
More and more non-standard measurement devices are using displacement sensors to collect length signals, which offer high precision, easy implementation, and convenient integration into information systems.
A displacement sensor, also known as a linear sensor, is a type of metal-inductive linear device that converts various measured physical quantities into electrical signals.
Based on the form of output signals, displacement sensors can be divided into two types: analog (continuous output) and digital (discrete output).
Commonly used displacement sensors are predominantly of the analog type, including potentiometric displacement sensors, inductive displacement sensors, self-adjusting angle machines, capacitive displacement sensors, eddy current displacement sensors, Hall effect displacement sensors, and optical grating displacement sensors.

The inductive displacement sensor is the most widely used category of sensors for measuring length in machining, with the vast majority of pen-type sensors belonging to this category. Its structure is simple, has a long service life, reliable manufacturing processes, good measurement linearity, and is resistant to temperature and shock, among many other advantages.
An inductive displacement sensor, as the name suggests, measures displacement using the principle of inductance variation, which can be further divided into mutual inductance, self-inductance, and differential pressure types. For inductance, its own variation is the reactance, with related variables including magnetic flux, impedance, terminal voltage, and current.
For a hollow coil, under constant power supply frequency, its own inductance L (mH) = (0.08D.D.N.N) / (3D + 9W + 10H), where D is the coil diameter, N is the number of turns, d is the wire diameter, H is the coil height, and W is the coil width. Don’t worry if you don’t understand; we just need to know that these letters represent values that do not change on their own, so once a hollow coil is made, its inductance is fixed.
So, how does an inductive position sensor measure variables? This involves the inductance with a magnetic core L = (k*μ0*μs*N²*S) / l, where μs is the relative permeability of the magnetic core inside the coil.
PS: This formula is missing a 0.08 compared to the hollow coil, making its effect more pronounced.

The differential pressure displacement sensor, scientifically known as LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer), operates on the same principle as a transformer and is a complex application of inductance. The Solartron sensor manual provides an explanation that essentially states: there are three sets of coils inside the sensor, sharing a single magnetic core. The primary coil is continuously powered, generating an alternating magnetic field like the input power in a transformer; when the core moves within the coils, the output voltage difference between the two secondary coils varies. By calculating this voltage difference, the displacement result can be obtained.
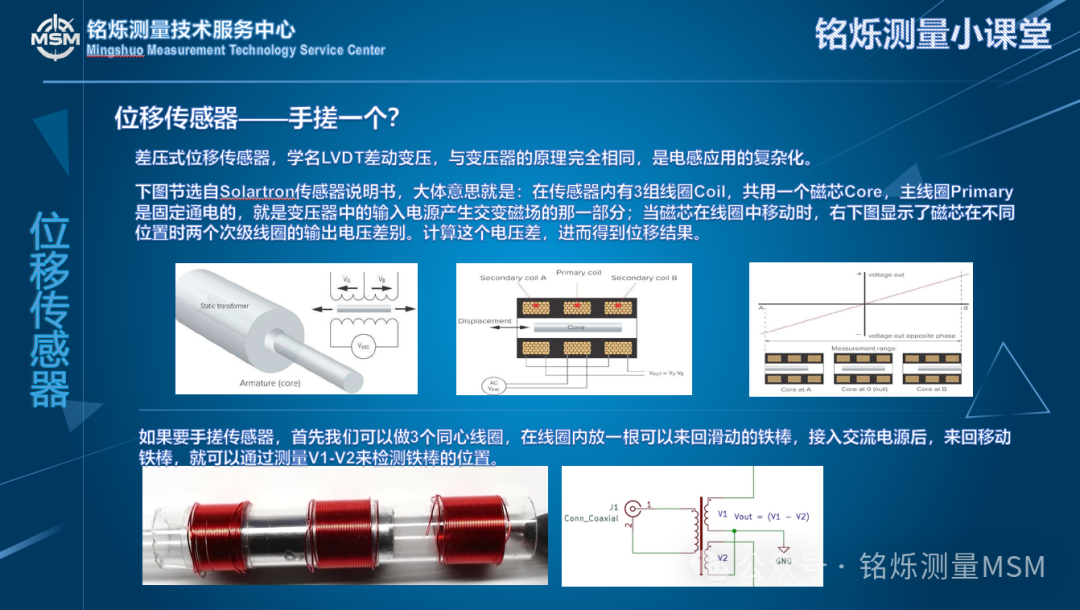
Here is a short video demonstrating a hand-cranked LVDT sensor. The content is quite long, and the signal processing part is from the 3rd to the 6th minute, which I have sped up; feel free to skip if you’re not interested.
With the rapid development of grating technology, the size of grating scales and reading heads has become increasingly smaller, while the stability and accuracy of grating measurements are highly desirable. Therefore, in recent years, grating displacement sensors have gained more attention. Simply put, a grating displacement sensor has a grating scale installed internally, and when the probe rod moves the grating scale, the reading head captures the position change data of the grating scale and transmits it to a display instrument, which shows the measurement value after accumulation.
Eddy current displacement sensors are less commonly used for length measurement in machining, but are more frequently used for measuring spindle vibration and runout. Their characteristic is ultra-high precision, but the downside is that the linear measurement range is relatively short, making them unsuitable for large stroke measurements. Eddy current sensors operate on the principle of eddy current induction; when the coil approaches a metallic conductor, the induced current in the conductor generates an induced magnetic field, which in turn affects the eddy current coil. This also shows that eddy current measurement is non-contact, allowing use in high-speed moving structures, but it is affected by electromagnetic interference and cannot measure non-conductors.

The potentiometric displacement sensor is one of the earliest methods used in measurement, originally derived from sliding rheostats. When the sliding end moves, the resistance value changes significantly, allowing the calculation of the movement distance. However, due to its contact measurement structure, the potentiometric sensor is subject to wear during use, resulting in a shorter lifespan and poorer measurement stability.
The capacitive displacement sensor operates on a principle similar to that of inductive sensors, but the change in reactance is replaced by capacitance. However, in practical applications, measuring capacitance is more challenging due to significant drift caused by external influences, and the smaller the gap between the capacitor plates and the area of the capacitor plates, the harder it is to measure and control. Therefore, capacitive sensors are used less frequently than inductive sensors for linear displacement. The most common capacitive sensor we encounter in daily life is the capacitive touchscreen.

That concludes our brief introduction to length measurement. In the next article, we will explore temperature measurement. If you have any questions about length measurement, please feel free to message me.