Key Knowledge Points in Chapter One:
Understand the characteristics, classifications, development, and applications of embedded systems, and be familiar with the logical composition of embedded systems.
Understand the main types of embedded processing chips, be familiar with the SoC development process, and comprehend the significance of IP cores.
Familiarize yourself with the encoding of Chinese and Western characters, the types and processing of digital text, and master the parameters, file formats, and main applications of digital images.
Understand the classification and composition of computer networks, be familiar with the main contents of the IP protocol, and master the composition of the internet and common access technologies.
1. What is an Embedded System
An embedded system is a shortened term for an embedded computer system. As the name suggests, it is a dedicated computer system designed and developed for specific applications, embedded within devices (or systems).
Distinction: Microcontroller, Embedded System, Microcontroller, Microprocessor, SoC, SoP, CPU, Central Register, IP Core
2. Common Characteristics of Embedded Systems
-
1. Specialized Embedded systems are closely integrated with specific applications, exhibiting strong specialization. -
2. Concealment Embedded systems are usually part of non-computer devices (systems), hidden within them and not known to the public; for example, ATMs and digital cameras. -
3. Resource Constraints Software and hardware resources are strictly limited. -
4. High Reliability For instance, embedded systems in automobiles, CNC machine tools, and transportation vehicles, where any malfunction could be fatal! -
5. Real-time Performance. -
6. Software Fixation.
Example Question

3. Applications of Embedded Systems
-
1. Consumer Application Products: -
1. Refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, microwaves, rice cookers, water heaters, etc., white goods. -
2. Televisions, set-top boxes, home theaters, digital cameras, camcorders, DVD players, MP3 players, PDAs, electronic dictionaries, gaming consoles, electronic keyboards, smart toys, etc. digital products. -
2. Industrial Application Products: -
1. CNC machine tools, industrial robots, mechatronic equipment, production line control, etc. industrial equipment. -
2. Automobiles, airplanes, railway locomotives, ships, elevators, etc.; X-ray machines, ultrasound diagnostic devices (B-ultrasound), computed tomography systems (CT), pacemakers, monitors, magnetic resonance imaging, electrocardiograms, blood pressure monitors, etc. medical electronic devices. -
3. Business Application Products: -
1. Telephones, fax machines, printers, scanners, copiers, etc. office equipment. -
2. Electronic scales, barcode readers, commercial retail terminals (POS), bank note counting machines, IC card readers, ATMs, vending machines, information kiosks, etc. financial electronic devices. -
3. Mobile phones, GPS navigators, modems, routers, hubs, switches, bridges, etc. communication devices. -
4. Military Application Products: -
1. Guidance and detonation of artillery, missiles, and smart bombs, etc. weapon control devices. -
2. Tanks, vessels, fighter jets, drones, etc. military electronic equipment. -
3. Radar, electronic countermeasures, navigation systems, etc. military communication equipment.
Sample Exam Questions
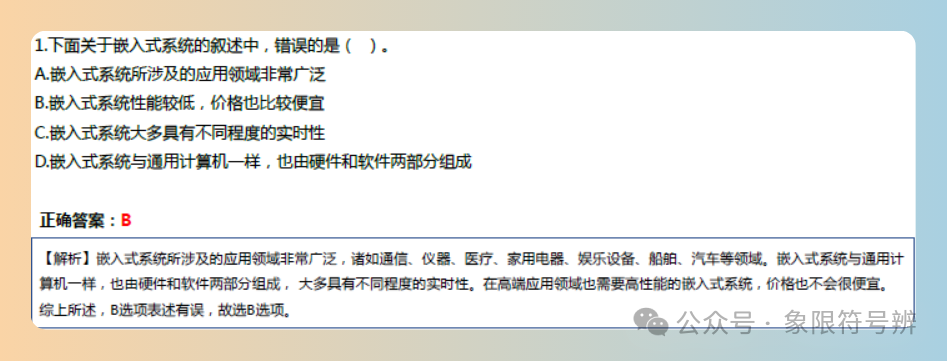


Alright, that’s all for this content.
Thank you for reading, and welcome to like, follow, and share.
See you next time!