Optimization of Wireless Sensor Network Coverage Based on Sparrow Algorithm
Abstract: This article mainly introduces how to use the Sparrow algorithm for optimizing the coverage of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN).
1. Wireless Sensor Network Node Model
This article is primarily based on the 0/1 model for optimization. In a two-dimensional plane, the sensing range of a sensor node is a circular area centered at the node with a radius of , which is commonly referred to as the “sensing disk” of the node. The sensing radius is related to the physical characteristics of the built-in sensor of the node. Assuming the position coordinates of the node are in the 0-1 sensing model, for any point on the plane, the probability of the node detecting an event occurring at a point within the area is: where is the Euclidean distance between the point and the node.
2. Coverage Mathematical Model and Analysis
Now assume the target monitoring area is a two-dimensional plane, and the number of identical structure sensor nodes deployed in the area is N, with each node’s position coordinates assumed to be initialized and the sensing radius r. The set of sensor nodes is represented as: where represents a circle centered at node with a monitoring radius r. It is assumed that the monitoring area is discretized into pixels, with the coordinates of the pixels being , and the distance between the target pixel and the sensor node is: The event of a pixel point in the target area being covered by the sensor node is defined as . The probability of this event occurring is the probability that pixel point is covered by the sensor node : We define the coverage rate of all sensor nodes in the target monitoring environment as the ratio of the covered area of the sensor node set to the area of the monitoring region, as shown in the formula: Our ultimate goal is to find a set of nodes that maximizes the coverage rate.
3. Sparrow Algorithm
For the principle of the Sparrow algorithm, please refer to: https://blog.csdn.net/u011835903/article/details/108830958 This algorithm is used to find the minimum value. Therefore, the fitness function is defined as the minimum of the uncovered rate, which means maximizing the coverage rate. As follows:
4. Experimental Parameter Settings
The parameters for wireless sensor coverage are set as follows:
%% Set WSN coverage parameters,
%% Default input parameters are integers. If you want to define decimals, please multiply by a coefficient to convert to integers before conversion.
%% For example, for a range of 1*1, R=0.03 can be converted to 100*100, R=3;
% Area range is AreaX*AreaY
AreaX = 100;
AreaY = 100;
N = 20 ;% Number of coverage nodes
R = 15;% Communication radius
The parameters for the Sparrow algorithm are as follows:
%% Set optimization parameters
pop=30; % Population size
Max_iteration=80; % Set maximum number of iterations
lb = ones(1,2*N);
ub = [AreaX.*ones(1,N),AreaY.*ones(1,N)];
dim = 2*N;% Dimension is 2N, N coordinate points
5. Algorithm Results
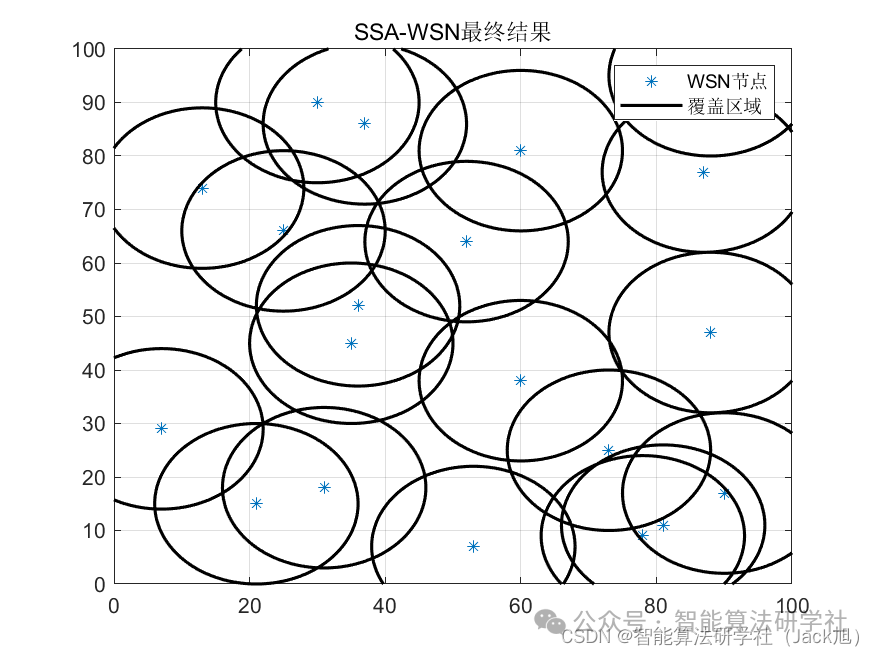
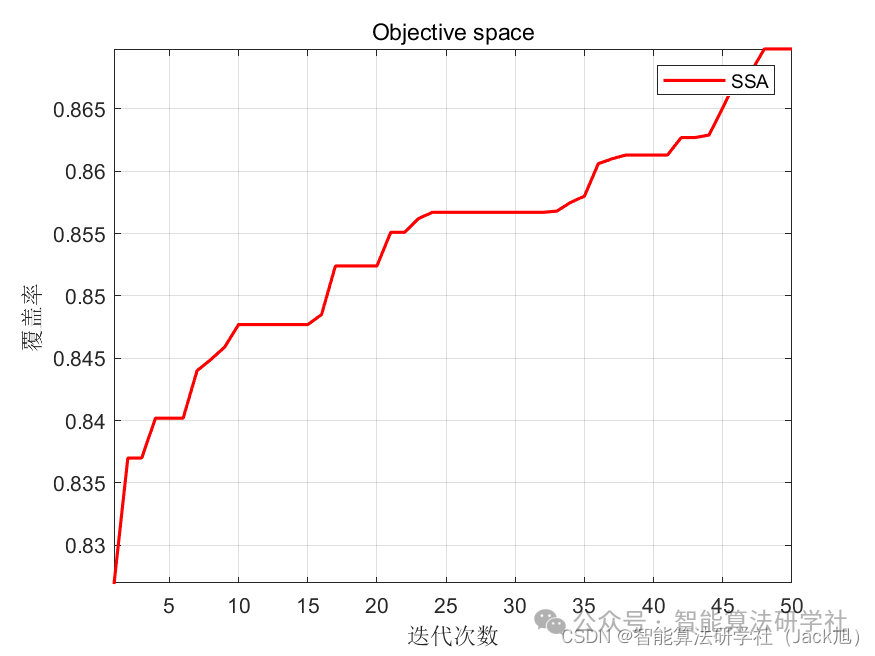
From the results, the coverage rate continuously increases during the optimization process, indicating that the Sparrow algorithm plays an optimizing role in coverage optimization.
6. References
[1] Shi Chaoya. Research on Coverage Optimization of Wireless Sensor Networks Based on PSO Algorithm [D]. Nanjing University of Science and Technology.
7. MATLAB Code
Click “Read the original text” to get it!