★ Beijing Tianrongxin Network Security Technology Co., Ltd. Zhang Yun
Abstract: The “Information Security Technology – Maturity Model for Information Security Protection Capability in Industrial Control Systems” (hereinafter referred to as the “Maturity Model”) serves as a national standard, providing a systematic maturity assessment framework for information security protection in industrial control systems, aimed at guiding industrial enterprises to comprehensively enhance their industrial control security protection capabilities. This article organizes the content of the “Maturity Model” standard, analyzes the key elements within the standard, and based on this, provides protective ideas for enterprises to carry out security protection construction according to the maturity model standard, offering theoretical guidance and practical reference for the information security protection of industrial control systems.
Keywords:Industrial Control Systems; Maturity Model; Information Security
1 Introduction
With the rapid development of information technology, industrial control systems face an increasing number of information security threats, making it increasingly critical to protect these systems from malicious attacks and unauthorized access. Therefore, the importance of information security protection for industrial control systems is becoming more prominent, and enhancing the information security protection capabilities of industrial control systems is crucial. To improve the comprehensive protection capabilities in the field of information security for industrial control systems and to implement the requirements of the “State Council’s Guidelines on Deepening the Development of the Industrial Internet with ‘Internet + Advanced Manufacturing'”, the China Electronics Standardization Institute, in collaboration with 41 units from industry, academia, and research, has developed and released the “Maturity Model” national standard after years of comprehensive consideration of existing information security technologies and the characteristics of industrial control systems.
The “Maturity Model” standard evaluates the protection level of enterprises from four aspects: organizational construction, institutional processes, technical tools, and personnel capabilities, providing a scientific basis and method for enterprises to assess and enhance their information security protection capabilities for industrial control systems, which is highly valuable for the construction of information security in industrial control systems.
2 Standard Overview
The “Maturity Model” provides a maturity model for information security protection capability in industrial control systems, stipulating the maturity level requirements for core protection objects and general security, and proposes methods for verifying capability maturity levels, applicable to relevant parties involved in the design, construction, and operation of industrial control systems for building information security protection capabilities, as well as verifying the maturity levels of enterprises’ information security protection capabilities for industrial control systems.
This maturity model is a model for measuring the capability maturity of enterprises, providing a reference benchmark for enterprises to assess their current practices, processes, and methods. The model includes three dimensions: security capability elements, capability maturity levels, and capability construction processes, as shown in Figure 1.
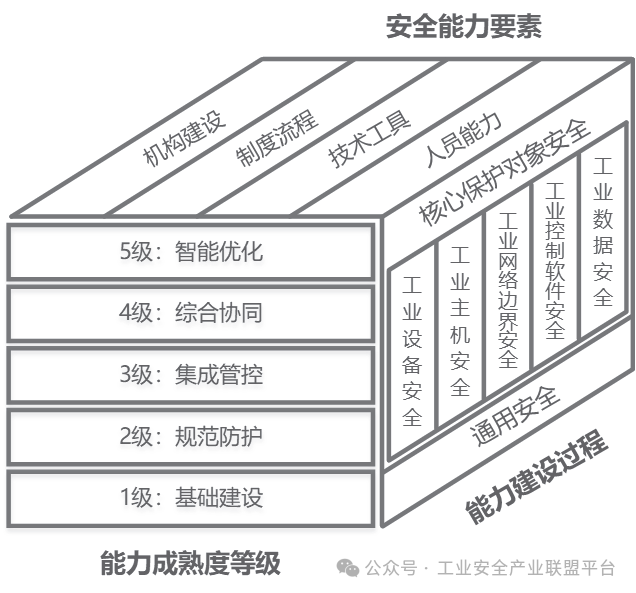
Figure 1 Maturity Model Architecture
(1) Security Capability Elements
Security capability elements quantify the security capabilities that industrial control systems should possess in the protection process from four aspects: organizational construction, institutional processes, technical tools, and personnel capabilities, serving as the main evaluation indicators for objectively assessing the security protection capabilities of enterprises’ industrial control systems.
Organizational construction is the foundation for ensuring the information security of industrial control systems, involving the establishment of information security organizations, distribution of responsibilities, communication, and collaboration. By clarifying organizational structure and responsibilities, enterprises can better implement information security strategies to address various information security threats and challenges.
The core role of institutional processes is to ensure that enterprises build and maintain a sound, systematic security management system and operational processes, thereby standardizing the security operation behaviors of personnel, ensuring that information security measures are effectively implemented, and promoting continuous optimization to adapt to evolving security challenges.
The main role of technical tools is to implement security requirements through effective technical means and product tools, protecting industrial control systems from various security threats, aiming to enhance the security, reliability, and resilience of the systems, ensuring the normal operation and production safety of industrial control systems.
The main role of personnel capabilities is to ensure that enterprises possess sufficient professional skills and knowledge to effectively execute information security protection work and continuously improve personnel’s security protection levels.
(2) Capability Maturity Levels
Capability maturity levels define the industrial control security protection capabilities of enterprises from low to high based on the capability levels of security capability elements, categorizing them into five different levels: Basic Construction Level, Normative Protection Level, Integrated Control Level, Comprehensive Coordination Level, and Intelligent Optimization Level. The classification of capability maturity levels allows for a more precise assessment of enterprises’ capabilities and levels in information security protection. By classifying levels, clear security protection goals and directions can be provided to enterprises, guiding them to gradually enhance their security protection capabilities.
(3) Capability Construction Process
The capability construction process proposes corresponding security protection requirements for a total of 10 process categories related to core protection objects and general protection objects, providing a systematic and hierarchical implementation framework for information security protection in industrial control systems, guiding and assessing the capability construction of industrial enterprises in information security protection, ensuring that the information security protection capabilities of industrial control systems are comprehensively enhanced and continuously optimized.
3 Analysis of Protection Construction Based on the Maturity Model Framework3.1 Analysis of Capability Maturity Model Levels
The process dimension of the information security protection capability construction for industrial control systems includes a total of 10 process categories, 40 process domains, and a total of 365 basic practices. The 10 process categories are divided based on core protection objects and general security. The specific content of the process categories and process domains can be referenced in Figure 2.
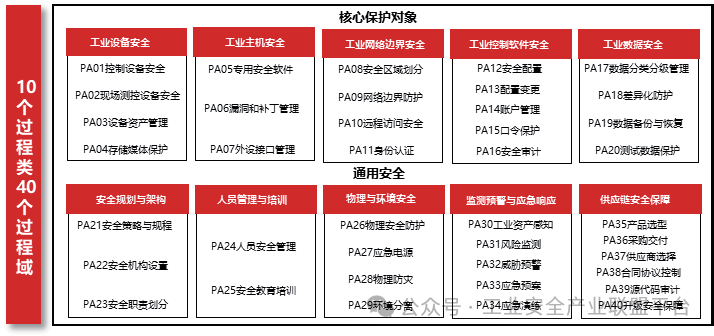
Figure 2 Process Categories and Domains of the Maturity Model
Based on the basic practice requirements of these 10 process categories in the dimension of security capability elements, the security protection requirements for each maturity level are analyzed below.
(1) Capability Maturity Level 1 – Basic Construction Level
This level is primarily based on the specific business scenarios and knowledge experience levels of enterprises, carrying out information security protection capability construction for industrial control systems based on the existing technical foundation and conditions of industrial control security, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Basic Construction Level Requirements Analysis
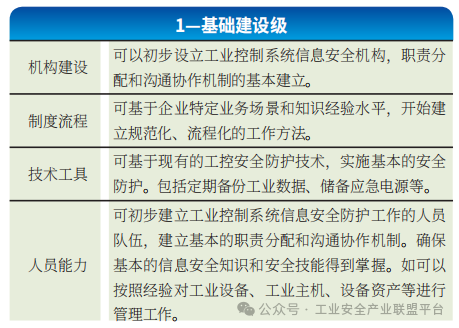
This level of construction has not yet formed a standardized, process-oriented working method, and related work largely relies on the subjective experience of information security personnel, with no requirements for documenting the construction process, making it impossible to replicate security construction work.
(2) Capability Maturity Level 2 – Normative Protection Level
Enterprises at this level can establish and document their industrial control security protection capability construction work, covering key areas such as industrial control equipment, industrial hosts, industrial networks, and industrial data, enabling enterprises to execute in a repeatable manner. Enterprises at this level can also conduct targeted security protection through the adoption of digital equipment and information technology means, building independent and replicable security protection capabilities at various levels, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Normative Protection Level Requirements Analysis
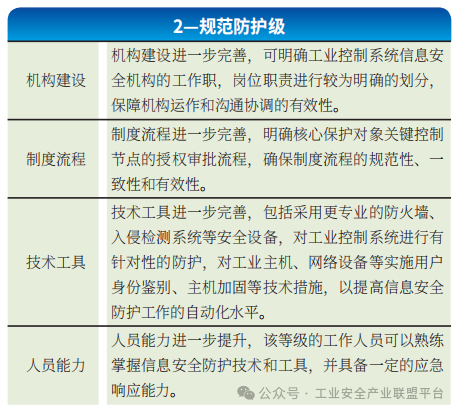
(3) Capability Maturity Level 3 – Integrated Control Level
Enterprises at this level further utilize integrated tools and systems to implement centralized and unified control over devices, hosts, systems, networks, and data within industrial control systems based on the normative protection measures already implemented. At this level, enterprises also integrate and optimize relevant protective regulations and establish a systematic management system to enhance the internal control security capabilities of enterprises in centralized management and unified control, as shown in Table 3. The main difference between this level and the normative protection level is the use of integrated tools to plan and manage information security in industrial control systems, improving work efficiency and protection capabilities.
Table 3 Integrated Control Level Requirements Analysis
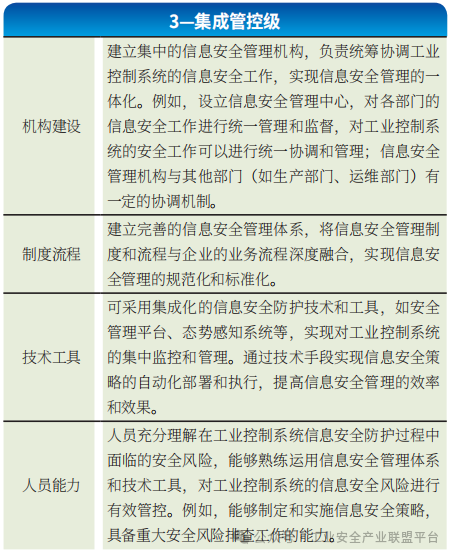
(4) Capability Maturity Level 4 – Comprehensive Coordination Level
Enterprises at this level can comprehensively consider security risk requirements when facing different production lines, plants, and related units along the industrial chain, carry out security protection construction work, and establish a multi-level, collaborative security management structure, utilizing situational awareness and centralized management technologies to achieve rapid response and effective defense against security threats, achieving comprehensive decision-making and coordinated protection capabilities, as shown in Table 4. The main difference between this level and the integrated control level is the strengthened requirements for comprehensive decision-making and coordinated protection in the execution process.
Table 4 Comprehensive Coordination Level Requirements Analysis
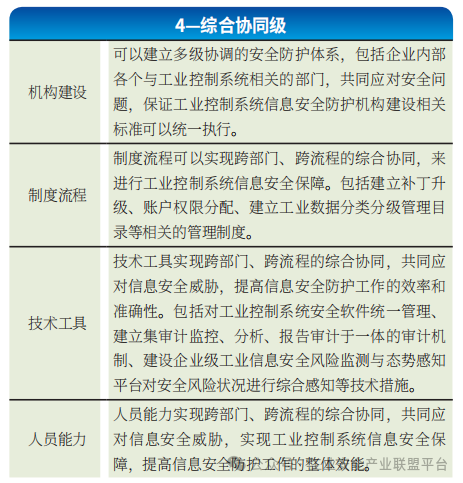
(5) Capability Maturity Level 5 – Intelligent Optimization Level
Enterprises at this level can utilize advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, proactive defense, and endogenous security to deeply integrate with existing security protection devices, systems, and institutional frameworks, thereby constructing a security protection system capable of intelligent evolution, creating a self-evolving and self-optimizing security protection system, as shown in Table 5. The main difference between this level and the comprehensive coordination level is the intelligent optimization and evolution capabilities in the execution process, enabling automatic optimization and adaptive improvement.
Table 5 Intelligent Optimization Level Requirements Analysis
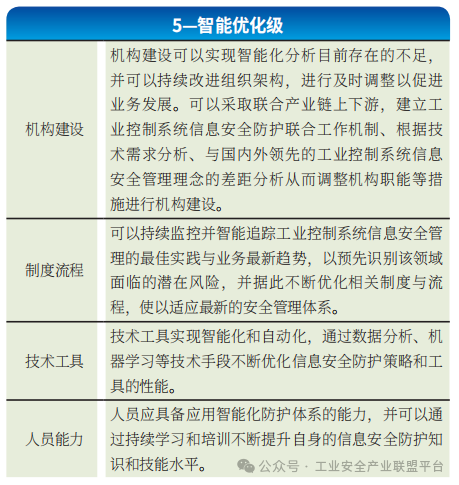
Based on an in-depth analysis of the requirements of the five levels of the maturity model for information security protection capabilities in industrial control systems, this article proposes a capability construction approach starting from the four key security elements: organizational construction, institutional processes, technical tools, and personnel capabilities. By leveraging the capability construction of these four security elements, the overall security protection capabilities of industrial enterprises can be gradually enhanced.
3.2 Ideas for Protection Capability Construction
(1) Organizational Construction
Establish a sound, pragmatic, effective, unified command, and coordinated security management organization, clarifying the security responsibilities of organizational members, which is the foundation for implementing and promoting security management.
Enterprises should set up a dedicated security management organization for industrial control systems, forming an information security coordination group led by the enterprise leader, composed of relevant departments such as information technology, production management, and equipment management. Under the guidance of the information security coordination group, each relevant department should clarify the responsible person for industrial control security according to the management mechanism, implement the responsibility system for industrial control security, and deploy security protection measures. Through the management mechanism, enterprises can achieve role and responsibility allocation for personnel involved in information security protection of industrial control systems and establish an effective work assessment mechanism.
(2) Security Management System
The network security management system is the management methods, norms, and rules that must be followed for the construction, operation, maintenance, and security management of industrial control systems; the network security management system documents can adopt a multi-level model to construct a clear hierarchical and relatively independent management system, facilitating enterprises to refer to and carry out system construction. The specific management system can refer to Figure 3.

Figure 3 Multi-Level Model Management System
(3) Technical Tools
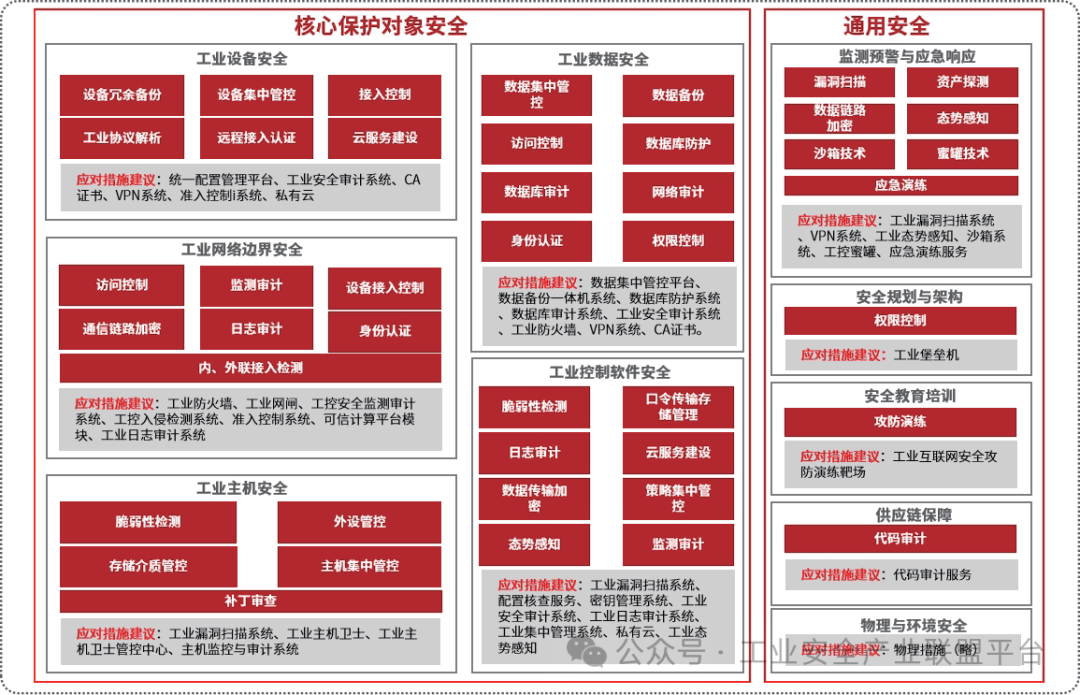
Figure 4 Technical Framework for Information Security Protection in Industrial Control Systems
Based on the requirements of the technical tools section of the five maturity levels in the 10 process categories of the “Maturity Model”, this article constructs a comprehensive technical framework for information security protection in industrial control systems, as shown in Figure 4. This framework elaborates on the key technical measures required to meet the technical tools requirements and recommends corresponding security products and services. Enterprises can refer to this framework, combine it with their assessed maturity level, and select appropriate technical measures and recommended security products and services to ensure compliance with national standard maturity level requirements, achieving systematic management and protection of information security.
(4) Personnel Capabilities
Enterprises can enhance personnel capabilities by providing relevant training for technical personnel or organizing relevant personnel to obtain related protective qualifications. By improving personnel capabilities, relevant personnel in enterprises can possess qualifications and practical experience in information security protection for industrial control systems, fully understand the security risks faced by enterprises in the information security protection process, and have the ability to control risks and propose improvement plans.
4 Steps for Enterprises to Apply the Maturity Model
Based on the previous analysis of the maturity model framework and its depth of protection construction, enterprises can effectively utilize this maturity model to strengthen the information security protection capabilities of industrial control systems according to their maturity levels. The actual application process is shown in Figure 5, providing specific guidance for step-by-step implementation.
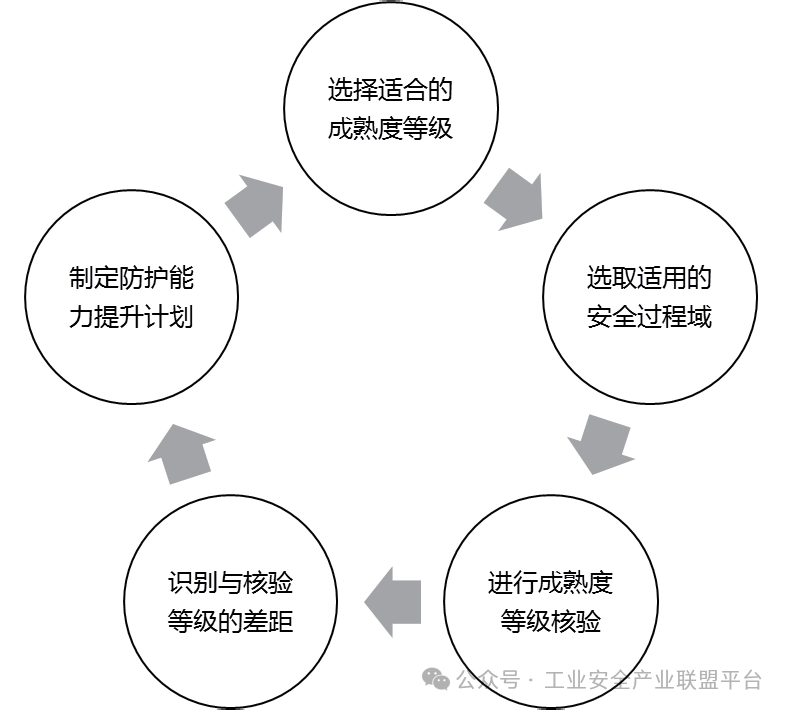
Figure 5 Steps for Using the Maturity Model
(1) Select the Appropriate Maturity Level
When using the maturity model, enterprises first need to define the maturity levels of information security protection capabilities for industrial control systems and, in conjunction with actual business situations, conduct a self-assessment of their information security protection capabilities for industrial control systems, which can be evaluated from aspects such as organizational construction, institutional processes, technical tools, and personnel capabilities. Based on the self-assessment results, enterprises select the desired maturity level for their information security protection capabilities for industrial control systems.
(2) Select Applicable Security Domains
After determining the desired maturity level, enterprises should select applicable process domains for information security protection based on the business scenario protection requirements covered by the core protection objects of industrial control systems. For process domains that are not applicable to the current business scenario protection requirements, they can be directly deleted without the need for corresponding level verification.
(3) Conduct Maturity Level Verification
Enterprises should conduct maturity level verification based on their understanding of the content of each process domain in the capability maturity model to check whether the level assessment is accurate.
(4) Identify and Verify Gaps with the Level
By comparing the security requirements of the selected security domains with their current security status, enterprises identify the current state of their information security protection capabilities and analyze the differences between this state and the verified level, determining specific goals and content for improvement based on the identified results.
(5) Develop a Protection Capability Enhancement Plan
Based on the identified gaps, enterprises develop a specific action plan for enhancing their information security protection capabilities for industrial control systems, gradually implementing improvement measures according to the action plan, and conducting regular reviews to ensure that security measures are effectively executed and adjusted according to the latest security threats and technological developments.
As enterprises’ business develops and changes, they can periodically review and clarify the appropriate maturity levels, following the steps for using the maturity model to re-determine levels, select security process domains, and gradually enhance their information security protection capabilities for industrial control systems. Thus, from identifying the target maturity level to the final implementation and review, a comprehensive cyclical system is formed. This “5-step method” closed-loop process ensures that enterprises can systematically enhance their information security protection capabilities for industrial control systems, enabling continuous improvement and adaptation to new security challenges.
5 Conclusion
The “Maturity Model” provides a comprehensive and systematic guiding framework for the construction of information security in enterprises’ industrial control systems. By following national standards and combining them with actual enterprise situations, enterprises can build a scientific and effective information security protection system, thereby ensuring the safe and stable operation of industrial control systems. This article conducts an in-depth study and analysis of the requirements of each level of the maturity model framework and, based on this, proposes ideas for the construction of information security protection for enterprises’ industrial control systems from the perspective of security capability elements, providing a reference for enterprises in building their cybersecurity systems.
References omitted.
Author Profile:
Zhang Yun (1986-) Female, from Handan, Hebei, Master’s degree, currently working at Beijing Tianrongxin Network Security Technology Co., Ltd., mainly engaged in research on industrial control system security and industrial internet security.
· end ·
Source | “Automation Expo” 2025 First Issue and “Industrial Control System Information Security Special Issue (Volume 11)”
Editor | He Min

For cooperation or consultation, please contact the WeChat ID of the Industrial Safety Industry Alliance platform secretary: ICSISIA20140417
Recommended Readings
Heavyweight | “Automation Expo” 2025 First Issue and “Industrial Control System Information Security Special Issue (Volume 11)” Online
Must-Read for the 2025 Two Sessions | These Industrial Information Security Proposals Will Rewrite Industry Rules
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology | Risk Warning for Preventing Network Attacks Targeting DeepSeek Local Deployment
Insights | Security Protection of Long-Distance Oil and Gas Pipeline Control Systems: Strategies, Practices, and Prospects
DeepSeek Analysis | Current Development and Future Prospects of Zero Trust Security Architecture in the Industrial Field
White Paper | Northeast University: 2024 Industrial Control Network Security Situation White Paper (Download Attached)
Recommended Read | The Five Network Security Technologies That Are About to Become Obsolete
Insights | Research on Encryption Technology for Industrial Programmable Control Systems
Recommended Read | DeepSeek Insights and Reflections from the Perspective of Security Professionals
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology | In 2024, China’s Information Security Sector Revenue Reaches 229 Billion Yuan
Attention | Results of Security Testing for Key Network Devices (19th Batch)
Power Safety | 2024 New Power System Safety Construction Guidelines Report (Download Attached)
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and Thirteen Departments | 2024 List of Typical Cases for the Application of Cybersecurity Technologies
Attention | Joint Issuance of the Implementation Plan for Improving Data Flow Security Governance by the National Development and Reform Commission, the National Data Bureau, and Six Other Departments