Article Outline
-
Wafer Manufacturing Equipment
-
Packaging Equipment
-
Testing Equipment
Wafer manufacturing equipment, packaging equipment, and testing equipment are important components of the semiconductor equipment industry. Below, we will provide a detailed introduction to these three types of semiconductor equipment.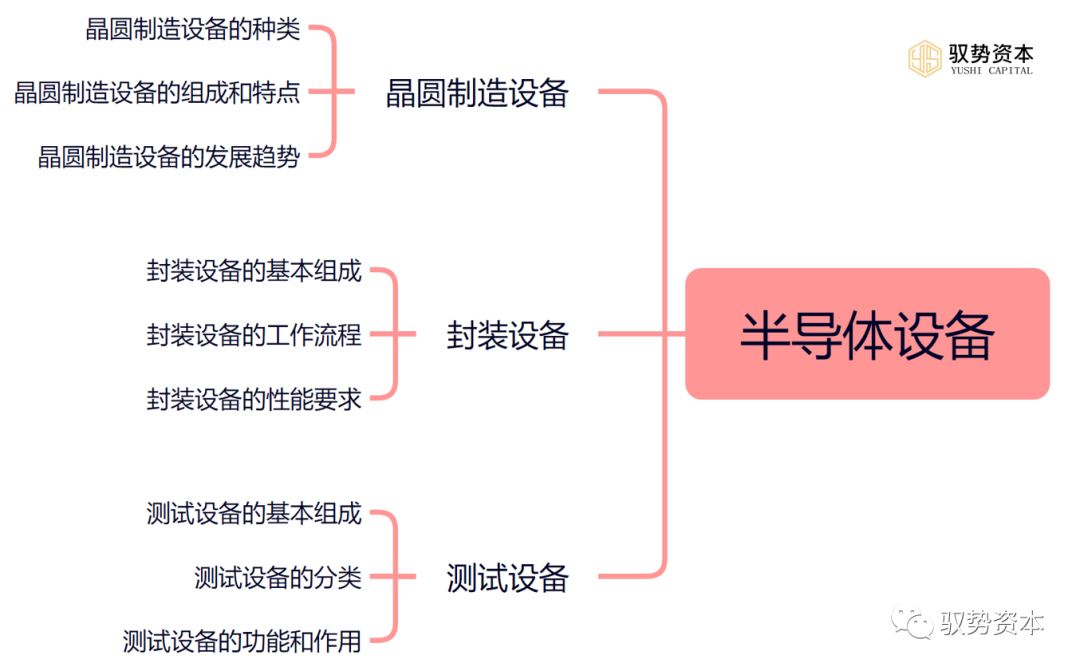
1. Wafer Manufacturing Equipment
1.1 Types of Wafer Manufacturing Equipment
Wafer manufacturing equipment is one of the most important devices in the semiconductor production process, mainly divided into front-end process equipment and back-end process equipment.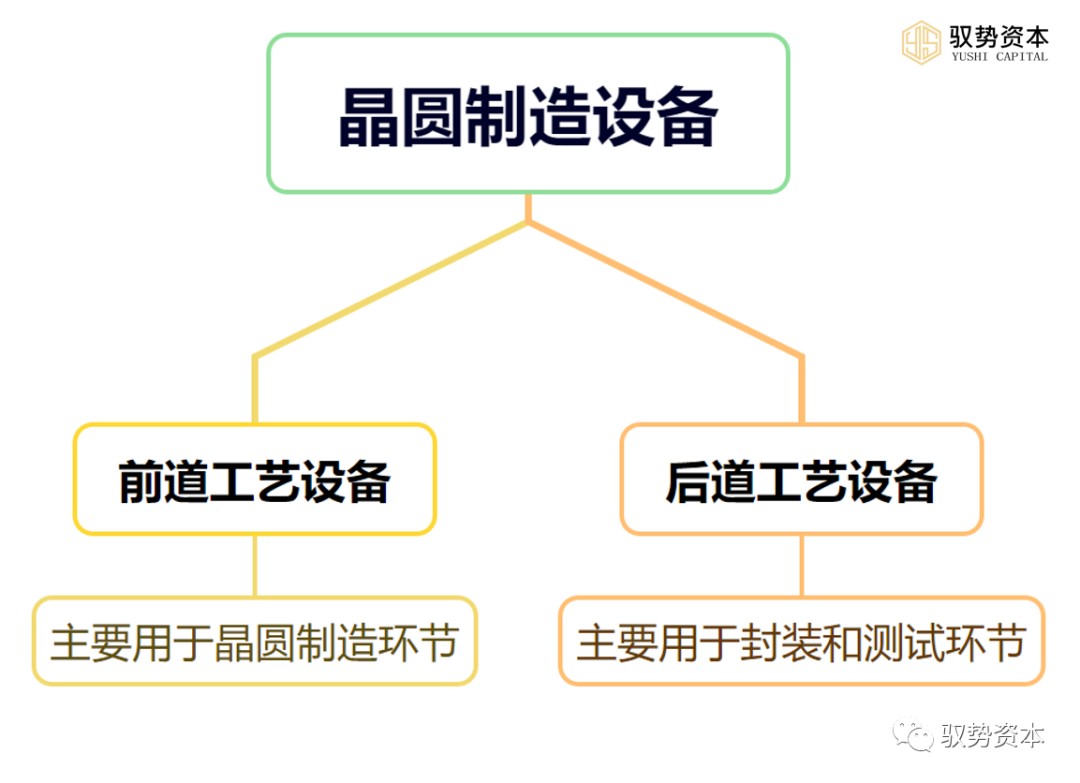 Front-end Process Equipment is crucial in the semiconductor manufacturing process, primarily used in the wafer manufacturing stage. Below is a detailed introduction to front-end process equipment:
Front-end Process Equipment is crucial in the semiconductor manufacturing process, primarily used in the wafer manufacturing stage. Below is a detailed introduction to front-end process equipment: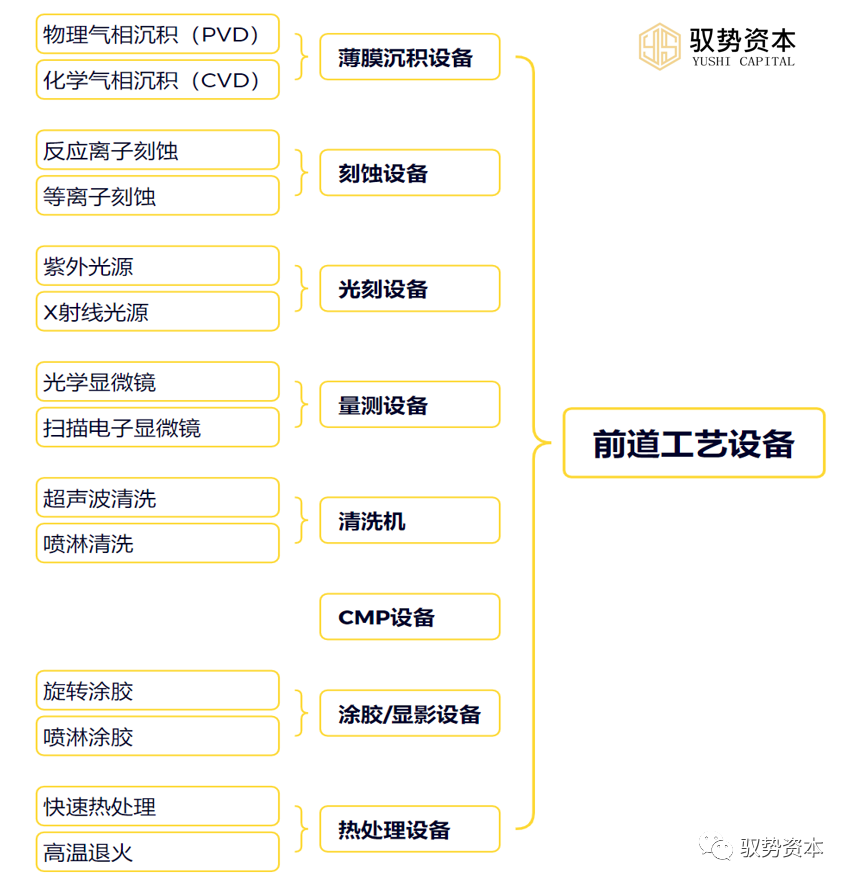
(1)Thin Film Deposition Equipment: Thin film deposition equipment is an important component of front-end process equipment, used to deposit various thin film materials, such as metals and oxides, on the wafer surface. Thin film deposition equipment typically employs techniques such as Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) to achieve uniform and stable thin film deposition.
(2)Etching Equipment: Etching equipment is used to etch the wafer surface to form the desired electrical traces and holes. Etching equipment typically employs techniques such as Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) or Plasma Etching to achieve high precision and efficiency in etching operations.
(3)Photolithography Equipment: Photolithography equipment is the core device in front-end process equipment, used to transfer circuit patterns onto the wafer surface. Photolithography equipment typically uses ultraviolet light sources or X-ray sources to achieve high-resolution and high-sensitivity lithography operations.
(4)Measurement Equipment: Measurement equipment is used to perform various measurements and inspections on the wafer surface to ensure the quality and reliability of the chips. Measurement equipment typically employs optical microscopes, Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM), etc., to achieve high precision and efficiency in measurement and inspection operations.
(5)Cleaning Equipment: Cleaning equipment is used to clean impurities and contaminants from the wafer surface, ensuring quality and stability during the chip manufacturing process. Cleaning equipment typically employs techniques such as ultrasonic cleaning and spray cleaning to achieve efficient and thorough cleaning operations.
(6)Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) Equipment: CMP equipment is used to flatten the wafer surface to ensure stability and precision during the chip manufacturing process. CMP equipment typically employs Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) technology to achieve high efficiency and precision in flattening operations.
(7)Coating/Developing Equipment: Coating/developing equipment is used to apply photoresist on the wafer surface and develop the photoresist to form the desired circuit patterns. Coating/developing equipment typically employs techniques such as spin coating and spray coating to achieve uniform and stable coating and developing operations.(8)Thermal Processing Equipment: Thermal processing equipment is used to heat the wafer to achieve the desired chemical reactions and physical changes. Thermal processing equipment typically employs Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) or high-temperature annealing techniques to achieve efficient and stable heating operations.Back-end Process Equipment is also crucial in the semiconductor manufacturing process, primarily used in the packaging and testing stages. Below is a detailed introduction to back-end process equipment: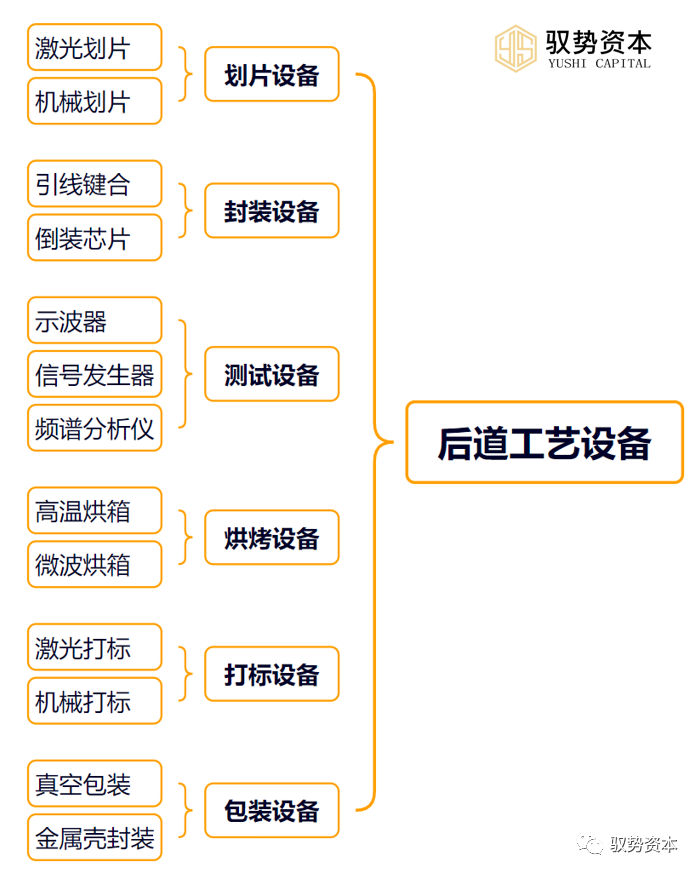 (1)Dicing Equipment: Dicing equipment is used to cut the wafer into individual chips for packaging and testing. Dicing equipment typically employs laser or mechanical dicing methods to achieve high precision and efficiency in dicing operations.(2)Packaging Equipment: Packaging equipment is used to encapsulate chips onto substrates to ensure their normal operation and lifespan. Packaging equipment typically employs methods such as wire bonding and flip-chip bonding to achieve high efficiency and reliability in packaging operations.(3)Testing Equipment: Testing equipment is used to perform functional and performance tests on chips to ensure their quality and reliability. Testing equipment typically employs oscilloscopes, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, etc., to achieve high precision and efficiency in testing operations.(4)Baking Equipment: Baking equipment is used to bake chips to eliminate residual stress inside the chips, improving their stability and reliability. Baking equipment typically employs high-temperature ovens or microwave ovens to achieve efficient and stable baking operations.(5)Marking Equipment: Marking equipment is used to mark the surfaces of chips for subsequent identification and management. Marking equipment typically employs laser marking or mechanical marking methods to achieve high precision and efficiency in marking operations.(6)Packaging Equipment: Packaging equipment is used to package chips to protect them from external environmental influences. Packaging equipment typically employs vacuum packaging or metal shell encapsulation methods to achieve high reliability in packaging operations.
(1)Dicing Equipment: Dicing equipment is used to cut the wafer into individual chips for packaging and testing. Dicing equipment typically employs laser or mechanical dicing methods to achieve high precision and efficiency in dicing operations.(2)Packaging Equipment: Packaging equipment is used to encapsulate chips onto substrates to ensure their normal operation and lifespan. Packaging equipment typically employs methods such as wire bonding and flip-chip bonding to achieve high efficiency and reliability in packaging operations.(3)Testing Equipment: Testing equipment is used to perform functional and performance tests on chips to ensure their quality and reliability. Testing equipment typically employs oscilloscopes, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, etc., to achieve high precision and efficiency in testing operations.(4)Baking Equipment: Baking equipment is used to bake chips to eliminate residual stress inside the chips, improving their stability and reliability. Baking equipment typically employs high-temperature ovens or microwave ovens to achieve efficient and stable baking operations.(5)Marking Equipment: Marking equipment is used to mark the surfaces of chips for subsequent identification and management. Marking equipment typically employs laser marking or mechanical marking methods to achieve high precision and efficiency in marking operations.(6)Packaging Equipment: Packaging equipment is used to package chips to protect them from external environmental influences. Packaging equipment typically employs vacuum packaging or metal shell encapsulation methods to achieve high reliability in packaging operations.
1.2 Composition and Characteristics of Wafer Manufacturing Equipment
Wafer manufacturing equipment mainly consists of the following parts: (1)Manipulator: Used for handling wafers and components, featuring high precision, high speed, and high reliability.(2)Control System: Used to control various parts of the equipment, including manipulators, conveyors, process equipment, and inspection equipment, to achieve automated production.(3)Process Equipment: Completes specific manufacturing steps according to process requirements, such as lithography, etching, thin film deposition, etc.(4)Inspection Equipment: Used to inspect the quality and performance of chips, including appearance inspection, functional testing, and performance testing.(5)Auxiliary Equipment: Such as deionized water equipment, compressed air equipment, etc., used to provide auxiliary materials required during the process.
(1)Manipulator: Used for handling wafers and components, featuring high precision, high speed, and high reliability.(2)Control System: Used to control various parts of the equipment, including manipulators, conveyors, process equipment, and inspection equipment, to achieve automated production.(3)Process Equipment: Completes specific manufacturing steps according to process requirements, such as lithography, etching, thin film deposition, etc.(4)Inspection Equipment: Used to inspect the quality and performance of chips, including appearance inspection, functional testing, and performance testing.(5)Auxiliary Equipment: Such as deionized water equipment, compressed air equipment, etc., used to provide auxiliary materials required during the process.
The characteristics of wafer manufacturing equipment are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
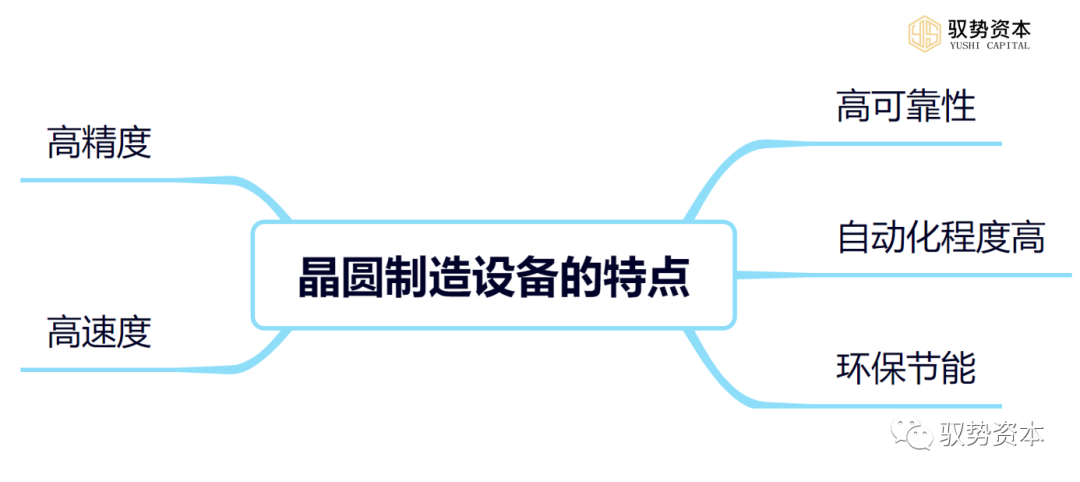
(1)High Precision: The precision requirements for wafer manufacturing equipment are very high, requiring operations at the nanometer level to ensure the quality and performance of chips.
(2)High Speed: Wafer manufacturing equipment operates at high speeds, capable of completing a large amount of manufacturing work in a short time, thus improving production efficiency.
(3)High Reliability: The reliability requirements for wafer manufacturing equipment are very high, as any failure can lead to significant production interruptions and product losses.
(4)High Degree of Automation: Wafer manufacturing equipment has a high degree of automation, capable of achieving automated production processes and process control, thus improving production efficiency and product quality.
(5)Environmental Protection and Energy Saving: With the increasing awareness of environmental protection, the design and manufacturing of wafer manufacturing equipment also pay more attention to environmental protection and energy saving, reducing the impact on the environment.
1.3 Development Trends of Wafer Manufacturing Equipment
With the continuous development and progress of semiconductor technology, wafer manufacturing equipment is also constantly evolving and improving. The future development trends of wafer manufacturing equipment mainly include the following aspects:
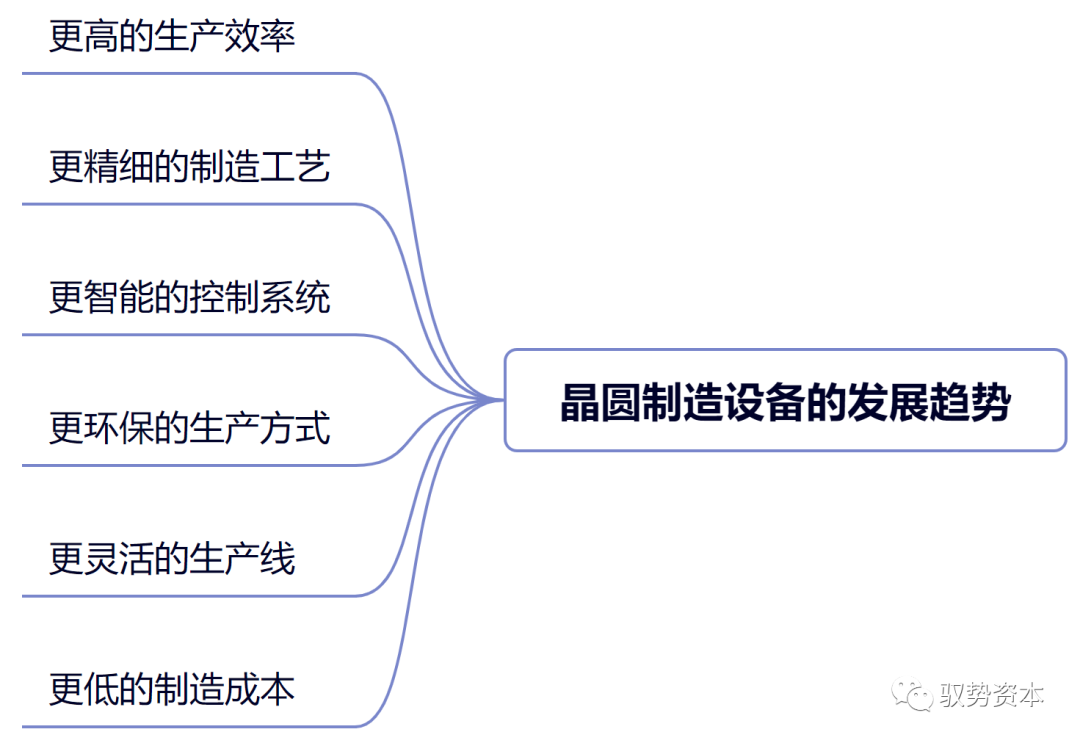
(1)Higher Production Efficiency: With the continuous expansion of the semiconductor market and increasing competition, wafer manufacturing equipment needs to achieve higher production efficiency to meet market demands. To improve production efficiency, wafer manufacturing equipment needs to realize faster speeds, higher precision, and more reliable stability. For example, manipulator equipment needs to achieve faster and more precise handling and positioning, while control systems need to achieve more efficient and stable control and scheduling.
(2)More Refined Manufacturing Processes: As the complexity of semiconductor chips continues to increase and process requirements become more refined, wafer manufacturing equipment needs to possess more refined manufacturing processes. For example, photolithography equipment needs to achieve finer lithography lines and higher resolution, while thin film deposition equipment needs to achieve more uniform and stable thin film deposition. Additionally, etching equipment, measurement equipment, etc., also need to continuously improve process technologies to meet more refined process requirements.
(3)Smarter Control Systems: With the continuous development of automation and artificial intelligence technologies, wafer manufacturing equipment needs to implement smarter control systems. By introducing artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other technologies, autonomous control and optimized scheduling of equipment can be achieved, improving production efficiency and product quality. For example, control systems can learn and analyze production data through machine learning algorithms to achieve fine control and optimization of the production process.
(4)More Environmentally Friendly Production Methods: With the increasing awareness of environmental protection and the tightening of policies and regulations, wafer manufacturing equipment needs to implement more environmentally friendly production methods. The manufacturing and use of equipment need to minimize environmental impact, such as adopting energy-saving designs and reducing waste emissions. Additionally, equipment also needs to continuously improve process technologies to reduce environmental pollution.
(5)More Flexible Production Lines: With changes in market demand and technological development, wafer manufacturing equipment needs to achieve more flexible production lines. Production lines need to have higher adaptability, scalability, and maintainability to accommodate different types and process requirements of chip production. For example, production lines can achieve flexible combinations and expansions of different equipment through modular design, and predictive maintenance and rapid repair of equipment can be achieved through intelligent maintenance systems.
(6)Lower Manufacturing Costs: To enhance market competitiveness, wafer manufacturing equipment needs to achieve lower manufacturing costs. Material selection, design optimization, and production processes of equipment all need to undergo cost control and optimization. For example, equipment can adopt new materials, optimize structural designs, and simplify production processes to reduce manufacturing costs. Additionally, equipment also needs to lower operational costs by improving production efficiency and reducing failure rates.
In summary, the development trends of wafer manufacturing equipment are multifaceted, including improving production efficiency, achieving more refined manufacturing processes, implementing smarter control systems, adopting more environmentally friendly production methods, achieving more flexible production lines, and lowering manufacturing costs. These development trends will help enhance the performance and market competitiveness of wafer manufacturing equipment, promoting the continuous development of the semiconductor industry.
2. Packaging Equipment
2.1 Basic Composition of Packaging Equipment
Packaging equipment is an indispensable part of the semiconductor manufacturing process, primarily used to encapsulate chips onto substrates to achieve circuit connections and protection, ensuring the normal operation and lifespan of the chips.Packaging equipment is typically divided into front-end and back-end processes: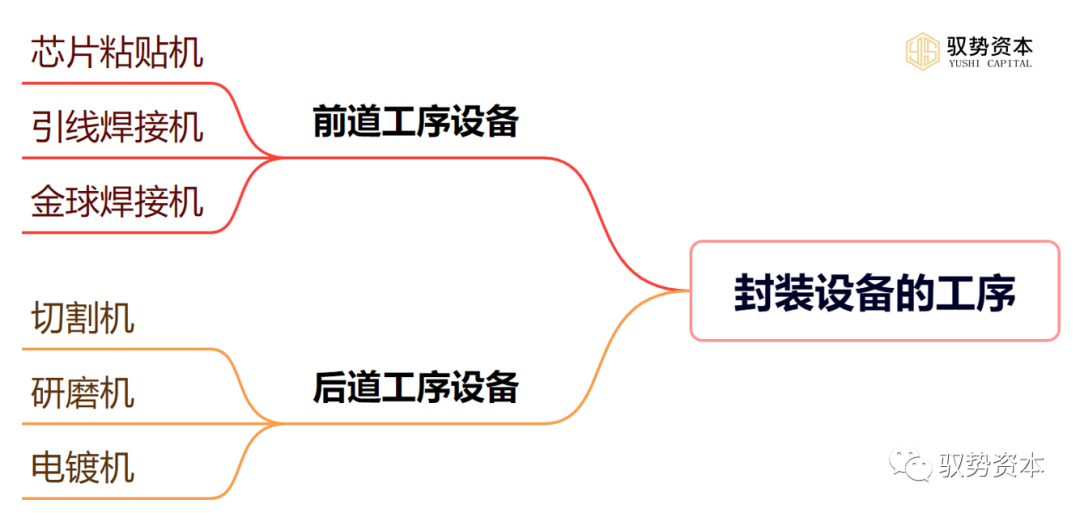 (1)Front-end Process Equipment: The front-end process involves attaching chips to substrates and achieving circuit connections. Common equipment includes chip attach machines, wire bonding machines, and ball bonding machines.(2)Back-end Process Equipment: The back-end process involves cutting, grinding, electroplating, and other treatments of the packaging body. Common equipment includes cutting machines, grinding machines, and electroplating machines.Packaging equipment is a crucial part of the semiconductor manufacturing process, and its basic composition includes the following main parts:
(1)Front-end Process Equipment: The front-end process involves attaching chips to substrates and achieving circuit connections. Common equipment includes chip attach machines, wire bonding machines, and ball bonding machines.(2)Back-end Process Equipment: The back-end process involves cutting, grinding, electroplating, and other treatments of the packaging body. Common equipment includes cutting machines, grinding machines, and electroplating machines.Packaging equipment is a crucial part of the semiconductor manufacturing process, and its basic composition includes the following main parts: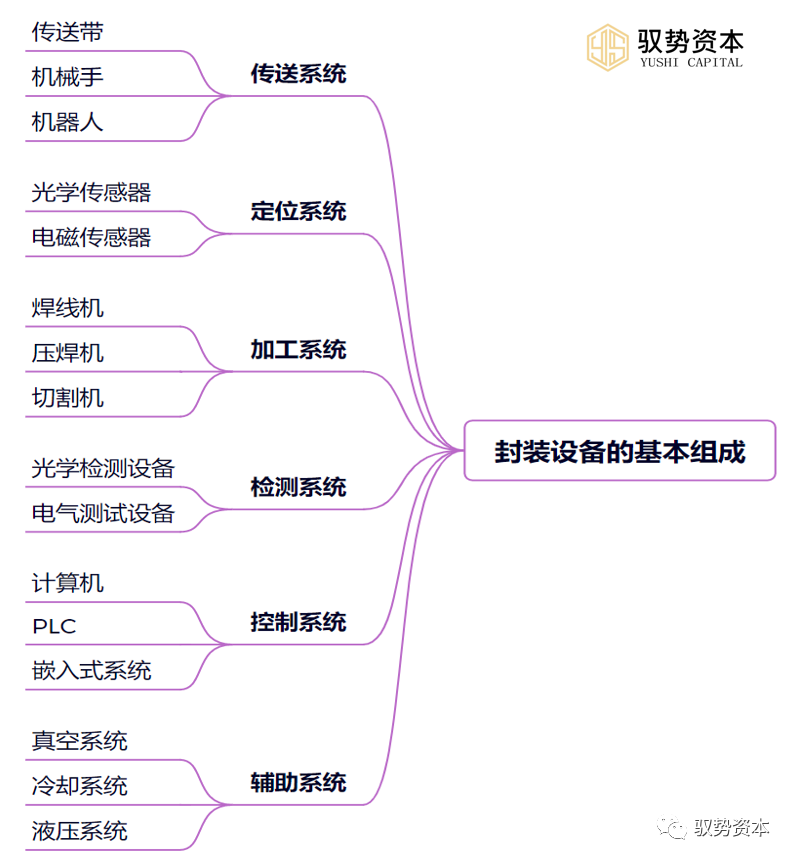 (1)Conveying System: The conveying system of packaging equipment mainly consists of conveyors, manipulators, or robots, used to transfer chips and substrates from one workstation to another. This conveying system needs to have high precision, high speed, and high reliability to ensure that the equipment can efficiently complete packaging tasks.(2)Positioning System: The positioning system of packaging equipment ensures that chips and substrates can be accurately placed in the correct positions. This positioning system typically consists of a series of sensors and controllers, such as optical sensors and electromagnetic sensors, to monitor and control the precise positions of chips and substrates.(3)Processing System: The processing system of packaging equipment is used to perform various processing operations between chips and substrates, such as welding, crimping, cutting, etc. This processing system typically consists of a series of machines and tools, such as wire bonders, compression welders, and cutting machines. These machines and tools need to be selected and configured according to different packaging requirements to meet the packaging needs of different types of chips.(4)Inspection System: The inspection system of packaging equipment is used to detect the connection quality and packaging quality between chips and substrates. This inspection system typically consists of a series of sensors and testing devices, such as optical inspection devices and electrical testing devices. These sensors and testing devices need to have high precision and efficiency to quickly and accurately detect defects and issues during the packaging process.(5)Control System: The control system of packaging equipment is used to control the operation of the entire equipment and coordinate the work of various systems. This control system typically consists of computers, PLCs, or embedded systems, used to receive signals from sensors and control the operation of the equipment according to preset programs and instructions. The control system needs to have high reliability, stability, and flexibility to ensure that the equipment can efficiently complete various packaging tasks.(6)Auxiliary Systems: Packaging equipment also requires auxiliary systems, such as vacuum systems, cooling systems, hydraulic systems, etc., to support the normal operation and processing operations of the equipment. These auxiliary systems need to be configured and used according to the specific needs of the equipment to ensure that the equipment can efficiently complete packaging tasks.In addition to the above main components, packaging equipment also needs to have high reliability, stability, precision, and efficiency. These characteristics need to be fully considered and guaranteed during the design, manufacturing, and use of the equipment. Meanwhile, with the continuous development and progress of semiconductor technology, packaging equipment also needs to be continuously upgraded and improved to meet the ever-changing market demands and technical requirements.
(1)Conveying System: The conveying system of packaging equipment mainly consists of conveyors, manipulators, or robots, used to transfer chips and substrates from one workstation to another. This conveying system needs to have high precision, high speed, and high reliability to ensure that the equipment can efficiently complete packaging tasks.(2)Positioning System: The positioning system of packaging equipment ensures that chips and substrates can be accurately placed in the correct positions. This positioning system typically consists of a series of sensors and controllers, such as optical sensors and electromagnetic sensors, to monitor and control the precise positions of chips and substrates.(3)Processing System: The processing system of packaging equipment is used to perform various processing operations between chips and substrates, such as welding, crimping, cutting, etc. This processing system typically consists of a series of machines and tools, such as wire bonders, compression welders, and cutting machines. These machines and tools need to be selected and configured according to different packaging requirements to meet the packaging needs of different types of chips.(4)Inspection System: The inspection system of packaging equipment is used to detect the connection quality and packaging quality between chips and substrates. This inspection system typically consists of a series of sensors and testing devices, such as optical inspection devices and electrical testing devices. These sensors and testing devices need to have high precision and efficiency to quickly and accurately detect defects and issues during the packaging process.(5)Control System: The control system of packaging equipment is used to control the operation of the entire equipment and coordinate the work of various systems. This control system typically consists of computers, PLCs, or embedded systems, used to receive signals from sensors and control the operation of the equipment according to preset programs and instructions. The control system needs to have high reliability, stability, and flexibility to ensure that the equipment can efficiently complete various packaging tasks.(6)Auxiliary Systems: Packaging equipment also requires auxiliary systems, such as vacuum systems, cooling systems, hydraulic systems, etc., to support the normal operation and processing operations of the equipment. These auxiliary systems need to be configured and used according to the specific needs of the equipment to ensure that the equipment can efficiently complete packaging tasks.In addition to the above main components, packaging equipment also needs to have high reliability, stability, precision, and efficiency. These characteristics need to be fully considered and guaranteed during the design, manufacturing, and use of the equipment. Meanwhile, with the continuous development and progress of semiconductor technology, packaging equipment also needs to be continuously upgraded and improved to meet the ever-changing market demands and technical requirements.
2.2 Workflow of Packaging Equipment
The workflow of packaging equipment is a very important part of the semiconductor manufacturing process. Below is a detailed introduction to the workflow of packaging equipment:
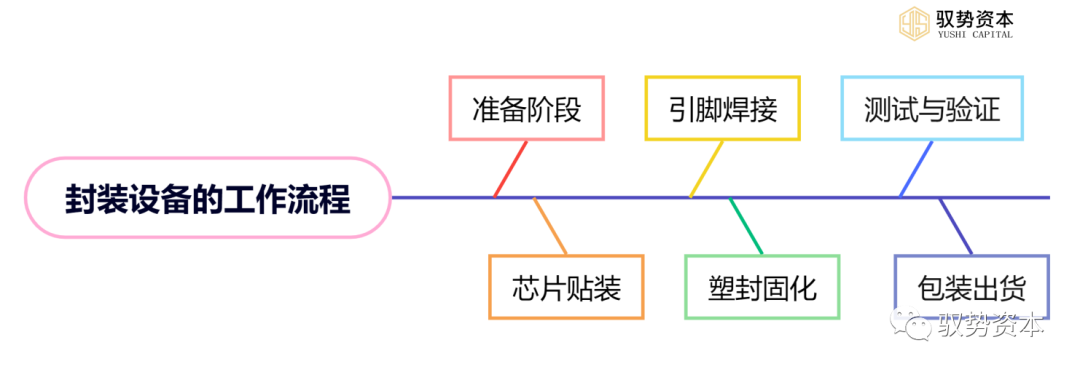
(1)Preparation Stage: In the preparation stage, suitable packaging equipment and its accessories are selected based on the type, specifications, and packaging requirements of the chips, and installation and debugging are performed. This stage also includes technical training and safety operation guidance for operators to ensure that the equipment can operate normally and safely.
(2)Chip Mounting: In the chip mounting stage, chips are placed on substrates, and packaging equipment is used to secure and connect them. This stage requires the use of precise manipulators and conveying devices to ensure that chips can be accurately placed on the substrates. At the same time, wire bonders and other equipment are needed to connect the pins of the chips to the pins of the substrates.
(3)Pin Welding: In the pin welding stage, wire bonders and other equipment are used to weld the pins of the chips to the pins of the substrates. This stage requires controlling factors such as welding temperature, time, and pressure to ensure welding quality and the electrical performance of the chips. At the same time, the results of the welding need to be inspected and recorded to ensure welding quality and consistency.
(4)Molding and Curing: In the molding and curing stage, molding materials are used to encapsulate the chips and substrates together, and curing is performed. This stage requires the use of precise conveying devices and heating systems to ensure the uniform distribution and curing effect of the molding materials. At the same time, factors such as curing temperature, time, and pressure need to be controlled to ensure molding quality and chip stability.
(5)Testing and Verification: In the testing and verification stage, the already packaged chips undergo functional and performance testing to ensure they meet design requirements and specifications. This stage requires the use of various testing devices and testing programs, such as oscilloscopes, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, etc., to detect the electrical performance and stability of the chips. At the same time, the testing results need to be recorded and analyzed to identify issues and areas for improvement.
(6)Packaging and Shipping: In the packaging and shipping stage, the tested chips are packaged and shipped. This stage requires the use of suitable packaging materials and containers to protect the chips from mechanical damage and environmental influences. At the same time, packaging design and shipping arrangements need to be made according to customer requirements to ensure that products can be safely and accurately delivered to customers.
2.3 Performance Requirements of Packaging Equipment
The performance requirements of packaging equipment are crucial to ensuring the quality, stability, and reliability of semiconductor devices. Below is a detailed introduction to the performance requirements of packaging equipment:
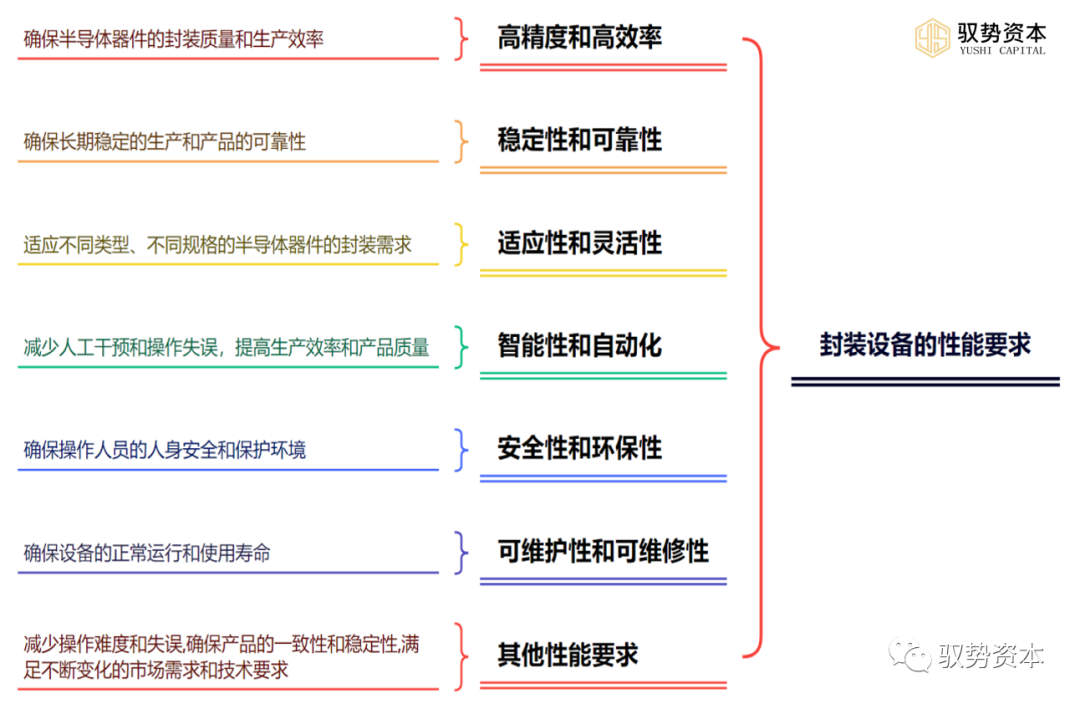
(1)High Precision and High Efficiency: Packaging equipment needs to possess high precision and high efficiency to ensure the packaging quality and production efficiency of semiconductor devices. High precision means that the equipment can accurately complete various operations, such as chip mounting, pin welding, molding curing, etc., to ensure that packaging positions, pin connections, and the uniform distribution of molding materials meet design requirements and specifications. High efficiency means that the equipment can quickly complete various operations, improving production efficiency to reduce production costs and meet market demands.
(2)Stability and Reliability: Packaging equipment needs to have stability and reliability to ensure long-term stable production and product reliability. Stability means that the equipment can maintain stable performance and precision during long periods of continuous production without failures or errors. Reliability means that the equipment can reliably complete various operations under specified conditions, ensuring product quality and performance.
(3)Adaptability and Flexibility: Packaging equipment needs to have adaptability and flexibility to meet the packaging requirements of different types and specifications of semiconductor devices. Adaptability means that the equipment can accommodate different types and specifications of chips and substrates to meet the packaging requirements of different products. Flexibility means that the equipment can flexibly adjust and optimize various parameters and operations to adapt to different production needs and changes.
(4)Intelligence and Automation: Packaging equipment needs to have intelligence and automation to reduce manual intervention and operational errors, improving production efficiency and product quality. Intelligence means that the equipment can automatically complete various operations according to preset programs and instructions and can perform self-detection and fault diagnosis. Automation means that the equipment can reduce human participation, increasing the degree of automation to minimize the impact of human factors on product quality.
(5)Safety and Environmental Protection: Packaging equipment needs to have safety and environmental protection features to ensure the safety of operators and protect the environment. Safety means that the equipment can ensure the safety of operators, avoiding safety accidents caused by improper operation or equipment failure. Environmental protection means that the equipment can use environmentally friendly materials and processes to reduce environmental impact and pollution.
(6)Maintainability and Repairability: Packaging equipment needs to have maintainability and repairability to ensure the normal operation and lifespan of the equipment. Maintainability means that the equipment can be easily maintained and serviced, such as cleaning and lubrication, to extend its lifespan. Repairability means that the equipment can be easily repaired and have parts replaced in case of failure, reducing downtime and lowering production costs.
(7)Other Performance Requirements: In addition to the above performance requirements, packaging equipment has other performance requirements, such as: operability, repeatability, and scalability. Operability means that the equipment can be easily operated and controlled to reduce operational difficulty and errors. Repeatability means that the equipment can repeatedly complete the same operations and production tasks to ensure product consistency and stability. Scalability means that the equipment can be upgraded and expanded according to production needs and technological advancements to meet the ever-changing market demands and technical requirements.
In summary, the performance requirements of packaging equipment are multifaceted, requiring comprehensive consideration of the equipment’s precision, efficiency, stability, reliability, adaptability, flexibility, intelligence, safety, environmental protection, and other performance requirements. These performance requirements need to be fully considered and guaranteed during the selection, design, manufacturing, and use of the equipment to ensure the quality, stability, and reliability of semiconductor devices.
3. Testing Equipment
3.1 Basic Composition of Testing Equipment
Testing equipment in semiconductor devices is a crucial link in ensuring the quality and reliability of semiconductor products. Testing equipment is the process of detecting and evaluating semiconductor products to ensure that their quality and performance meet requirements. The basic composition of testing equipment includes the following main parts:
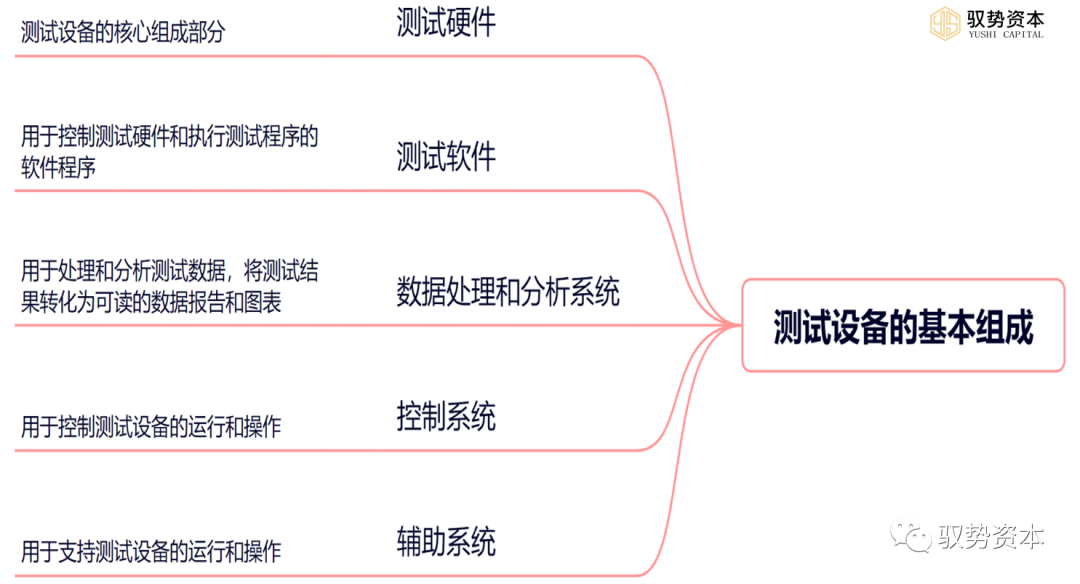
(1)Testing Hardware: Testing hardware is the core component of testing equipment, mainly including test interface boards, probe cards, and test sockets. Test interface boards are devices used to connect testing programs and testing hardware, probe cards are intermediate devices used to connect the tested chips and test interface boards, and test sockets are sockets used to hold the tested chips.
(2)Testing Software: Testing software is the program used to control testing hardware and execute testing programs. Testing software needs to be developed and optimized for different tested chips and testing projects to ensure the accuracy and reliability of testing results.
(3)Data Processing and Analysis System: The data processing and analysis system is used to process and analyze testing data, converting testing results into readable data reports and charts. The data processing and analysis system also needs to statistically analyze testing results to identify existing problems and areas for improvement.
(4)Control System: The control system is used to control the operation and operation of testing equipment, including mechanical motion systems, temperature control systems, pressure control systems, etc. The control system needs to cooperate with testing software to achieve automated testing and control.
(5)Auxiliary Systems: Auxiliary systems are used to support the operation and operation of testing equipment, including cooling systems, cleaning systems, lighting systems, etc.
3.2 Classification of Testing Equipment
Testing equipment in semiconductor devices can be classified in various ways based on different classification methods. Below are some common classification methods and corresponding types of testing equipment:
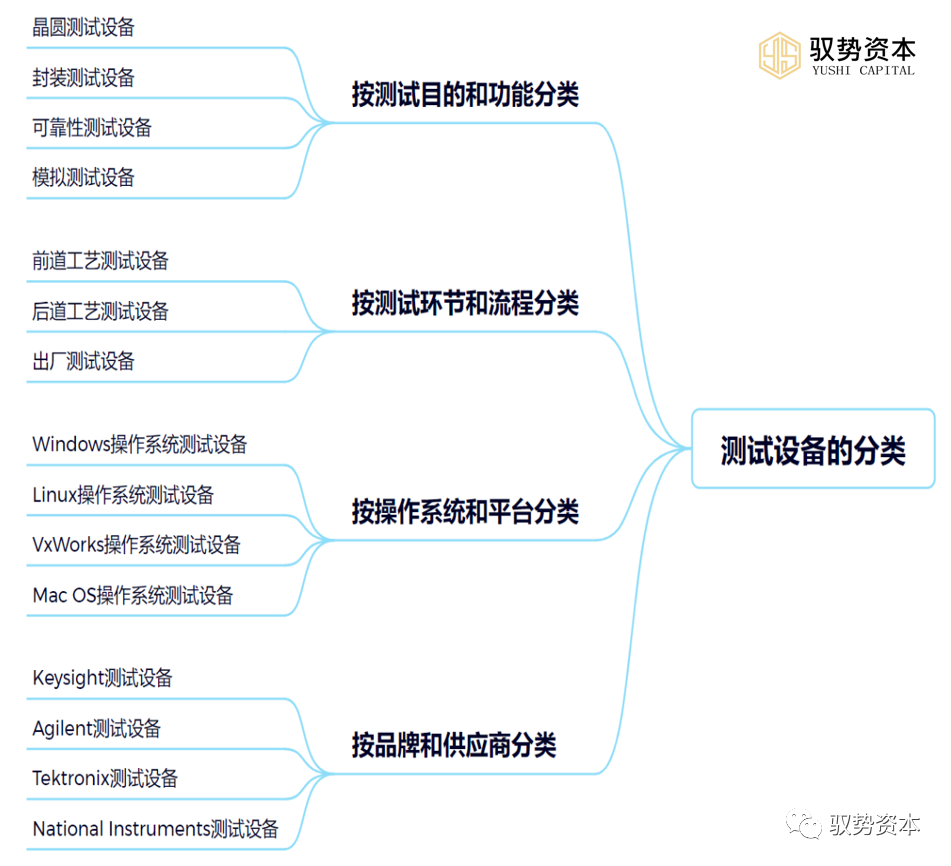
1. Classification by Testing Purpose and Function
(1)Wafer Testing Equipment: Used to test wafers during the manufacturing process, detecting the functionality and performance of chips. Wafer testing equipment typically includes test interface boards, probe cards, test sockets, and testing programs and data processing systems.
(2)Package Testing Equipment: Used to test the quality of packaging and the performance of chips after chip packaging is completed. Package testing equipment typically includes test sockets, testing programs and data processing systems, as well as mechanical operation platforms.
(3)Reliability Testing Equipment: Used to evaluate and test the reliability of chips, detecting their stability and reliability under different environmental conditions. Reliability testing equipment typically includes environmental simulation devices, testing programs and data processing systems, as well as test samples.
(4)Emulation Testing Equipment: Used to test the performance and functionality of analog circuits in chips. Emulation testing equipment typically includes signal generators, oscilloscopes, logic analyzers, and testing programs and data processing systems.
2. Classification by Testing Stages and Processes
(1)Front-end Process Testing Equipment: Used to test front-end processes during chip manufacturing, detecting the quality and stability of processes such as thin films, lithography, and etching. Front-end process testing equipment typically includes optical microscopes, electron microscopes, X-ray diffractometers, and testing programs and data processing systems.
(2)Back-end Process Testing Equipment: Used to test back-end processes during chip manufacturing, detecting the quality and stability of processes such as metal wiring and packaging. Back-end process testing equipment typically includes probe stations, scanning electron microscopes, energy dispersive spectrometers, and testing programs and data processing systems.
(3)Out-off-line Testing Equipment: Used to perform final testing on completed chips, detecting their functionality and performance. Out-off-line testing equipment typically includes test interface boards, probe cards, test sockets, and testing programs and data processing systems.
3. Classification by Operating System and Platform
(1)Windows Operating System Testing Equipment: Testing equipment based on the Windows operating system, using general PC hardware platforms and the Windows operating system, implementing chip testing by installing corresponding testing software.
(2)Linux Operating System Testing Equipment: Testing equipment based on the Linux operating system, using general PC hardware platforms and the Linux operating system, implementing chip testing by installing corresponding testing software.
(3)VxWorks Operating System Testing Equipment: Testing equipment based on the VxWorks operating system, using general PC hardware platforms and the VxWorks operating system, implementing chip testing by installing corresponding testing software. The VxWorks operating system is typically used in applications requiring high real-time performance.
(4)Mac OS Operating System Testing Equipment: Testing equipment based on the Mac OS operating system, using general Mac hardware platforms and the Mac OS operating system, implementing chip testing by installing corresponding testing software. The Mac OS operating system is typically used in special application scenarios such as graphics processing.
4. Classification by Brand and Supplier
(1)Keysight Testing Equipment: Keysight is a globally recognized manufacturer of electronic measurement instruments, providing a range of testing equipment in semiconductor devices, including digital multimeters, signal generators, oscilloscopes, and corresponding software.
(2)Agilent Testing Equipment: Agilent is another globally recognized manufacturer of electronic measurement instruments, providing a range of testing equipment in semiconductor devices, including spectrometers, chromatographs, mass spectrometers, and corresponding software.
(3)Tektronix Testing Equipment: Tektronix is a company focused on real-time testing and measurement, providing a range of testing equipment in semiconductor devices, including digital oscilloscopes, logic analyzers, protocol analyzers, and corresponding software.
(4)National Instruments (NI) Testing Equipment: National Instruments is a company focused on virtual instrument technology, providing a range of testing equipment in semiconductor devices, including data acquisition cards, multifunction instrument modules, and corresponding software.
3.3 Functions and Roles of Testing Equipment
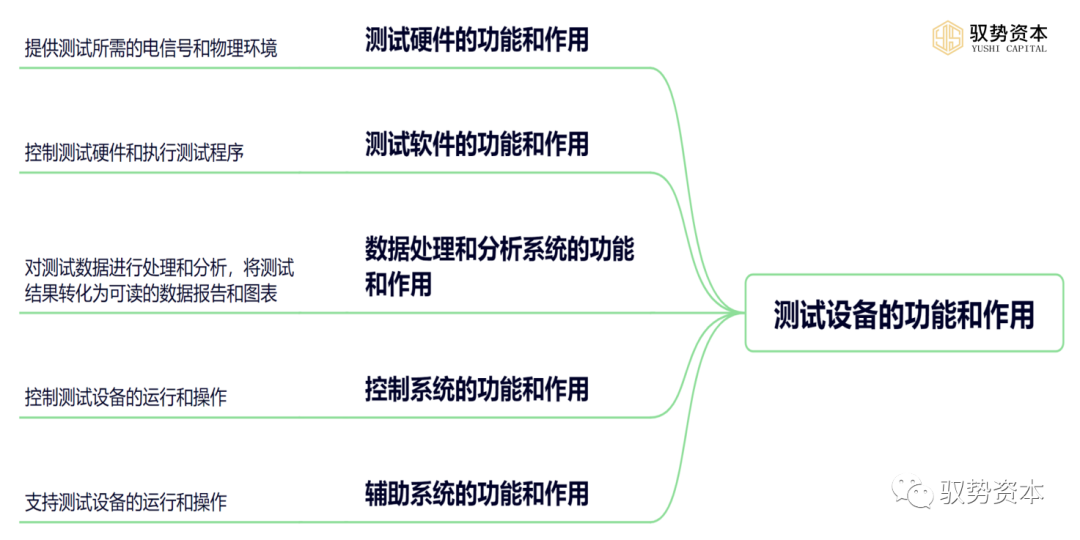
(1)Functions and Roles of Testing Hardware: The main function of testing hardware is to provide the electrical signals and physical environment required for testing, such as voltage, current, temperature, pressure, etc. At the same time, testing hardware also needs to precisely control and measure the tested chips to ensure the accuracy and reliability of testing results.
(2)Functions and Roles of Testing Software: The main function of testing software is to control testing hardware and execute testing programs. Testing software needs to cooperate with testing hardware to achieve automated testing and control of the tested chips. At the same time, testing software also needs to process and analyze testing data to identify existing problems and areas for improvement.
(3)Functions and Roles of Data Processing and Analysis Systems: The main function of data processing and analysis systems is to process and analyze testing data, converting testing results into readable data reports and charts. Data processing and analysis systems also need to statistically analyze testing results to identify existing problems and areas for improvement. Additionally, data processing and analysis systems need to provide data storage and management functions to ensure the reliability and traceability of data.
(4)Functions and Roles of Control Systems: The main function of control systems is to control the operation and operation of testing equipment, including mechanical motion systems, temperature control systems, pressure control systems, etc. Control systems need to cooperate with testing software to achieve automated testing and control. Additionally, control systems need to provide safety protection functions to ensure the safety of equipment and personnel.
(5)Functions and Roles of Auxiliary Systems: The main function of auxiliary systems is to support the operation and operation of testing equipment, including cooling systems, cleaning systems, lighting systems, etc. Auxiliary systems need to be configured and used according to the needs of the equipment to ensure the stability and reliability of the equipment.
END