
Robotics technology is a high-tech field that integrates various disciplines, including computer science, control theory, mechanics, information and sensing technology, artificial intelligence, and bionics. It is an area of active research and increasing application in contemporary society. The application of robots is an important indicator of a country’s industrial automation level.
Robots do not simply replace human labor in a straightforward sense; rather, they are anthropomorphic electronic mechanical devices that combine the strengths of both humans and machines. They possess humans’ ability to quickly respond to and analyze environmental conditions, as well as machines’ endurance for prolonged work, high precision, and resistance to harsh environments. In a sense, they are also products of the evolution of machines. They are essential production and service equipment in both industrial and non-industrial sectors, as well as indispensable automation devices in advanced manufacturing technology.

Typically, robots can be categorized into three generations based on their development process: the first generation is a “remote-controlled operator”; the second generation is controlled by pre-programmed instructions, allowing the robot to automatically repeat certain tasks; the third generation is intelligent robots, which use various sensors and measuring devices to gather environmental information and apply intelligent technologies for recognition, understanding, reasoning, and ultimately making planning decisions, enabling autonomous actions to achieve predetermined goals.
This broad overview cannot adequately convey the arduous journey of robotics technology development. To detail this journey, one must consider the development of robots in various countries. From a holistic perspective, the development of robots in different countries, while interconnected, also exhibits significant differences. Different historical and social contexts have led to varying perceptions of robotics technology, resulting in different policies and outcomes, which in turn influence people’s thoughts and the development of social history.
The birthplace of robots is the United States, where the world’s first industrial robot was developed in 1962. After more than 30 years of development, the U.S. has become one of the world’s leading countries in robotics, with a solid foundation and advanced technology. Looking at its history, the path has been winding and uneven.
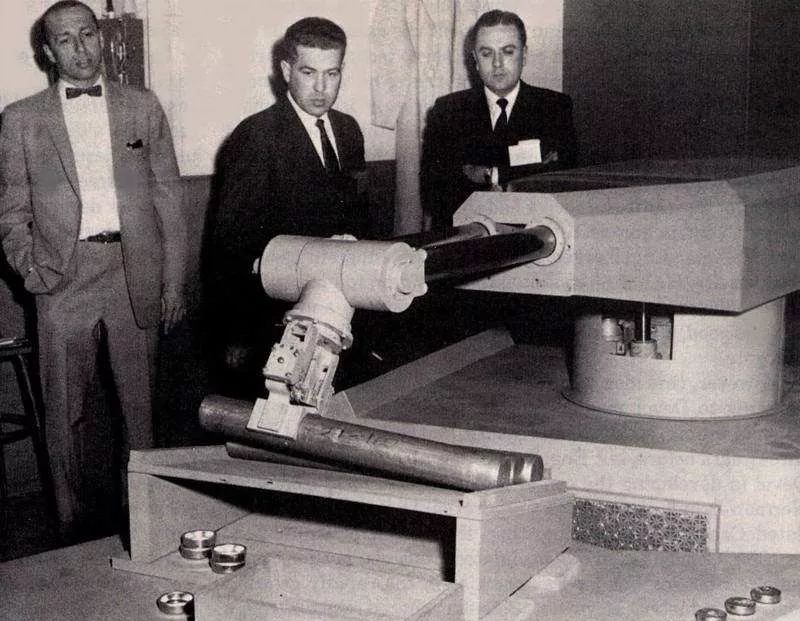

During the 1960s to mid-1970s, the U.S. government did not prioritize industrial robots as a key development project, only conducting some research in a few universities and companies. For businesses, seeing only immediate benefits and lacking government financial support, they preferred to miss good opportunities and stick to rigid automation devices rather than risk applying or manufacturing robots. Additionally, with the unemployment rate in the U.S. reaching 6.65%, the government feared that developing robots would lead to more job losses, resulting in a lack of investment and organization for robot development. This can be seen as a strategic decision error by the U.S. government. After the late 1970s, although the government and business community began to take notice, the focus remained on researching robot software and developing advanced robots for specialized fields such as military, space, ocean, and nuclear engineering, which allowed Japan’s industrial robots to surpass the U.S. in both industrial production applications and robot manufacturing, creating strong competitiveness in the international market.

It was not until the 1980s that the U.S. began to feel the urgency of the situation, leading both the government and the business community to take robots seriously, as reflected in their policies. On one hand, they encouraged the industrial sector to develop and apply robots; on the other hand, they formulated plans, increased investments, and raised research funding for robots, viewing robotics as a hallmark of America’s re-industrialization, which led to rapid development in U.S. robotics.
By the mid-1980s, as major manufacturers increasingly matured in their use of robots, the performance of first-generation robots no longer met actual needs. The U.S. began producing second-generation robots equipped with vision and tactile sensing, quickly capturing 60% of the U.S. robot market.
Although the U.S. has taken a winding path in its robotics development, emphasizing theoretical research while neglecting applied development, its robotics technology remains internationally leading. Its technology is comprehensive, advanced, and highly adaptable.
In contrast, the U.K. has taken a markedly different path. Although Hall Automation developed its own robot, RAMP, in 1967, the British government’s Lighthall report in the early 1970s imposed strict measures limiting the development of industrial robots, leading to a severe decline in the robotics industry, placing it nearly last in Western Europe.
However, the rapid international growth of robotics soon made the British government realize that its lagging robotics technology significantly diminished its products’ competitiveness in the international market. Starting in the late 1970s, the British government adopted a supportive stance, implementing a series of policies and measures to promote robotics development, such as widely publicizing the importance of using robots, providing financial subsidies to companies purchasing robots, and actively promoting collaboration between research institutions and businesses, leading to a flourishing period of widespread application and vigorous research in British robotics.

This indicates that the development of new technologies does not depend on human will; those who adapt and strive to develop will progress, while those who isolate themselves and reject it will fall behind due to their inability to keep pace with the times.
In contrast to the lessons learned by the U.K., France embraced artificial intelligence technology early on and made significant progress. France not only ranks among the world’s leaders in the number of robots but also excels in the application level and range of robotics. This is largely due to the French government’s early emphasis on robotics technology, particularly focusing on conducting research on robot applications. The development of robotics in France has been relatively smooth, mainly because the government has supported research programs that establish a complete scientific and technological system, coordinating basic technology research projects with industrial support for application and development, enabling rapid growth and widespread adoption of robots in French enterprises.

Germany, France’s neighbor, ranks third in the world in the total number of industrial robots, following Japan and the U.S. However, it lagged behind the U.K. and Sweden by about five to six years in introducing robots. The reason for this delay is that Germany’s robotics industry faced economic downturns at the outset. Nevertheless, the social environment in Germany is conducive to the development of the robotics industry. Factors such as labor shortages due to war and a high national technical skill level create favorable conditions for implementing robotics.

By the mid to late 1970s, the government began using administrative measures to promote the adoption of robots; the “Improving Labor Conditions Plan” mandated that robots must replace ordinary workers in dangerous, toxic, or harmful jobs. This plan opened up a broad market for robot applications and promoted the development of industrial robotics technology.

The German people are practical and have always adhered to the principle of combining technological applications with social needs. In addition to applying robots primarily in the automotive industry, Germany has notably modernized its textile industry by replacing old machinery with modern automated equipment, computers, and robots, reducing costs and improving quality, thus revitalizing an industry that was once considered “on the verge of collapse” by 1984. Simultaneously, Germany recognized the role of advanced automation technologies, including robotics, in industrial production and set a goal to transition to advanced, sensory intelligent robots after 1985. After nearly ten years of effort, Germany has achieved a recognized leading position in the research and application of intelligent robotics worldwide.
In contrast, the former Soviet Union (mainly Russia) also advanced in robotics technology. The exploration of robotics theory and practice began in the late 1950s, with prototype research commencing in the late 1950s. In 1968, they successfully trialed a deep-sea robot, and in 1971, they developed a versatile factory robot.
As early as the ninth five-year plan (1970-1975), the Soviet Union included the development of robots in its national science and technology development program. By 1975, it had developed 120 robots of 30 different models. After 20 years of effort, the Soviet Union’s robots were among the world’s leaders in quantity and quality. The state purposefully arranged for the advancement of science and technology to drive social production, planning the research, production, application, promotion, and enhancement of robotics systematically and step by step.

Although the Soviet Union’s technology was advanced, it operated under a planned economy. A common issue of planned economies is their disconnection from the market, preventing their technology applications from achieving the leaps seen in other Western capitalist countries. In stark contrast, Japan achieved tremendous success.

In the late 1960s, Japan was experiencing rapid economic growth, with an annual growth rate of 11%. After World War II, Japan faced a labor shortage, which was exacerbated by rapid economic development. In response, Kawasaki Heavy Industries imported robots and technology from Unimation in the U.S. in 1967, establishing a production workshop and trialing the first Kawasaki “Unimate” robot in 1968.
Due to the significant labor shortage in Japan at that time, robots were welcomed as a “savior” in enterprises. The Japanese government adopted proactive economic support policies, encouraging the development and promotion of robotics, further motivating entrepreneurs to engage in the robotics industry. Particularly, a series of economic incentives for small and medium-sized enterprises, such as low-interest funding from government banks, encouraged the establishment of “long-term robot leasing companies,” which purchased robots and leased them to users at low monthly rents, alleviating the financial burden of acquiring robots. The government also offered special discounts on computer-controlled teach-repeat robots, where enterprises could enjoy a 40% discount and an additional 13% price subsidy. Furthermore, the government funded specialized knowledge and technical guidance for small businesses in applying robots. This series of supportive policies led to the rapid development of Japan’s robotics industry, which by the mid-1980s had become the “Robot Kingdom,” with the highest production and installation numbers internationally.
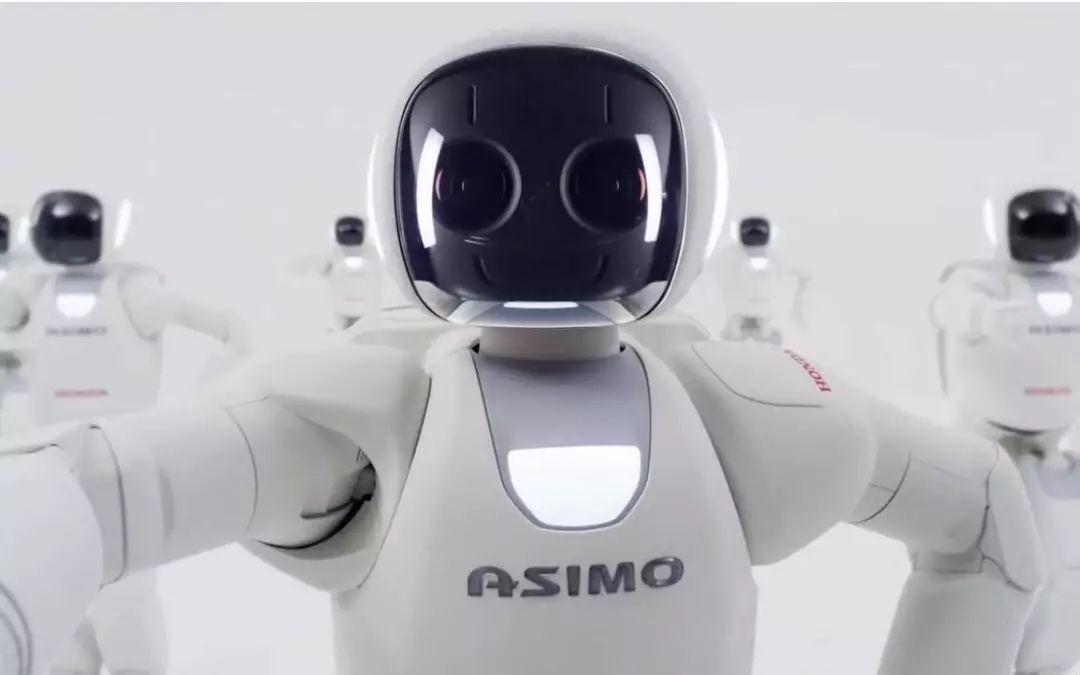

According to Kanji Yonemoto, a managing director of the Japan Industrial Robot Association, “The development of robotics in Japan has gone through a cradle period in the 1960s, a practical period in the 1970s, and has entered a period of widespread improvement in the 1980s.” He officially designated 1980 as the “Year of Popularization of Industrial Robots,” marking the start of broad promotion and use of robots across various fields.
The Japanese government and enterprises fully trusted and boldly utilized robots. Robots did not disappoint expectations, significantly contributing to solving labor shortages, improving productivity, enhancing product quality, and reducing production costs, becoming an indispensable force for Japan to maintain economic growth and product competitiveness.

Japan’s extensive use of robots in the automotive and electronics industries has significantly increased production volumes and improved quality while greatly reducing manufacturing costs. This enabled Japanese vehicles to penetrate the market in the U.S., known as the “Automobile Kingdom,” with a price advantage, and Japan began exporting practical robots to the birthplace of robotics. At this time, affordable and high-quality Japanese home appliances flooded the U.S. market, causing significant regret for “Uncle Sam.” By manufacturing and using robots, Japan enhanced its national strength and reaped substantial benefits, compelling countries like the U.S., U.K., and France to adopt measures to catch up. In the 1980s and 1990s, Japan was referred to as the “World Factory,” with robotics technology playing a crucial role.
With the advent of reform and opening up, China also entered an era of rapid economic development. However, it is essential to recognize that China’s product competitiveness stems from its inexpensive labor, which cannot solve all problems. The rising living standards will inevitably lead to higher wages, a trend that cannot be overlooked. If we continue to “exploit” workers without developing new technologies and improving labor capabilities, China’s labor resources may soon be depleted, leading to economic stagnation and potential regression similar to Japan’s current situation. Therefore, China must focus on the future and emphasize the development of robotics technology.
In recent years, several trends have emerged in the domestic and international robotics field:
1. The performance of industrial robots continues to improve (high speed, high precision, high reliability, easy operation and maintenance), while the price of individual units continues to decline.
2. Mechanical structures are evolving towards modularization and reconfigurability. For example, the integration of servo motors, reducers, and detection systems within joint modules; constructing entire robots using joint modules and link modules in a reconfigurable manner.
3. Industrial robot control systems are evolving towards open controllers based on PC technology, facilitating standardization and networking; the integration of components is increasing, with control cabinets becoming more compact and adopting modular structures; significantly enhancing system reliability, ease of operation, and maintainability.
4. The role of sensors in robots is becoming increasingly important. In addition to traditional position, speed, and acceleration sensors, assembly and welding robots are also utilizing vision and tactile sensors, while remote-controlled robots are employing multi-sensor fusion technologies, including vision, auditory, tactile, and other sensory modalities for environmental modeling and decision control; multi-sensor fusion configuration technologies have already been successfully applied in commercial systems.

5. The role of virtual reality technology in robotics has evolved from simulation and rehearsal to process control, allowing remote robot operators to feel as if they are in the remote operational environment.
6. The contemporary development of remote-controlled robot systems is characterized not by the pursuit of fully autonomous systems but by a focus on human-robot interaction control, constituting a complete monitoring and remote control operation system through remote control combined with partial autonomy. The “Sojourner” robot sent to Mars by the U.S. is the most famous example of this system’s successful application.

China’s intelligent and special robots have also achieved significant results under the support of the “863” program. Among these, underwater robots at depths of 6000 meters have reached world-leading levels, and various types of robots, including directly remote-controlled robots, dual-arm coordinated control robots, wall-climbing robots, and pipeline robots, have been developed. Substantial work has also been done in the development and application of foundational technologies such as robot vision, tactile, auditory, and other sensory modalities, establishing a certain development foundation. However, in areas such as multi-sensor information fusion control technology, remote-controlled plus partial autonomy systems, intelligent assembly robots, and robotic mechanization, development is just beginning, and there is still a significant gap compared to advanced international levels. Focused and systematic efforts are needed to build practical technologies and products based on existing achievements.
Images and text reproduced from Sensor Technology
Reviewed by: Tang Cuimei, Huo Xiaoyin, Liu Jia

