremely rapid response, edge computing capabilities surpass those of traditional cloud architectures. This addresses the main pain points of Industry 4.0 and allows AI to interact or differentiate interactions at sufficiently powerful computing edges, enabling distributed artificial intelligence (DAI) to be realized at the edge, performing tasks that previous computing models could not accomplish, such as collaborative operations in smart transportation, industrial robotics, and defense.
For instance, in vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications, the traditional method is V2 cloud 2 cloud 2 X, which relies on old models. With the support of edge computing technology, the new exploration is to bypass the ‘cloud’ and connect V directly to X.
The future society will be a ‘service-oriented society’, where everything can become a ‘service’. As business models continue to evolve, the demand for personalized/customized services will grow, and decentralized technologies such as edge computing and boundary-less communication will play a crucial role in this transformation.
(The author is the CEO of N22 Technologies and a senior figure in the edge computing industry; Editor: Xie Lirong)
(This article was first published in the May 27, 2019 issue of Caijing Magazine)

