Key Knowledge Points in Chapter One:
Understand the characteristics, classifications, developments, and applications of embedded systems, and be familiar with the logical components of embedded systems.
Understand the main types of embedded processing chips, be familiar with the development process of SoC, and grasp the significant importance of IP cores.
Be familiar with the encoding of Chinese and Western characters, as well as the types and processing of digital text, and master the parameters, file formats, and main applications of digital images.
Understand the classifications and components of computer networks, be familiar with the main content of the IP protocol, and master the composition of the Internet and commonly used access technologies.
1. Composition and Types of Computer Networks
A computer network is a system that connects many geographically dispersed computers and other intelligent devices for the purpose of communication and resource sharing, using communication devices, transmission lines, and network software. It is a type of data communication system.
1. Composition of Computer Networks
Intelligent electronic devices such as computers: These are the communication terminals of the network, such as mobile phones, TV set-top boxes, monitoring and alarm devices, kitchen sanitary equipment, etc.;
Data communication links: These include twisted pairs, coaxial cables, optical fibers for data transmission, and various communication control devices (such as network cards, hubs, switches, modems, routers, etc.) necessary for effectively and reliably transmitting data, forming the data communication links between computers and communication devices, and between computers themselves;
Communication protocols: To ensure the interconnection of the network, computers and communication control devices must adhere to a set of rules and conventions, which are referred to as communication protocols, or simply protocols;
Network software: The function of communication software is to implement network communication protocols, and they are generally included in the operating system. This also includes network applications, such as email programs, browser programs, instant messaging software, online gaming software, etc.
2. Types of Computer Networks
Based on the transmission medium used, networks can be divided into wired and wireless networks; based on the nature of network use, they can be divided into public and private networks; based on the scope of use and target audience, they can be classified into enterprise networks, government networks, financial networks, and campus networks;
In more cases, people classify computer networks based on the geographical coverage:
-
• Local Area Network (LAN): The geographical range of the network is small (e.g., a few km), usually belonging to a single unit, which is self-built and self-managed; -
• Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): Also known as a city network, its coverage is between 5 to 50 km. -
• Wide Area Network (WAN): Also known as a long-distance network, its range can be from tens to thousands of km, or even larger. Wide area networks often cover a country, region, or span multiple continents, forming an international computer network.
2. Ethernet LAN
Ethernet LANs are commonly found in companies, schools, institutions, and homes, and are the most popular form of computer networks, with an estimated millions of LANs worldwide; currently, switched Ethernet using switches is popular.
The main characteristics of computer LANs are:
-
• Owned by a single unit, self-built and self-managed, with a limited geographical range. -
• Uses specially laid transmission media for networking and data communication. -
• High data transmission rates (10 Mb/s to 10 Gb/s), short latency, and low error rates (10^-8 to 10^-11).
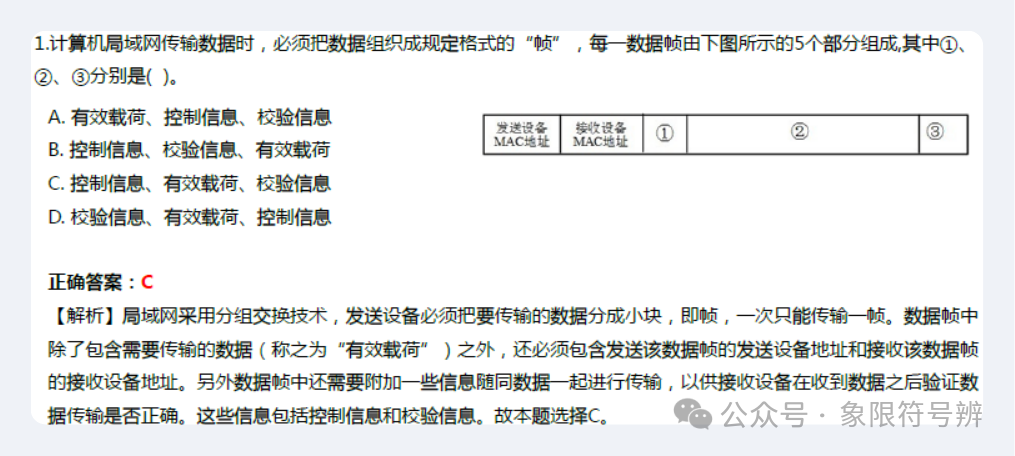
LANs use packet switching technology, with the data format as follows:
| Sender Device MAC Address | Receiver Device MAC Address | Control Information | Payload (Data Being Transmitted) |
Classification of LANs
-
• Based on the transmission medium used, it can be divided into wired and wireless networks; -
• Based on the topology of terminal devices interconnecting in the network, it can be divided into star networks, ring networks, bus networks, hybrid networks, etc.; -
• Based on the access control methods used for the transmission medium, it can be divided into Ethernet, FDDI networks, and token networks, etc. Different types of LANs adopt different communication protocols. Currently, Ethernet is widely used, forming a network centered around hubs or switches.
3. Wireless LAN
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a product of the combination of Ethernet and wireless communication technology. It uses radio waves for data transmission, and its working principle is fundamentally the same as that of wired Ethernet.
-
• The greatest advantage of WLAN: It allows for easy relocation of computers or changes in network composition. -
• WLAN uses radio waves for transmission, primarily utilizing the 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz frequency bands. -
• The protocols used in WLAN are mainly IEEE 802.11 (commonly known as WiFi). -
• WLAN requires devices such as wireless network cards and wireless access points to be constructed. Wireless access points are also known as “hotspots,” which act as wireless switches or hubs, similar to base stations in mobile communication.
Another technology for constructing WLAN is Bluetooth. It is a short-range, low-rate, low-cost wireless communication technology aimed at eliminating connection cables between mobile terminal devices like mobile phones and tablets, as well as between them and some peripheral devices (like headsets, mice, etc.), forming a wireless personal area network within a few meters.
Sample Questions

Alright, that’s it for this content.
Thank you for reading, and feel free to like, follow, and share.
See you next time!