Memory is divided into two main categories: volatile memory (RAM) and non-volatile memory (external storage). The former loses data immediately when power is cut, while the latter is unaffected by power outages and retains data persistently.

Classification of semiconductor memory and global market share
– 1 –
SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) and DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
Basic Composition:
SRAM‘s basic unit consists of at least 6 transistors: 4 field-effect transistors (M1, M2, M3, M4) form two cross-coupled inverters, and 2 field-effect transistors (M5, M6) are used as control switches for the bit lines. These transistors form a latch (flip-flop) that locks binary values 0 and 1 when powered, hence SRAM is called “Static Random Access Memory.” Besides 6-transistor designs, SRAM can also be constructed with 8, 10, or even more transistors.
DRAM consists of many repeating bit cells, each basic unit is made up of a capacitor and a transistor (also known as a 1T1C structure). The capacitor corresponds to binary values 0 and 1 through charging and discharging, while the transistor controls the capacitor’s charge and discharge. Due to leakage in the capacitor, DRAM must be refreshed before data changes or power loss occurs; otherwise, data will be lost, which is why DRAM is referred to as “Dynamic Random Access Memory.”
Application Scenarios:
DRAM has a simple structure, allowing for very high density, higher capacity per unit volume, and lower cost. However, DRAM has slower access speeds and higher power consumption, while SRAM’s characteristics are completely opposite.
SRAM is not only used in caches but is also commonly found in FPGAs, as lookup tables (LUTs) are primarily suited for SRAM production, and currently, most FPGAs are based on SRAM technology.
SRAM is fast enough to typically serve as cache for central processing units (CPUs), while DRAM is inexpensive and has a large capacity, usually used as memory. SRAM is expensive, has a small market, and is estimated to reach a market size of $530 million by 2025.DRAM has a broad future market, with the global total output value of the DRAM industry expected to reach $91.54 billion in 2022.
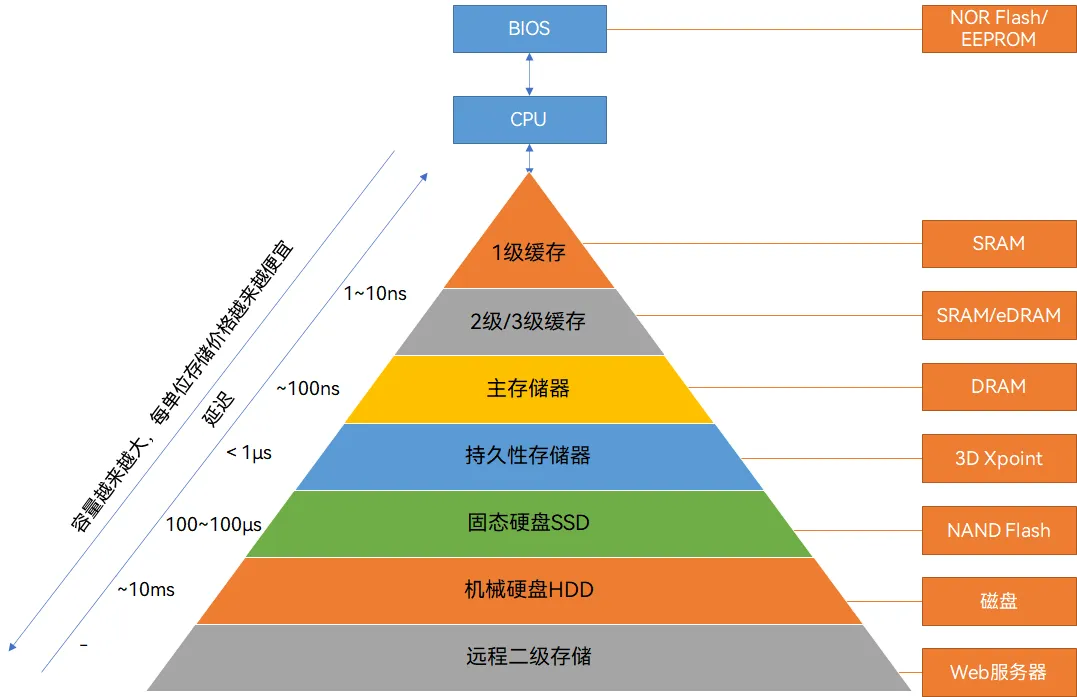
Typical memory hierarchy in computer systems and the use of storage technologies
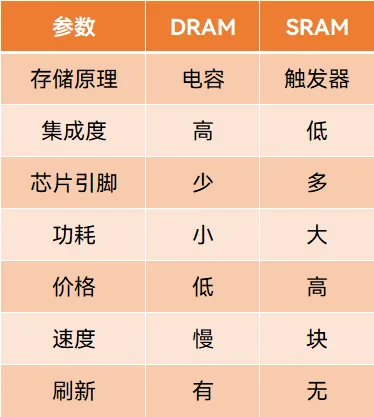
Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of DRAM and SRAM
Major suppliers of SRAM include Renesas Electronics, Cypress (acquired by Infineon), ON Semiconductor, Microchip, and other foreign manufacturers, with domestic ISSI (acquired by Junzheng).
Key players in the DRAM market include:
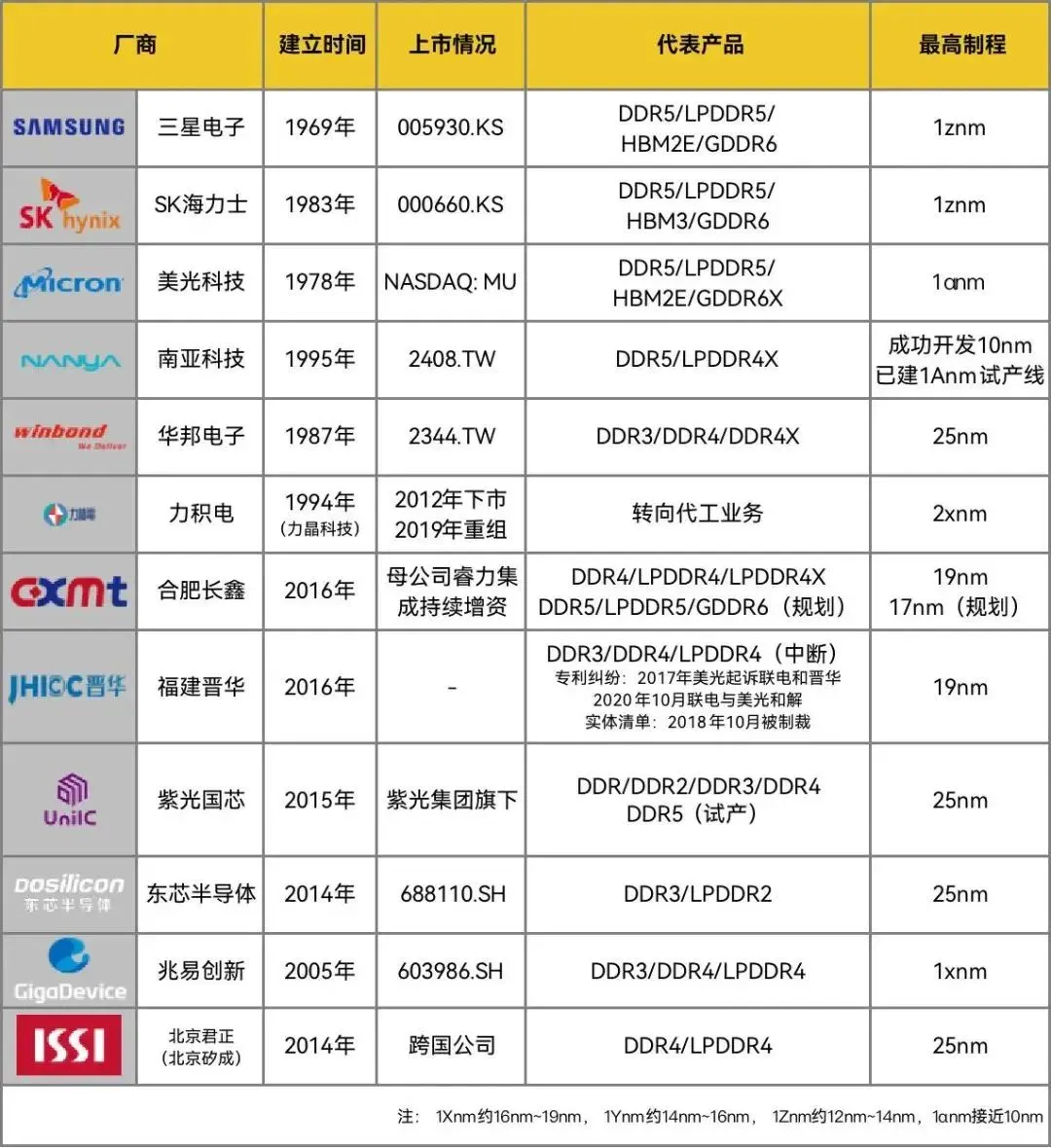
– 2 –
EEPROM, Nor Flash, and NAND Flash
EEPROM: A non-volatile memory that supports electrical erasure and plug-and-play, characterized by small size, simple interface, reliable data retention, online rewritability, and low power consumption.
NOR Flash: A type of code flash memory chip, one of the main application technologies in embedded storage chips, used to store code and some data. It features random access, high reliability, fast read speeds, and executable code, providing performance and cost advantages in low to medium capacity applications. Due to the need for internal instruction execution, system data exchange, user data storage, and vendor configuration data storage in end electronic products, it is an indispensable component.
NAND Flash: A type of data flash memory chip, it is the core of massive data storage, capable of achieving large capacity storage, high write and erase speeds, and is widely used for large data storage. It has four different storage technologies: SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC, representing the number of bits stored per cell as 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. As storage density increases from SLC to QLC, the cost per bit decreases, but performance, power consumption, reliability, and P/E cycles (the number of erase/write cycles, i.e., lifespan) decrease as well.
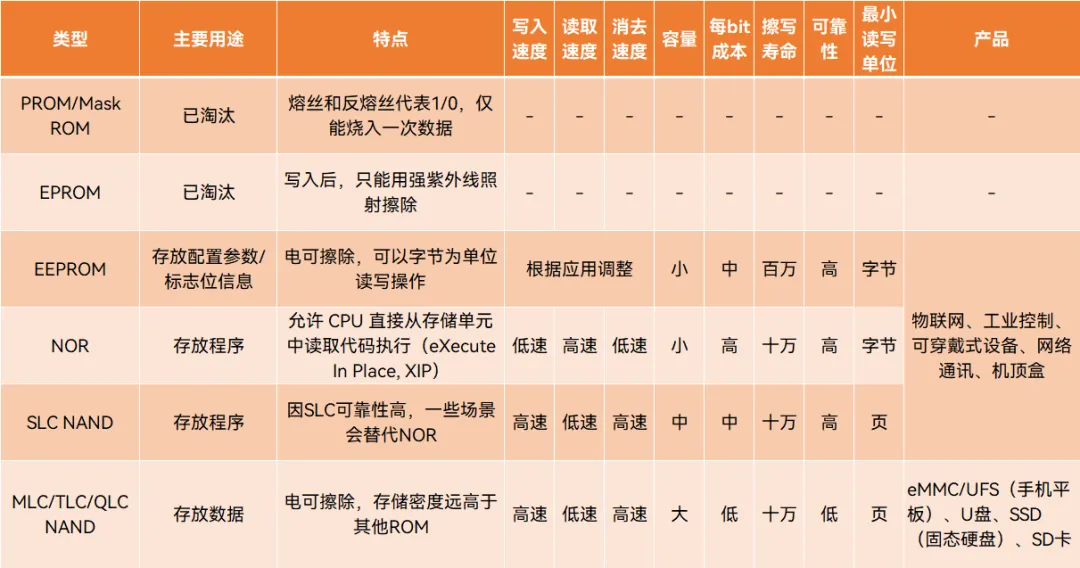
Applications:
EEPROM and NOR Flash have some overlap, and there has been industry discussion about using NOR Flash to replace EEPROM. However, compared to NOR Flash, EEPROM has a smaller capacity and a higher number of erase/write cycles, which is why EEPROM, with nearly forty years of history, has not been eliminated, and some applications still require it.In control chips, auxiliary chips solve the data storage needs of module chips, such as storing lens and image correction parameters in smartphone camera modules, parameters and configuration files in LCD panels, control parameters in Bluetooth modules, and temperature parameters in memory module temperature sensors.
NOR Flash is mainly used in low-power Bluetooth modules, TWS headphones, mobile phone touch and fingerprint sensors, TDDI (touch screens), AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode panels), wearable devices, automotive navigation, and security chips.
Major Manufacturers:
The global market size of EEPROM is only $714 million, with foreign manufacturers including STMicroelectronics, Microchip (which acquired Atmel), ON Semiconductor, ABLIC, and Rohm, with little new product introduction in recent years. Domestically, GigaDevice has entered the global top three, while Huizhou Microelectronics, Shanghai Fudan Microelectronics, and Hua Hong Semiconductor have maintained a certain market share as established manufacturers.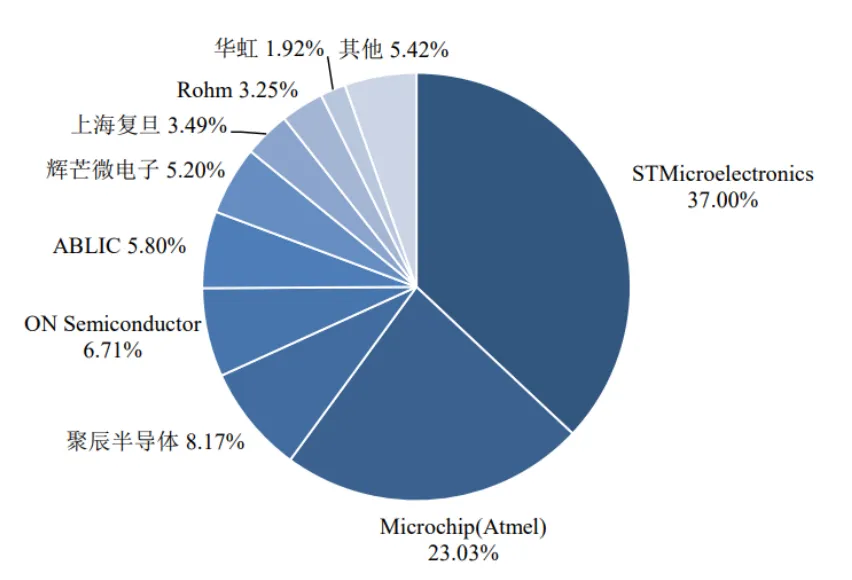
Global market share of EEPROM
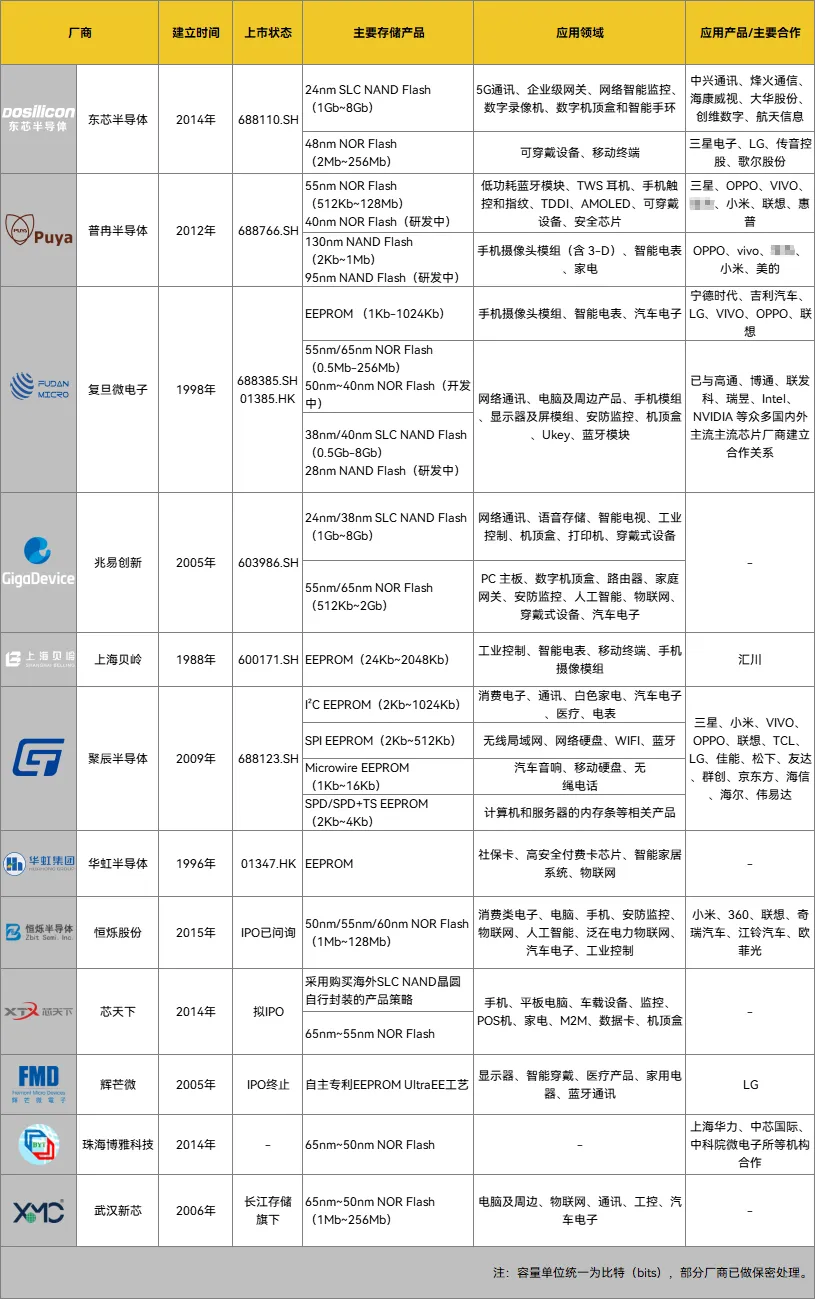
Overview of domestic small and medium capacity non-volatile memory companies
Currently, Samsung Electronics, Kioxia, Western Digital, Micron Technology, Intel, and SK Hynix together hold over 98% of the global NAND Flash market, and all are IDM manufacturers.
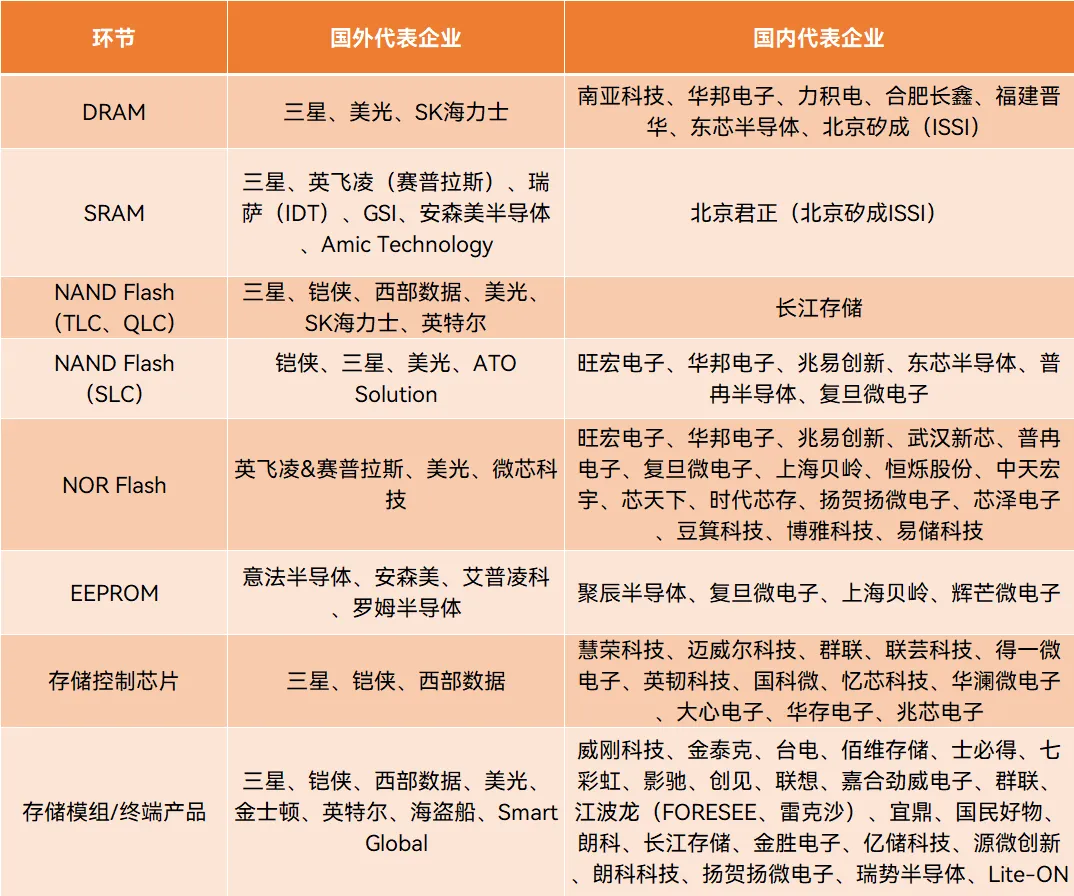
Summary of memory chip manufacturers as follows:
Welcome to follow IC Trading Circle
IC Trading Circle group (add WeChat hr59110 to request a free join link)

Featured Articles
Paid Learning:
Sales Case – How Chip Sales Win Customers
Revealing the Hidden Rules of Chip Workers’ Earnings
Related to Agents:
How Chip Traders Make Money from Information
Transforming Domestic Chips, Agents Need to Change Their Thinking
Discussing the PM Position of Agents
Talking about Chip Agent Sales
Discussing Entrepreneurship as a Chip Agent
Styles and Characteristics of Chip Agent Owners
Market Related:
Major Restructuring of Domestic Chip Companies This Year or Next
Funding Difficulties, Domestic Automotive Chip Companies Need to Change
In the Future, 90% of Domestic Chip Design Companies Will Be Eliminated or Integrated
Chaos and Cashing Out in Chip Startups
Current Status and Future Analysis of Domestic Automotive Grade MCUs