On May 16, the People’s Bank of China released the financial industry standard ‘Guidelines for Financial Applications of IoT Technology’ (JR/T 0338—2025) (hereinafter referred to as ‘the Guidelines’), which took effect on the same day. It is reported that the drafting units of this document include several branches of the People’s Bank, state-owned banks, joint-stock banks, urban commercial banks, rural commercial banks, and rural credit cooperatives.

The Guidelines aim to promote the healthy development of IoT technology in financial applications, ensure the security of IoT technology applications in the financial sector, assist in the digital transformation of the financial industry, and facilitate the integration of emerging technologies with industry development. It includes content related to the architecture, functions, and security of IoT technology financial applications, applicable to all participants in the financial industry.
The architecture of IoT technology financial applications consists of four levels, and each of the three application models has two implementation methods.
The Guidelines point out that the IoT financial application domain is based on the existing IoT application domain and financial application domain, mutually empowering each other. The architecture of the IoT application domain, IoT financial application domain, and financial application domain consists of four levels: device layer, communication layer, platform layer, and application layer.
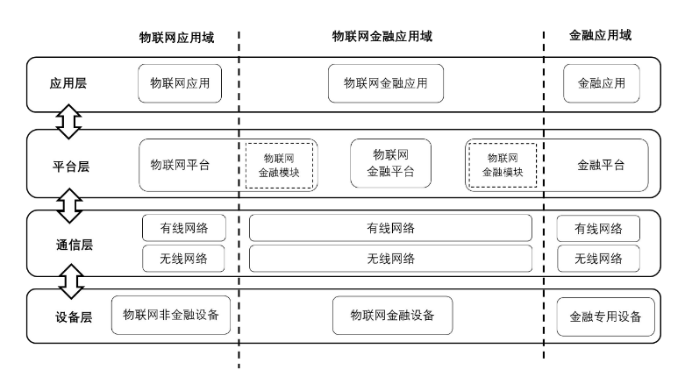
Among them, the device layer includes three types of devices: non-financial IoT devices, financial-specific devices, and IoT financial devices. In a specific application scenario, each device’s type is unique.
The deployment forms of various devices in the device layer include the following situations: devices connect to the platform without mounting sub-devices, transmitting information and interacting with the platform; devices connect to the platform while mounting sub-devices, where the device receives information from its sub-devices, transmits all information, and interacts with the platform; distributed multiple devices, where multiple devices collaboratively process information, with one or more devices connecting to the platform, transmitting all collaboratively processed information and interacting with the platform.
Regarding the communication layer, the communication networks used in the IoT application domain, IoT financial application domain, and financial application domain include wired and wireless networks, with the specific communication network determined based on actual conditions.
The platform layer includes IoT platforms, financial platforms, IoT financial platforms, and IoT financial modules.
The application layer includes IoT applications, financial applications, and IoT financial applications.
In terms of application models, based on different scenarios, the application of IoT technology in the financial sector can be summarized into three reference models: financial platforms introducing IoT data, IoT platforms introducing financial data, and IoT financial platforms introducing both IoT data and financial data.
Among them, the financial platform introducing IoT data involves building an IoT financial module within the financial platform, introducing IoT data from the IoT platform, supported by the financial platform for IoT financial applications.
The IoT platform introducing financial data involves building an IoT financial module within the IoT platform, introducing financial data from the financial platform, supported by the IoT platform for IoT financial applications.
The IoT financial platform introducing both IoT data and financial data involves an independent IoT financial platform that separately introduces IoT data and financial data from the IoT platform and financial platform, supported by the IoT financial platform for IoT financial applications.
The Guidelines mention that each of these three application models has two implementation methods, which are specifically introduced.
The functions of IoT technology financial applications involve devices, platforms and modules, communication, and applications.
The functions of IoT technology financial applications include four parts:
First, the functions of IoT financial devices, including anomaly response, geographic location reporting, positioning technology, and internet protocol support.
Second, the functions of IoT financial platforms and modules, including device access, device management, business analysis, connection management, geographic location reporting, and internet protocol support. Among them, in terms of device access, IoT financial platforms and modules can conduct identity verification and authentication for various access devices and users who use or manage devices, and the platform and modules support complex and diverse device access, such as multi-network access, multi-protocol access, system integration access, rapid access, and concurrent access.
Third, the communication functions of IoT financial technology. IoT financial communication uses the corresponding communication network based on specific business scenario requirements, and if it supports internet protocols, it must comply with the relevant regulations of national and industry management departments, supporting IPv6.
Fourth, the application functions of IoT financial applications. IoT financial applications provide corresponding service functions based on specific business scenario requirements.
IoT technology financial application security proposes specific requirements from four parts.
No matter what kind of emerging technology is applied in the financial industry, security is of utmost importance. The Guidelines also point out the security of IoT technology financial applications from four aspects.
First, the security of IoT financial devices. Overall, IoT financial devices must comply with the relevant content regarding physical security, access security, communication security, data security, and device security in Chapters 5 and 6 of GB/T 36951.
The Guidelines also propose specific requirements from seven aspects, including startup chain security, command legality, version upgrades, vulnerability fixes, device interfaces, memory clearing, and security modules.
Second, the security of IoT financial platforms and modules. Overall, the physical environment security, communication network security, regional boundary security, computing environment security, and operation and maintenance management security of IoT financial platforms and modules must meet the second-level security requirements or above in Chapters 7 to 9 of JR/T 0071.2.
The Guidelines also propose specific requirements from six aspects, including access security, data collection, data storage, data usage, data deletion and destruction, and key security. Among them, regarding key security, the platform and modules must have the capability to manage the entire lifecycle of keys, including generation, storage, and issuance, considering three factors: having the capability for secure storage and management of keys, avoiding the use of the same device key; ensuring that data encryption, decryption, digital signature, and other technologies comply with the requirements of national cryptography management departments and financial industry management departments; and promptly replacing keys in case of key leakage or expiration.
Third, the security of IoT financial communication. Overall, the security of IoT financial communication must comply with the relevant content in Chapter 6 of GB/T 37025.
The Guidelines propose specific requirements from two aspects, including identity verification and communication methods. In terms of communication methods, suitable communication methods can be adopted based on actual needs. Common communication methods and the factors to consider when using them are:
When using Bluetooth for transmission, it must comply with the relevant content in Chapter 6 of GB/T 38648.
When using wireless communication networks (Wi-Fi) for transmission, WPA2, WPA3, or higher security encryption methods must be used, and devices must reject unprotected Wi-Fi connections; in network environments with additional security requirements, two-factor authentication should be used when accessing Wi-Fi.
When devices use ZigBee protocol for network access, ZigBee 3.0 or higher versions should be adopted, and authorization matching should be conducted in security mode, such as using the installation code (Install Code) or pre-installed key (Pre-Install Key) matching method; if using versions below ZigBee 3.0, security mechanisms to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks should be in place.
Fourth, the security of IoT financial applications. Overall, the general security, session security, and common attack prevention of IoT financial applications must comply with the relevant content in Section 3.4 of JR/T 0095.
The Guidelines also propose specific requirements from four aspects, including permission management, operating environment, operation maintenance, and logical design.
Finally, in the appendix of the Guidelines, typical scenarios of IoT technology in financial applications are described, including mortgage credit monitoring, financial equipment management, financing management of leased objects, automatic payment for smart appliances, anti-counterfeiting traceability, and in-vehicle payments, and it is pointed out that in actual applications, suitable application models can be selected based on specific business needs.
The articles shared by this public account are original or edited and organized based on online searches, and the copyright of the articles belongs to the original author, for readers’ learning and reference only, and are prohibited for commercial use. Due to numerous reprints, it is impossible to find the true source. If the source is misattributed, or if there are infringements in the software, materials, etc., contained in the images, text, and links used in the article,please contact the backend administrator for deletion!
Previous Reviews
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology: Building an ‘Upgraded Version’ of Intelligent Manufacturing!
Latest News: Liu Liehong, Director of the National Data Bureau, Attends the 2025 Global Digital Economy Conference, Promoting Urban Digital Transformation in Three Aspects.