
 Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc.Introduction:
Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc.Introduction:
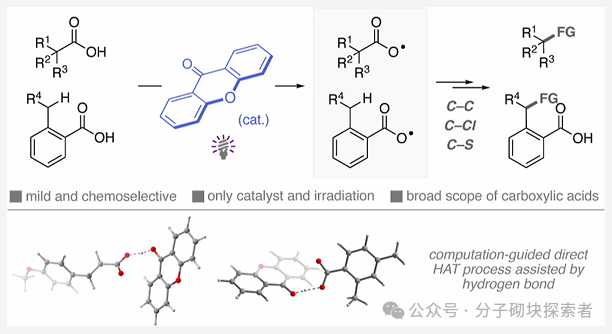
The carboxyl radical, as a highly reactive intermediate, is expected to open unique transformation pathways for radical chemistry. However, the current methods for directly generating carboxyl radicals from carboxylic acids mostly rely on environmentally unfriendly processes, and their applications are mainly limited to decarboxylation functionalization reactions.
This study proposes a new strategy mediated by photoactivated ketone catalysts, which directly generates carboxyl radicals through the hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) process of the O-H bond in carboxylic acids. By combining theoretical predictions with experimental validation, a chemical selective O-H hydrogen atom transfer catalytic system based on hydrogen bonding interactions between ketone photocatalysts and carboxylic acids has been developed—this system can selectively activate strong O-H bonds while leaving weaker C-H bonds unaffected. This approach has broad substrate applicability and excellent functional group compatibility, successfully applied to the direct decarboxylation functionalization of primary, secondary, and tertiary aliphatic carboxylic acids (including bioactive molecules). The study also achieved the preparation of benzoyloxy radicals, successfully realizing the selective alkylation of C(sp3)-H bonds in ortho-substituted benzoic acids through a 1,5-hydrogen atom transfer process.
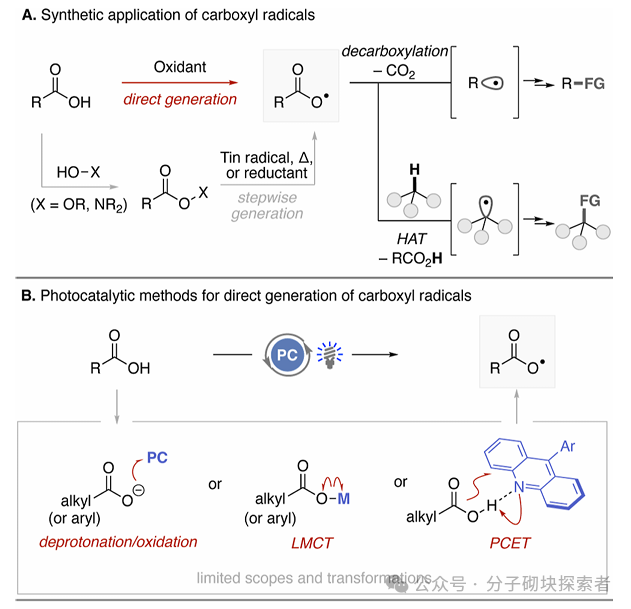
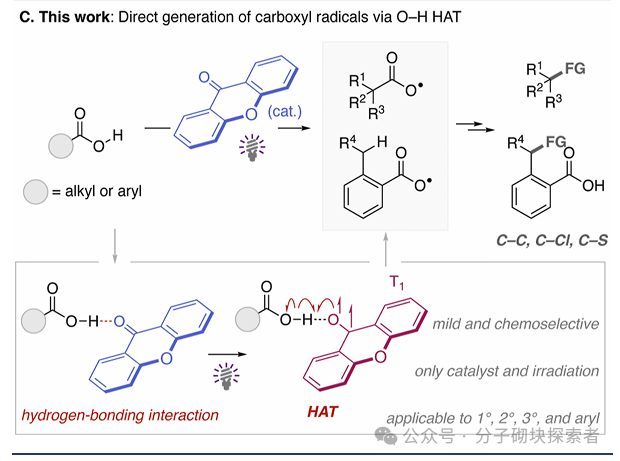 Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc.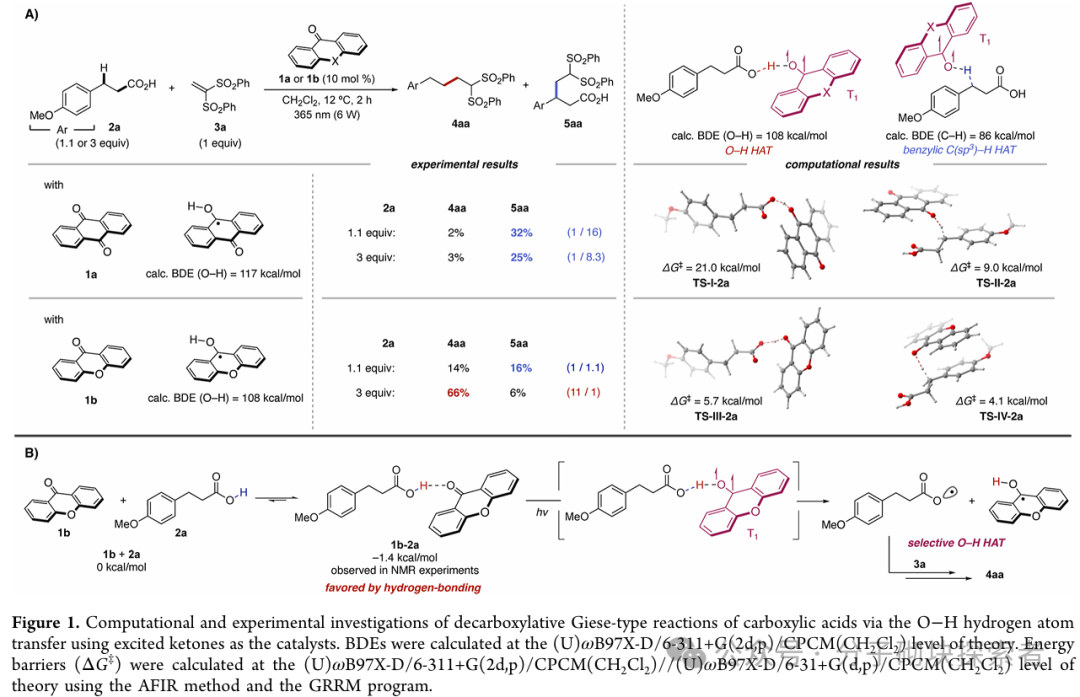
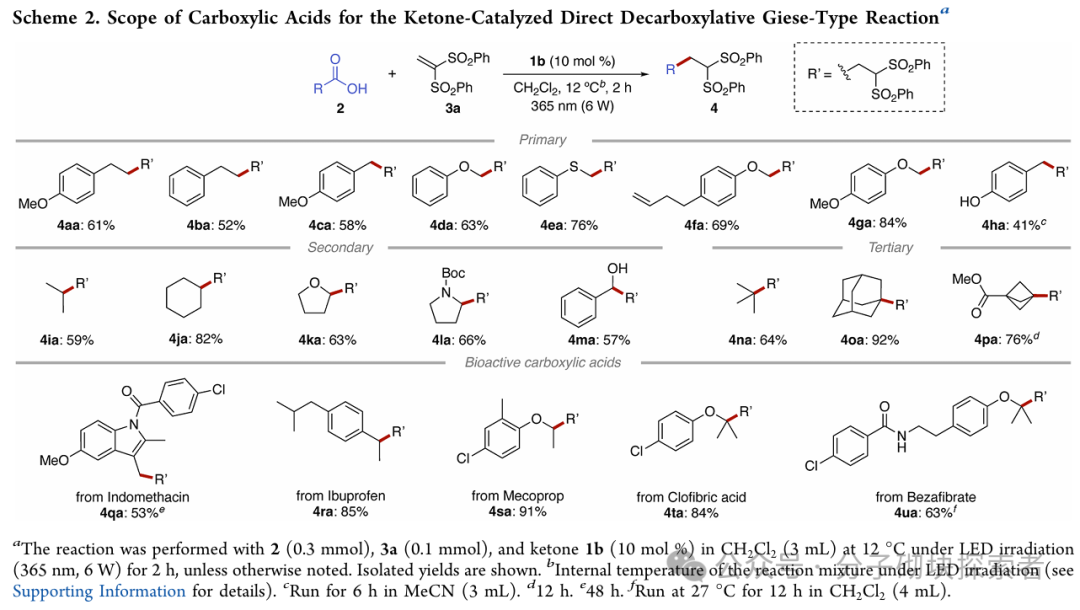
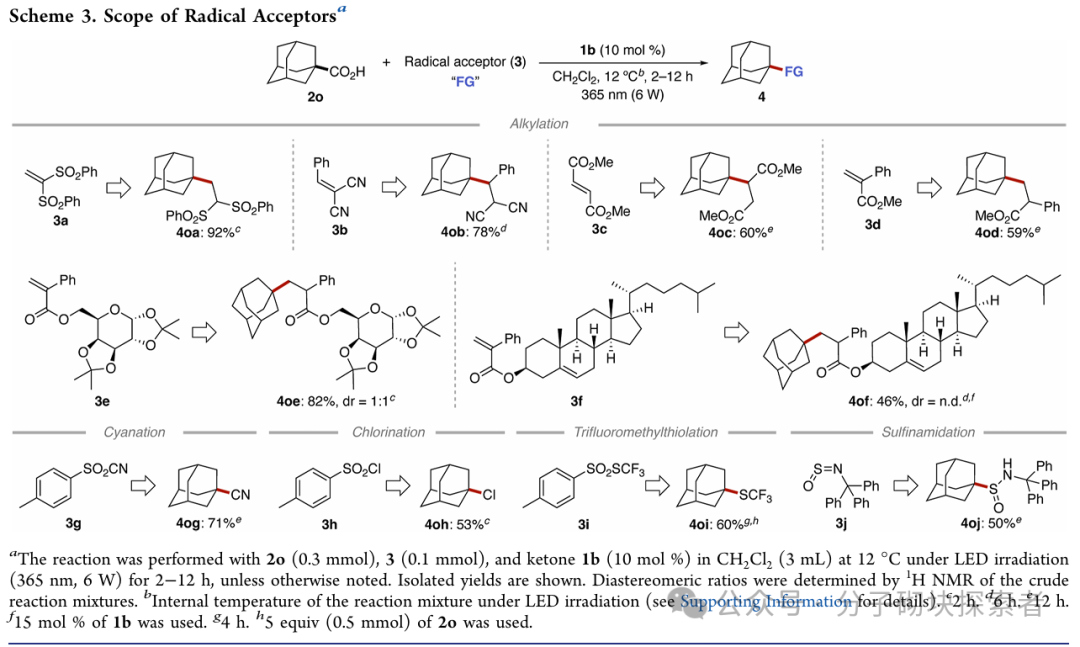
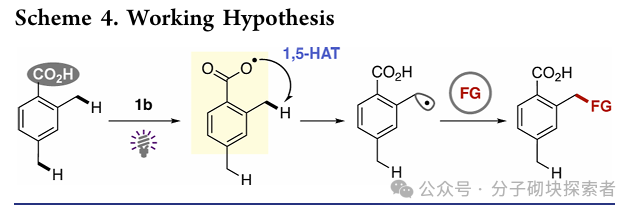
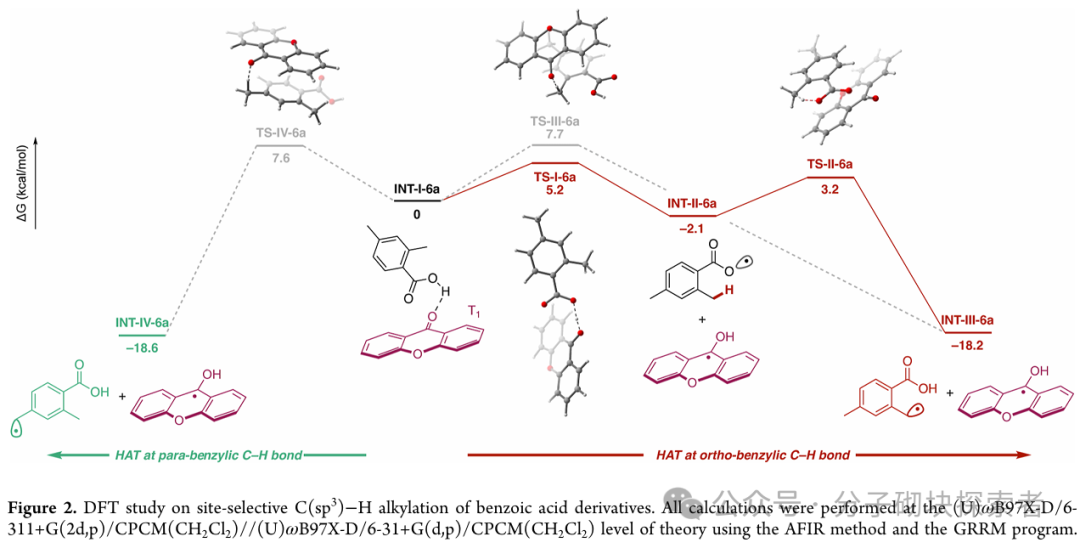 Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc. Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc.
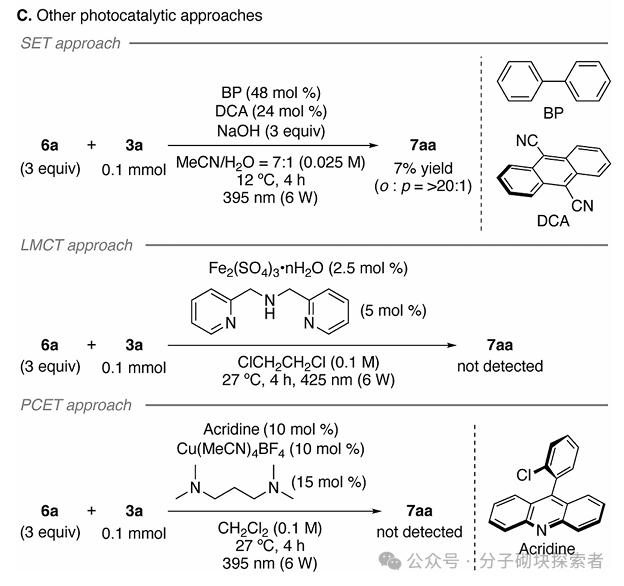
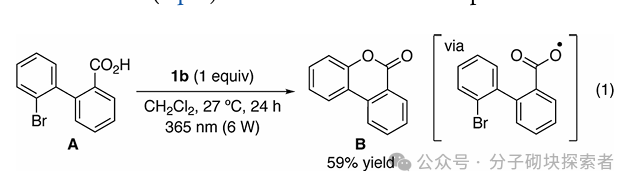 Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Image source: J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Conclusion:
A novel alkali-free, metal-free photocatalytic strategy has been developed, generating carboxyl radicals through direct hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) from the O-H bond of carboxylic acids. This study utilizes inexpensive and readily available xanthone as the HAT catalyst, successfully overcoming the challenge of selective cleavage of O-H bonds. Based on the hydrogen bonding interactions between xanthone and carboxylic acid substrates, this system can selectively activate O-H bonds even in the presence of weaker C(sp³)-H bonds. This chemically selective O-H hydrogen atom transfer process enables the decarboxylation functionalization of various aliphatic carboxylic acids, including bioactive compounds. The approach can also achieve selective alkylation of ortho-benzyl C(sp³)-H bonds in benzoic acid derivatives by generating benzoyloxy radicals. This is the first report utilizing direct HAT catalysts for the selective C(sp³)-H functionalization of benzoic acid derivatives. This research, through the organic combination of theoretical and experimental methods, reveals new reaction characteristics of xanthone as a chemically selective O-H direct HAT reagent, with ongoing in-depth studies being pursued.
References
Direct Generation of Carboxyl Radicals from Carboxylic Acids Catalyzed by Photoactivated Ketones
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025,
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c04571