Introduction
The camera, as a standard feature of smartphones, has developed rapidly. Many manufacturers have launched phones that focus on photography and videography, achieving impressive sales. So, what secrets lie behind the camera, the key component affecting photo quality? This article will introduce some basic knowledge and structure of cameras.
1. Classification of Camera Modules1. By Pixel Count (Based on Chip Pixels)
1 0.3MP (VGA) module (640×480)
2 1.3MP (SXGA) module (1280×1024)
3 2.0MP (UXGA) module (1600×1200)
4 3.0MP (QXGA) module (2048×1536)
5 5.0MP (QSXGA) module (2592×1944)
6 8.0MP …… module (3264×2448)
7 12.MP …… module (4040×3032)2. By Focusing Method (Lens Function)
1 FF module (Fixed Focus)
2 AF module (Auto Focus)
3 ZOOM module (Optical Auto Zoom)
3. By Connection Method
1 BTB
2 ZiF Gold Finger
3 Socket
4 Reflow (SMT)
2. Working Principle of Camera Modules
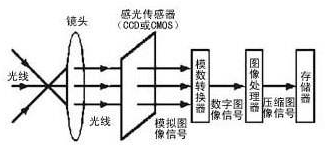
Light from the scene is projected onto the surface of the image sensor through the lens (LENS), then converted into an electrical signal. After being converted from analog (A/D) to digital image signals, it is processed by the digital signal processing chip (DSP), allowing the image to be displayed on the screen.
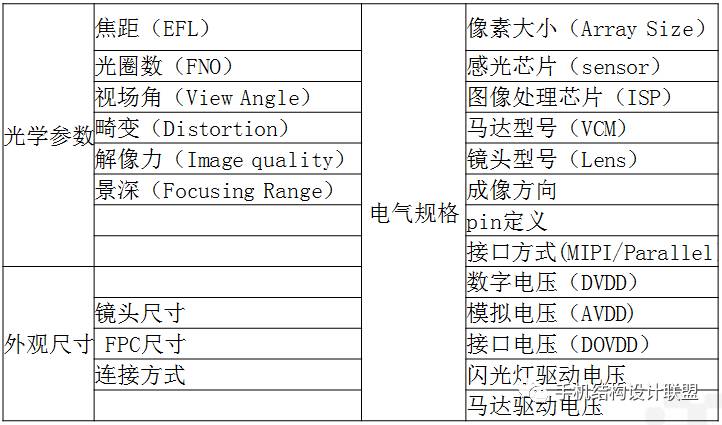
3. Technical Specifications of Camera Modules
Technical specifications are divided into three categories: physical parameters (i.e., dimensions), optical parameters, and electrical specifications.
Physical parameters: lens size, FPC size, connection method, etc.
Optical parameters: focal length, aperture number, field of view, distortion, resolution, depth of field, etc.
Electrical specifications: pixel count, imaging direction, PIN angle definition, interface method, chip type, etc.;
4. Module Structure and Components
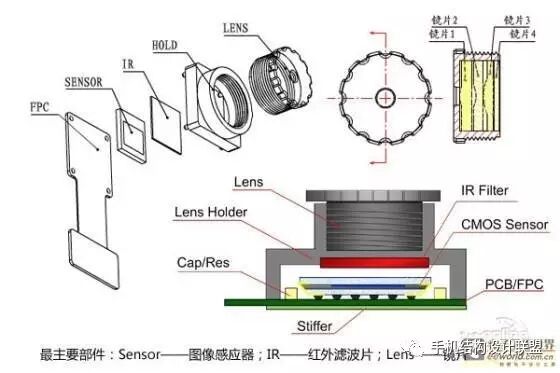
The components of the module include the following categories:
1. Optical Lens (LENS)
2. Image Sensor (SENSOR)
3. AF Drive Component
4. Lens Holder (HOLDER)
5. Infrared Filter (IR FILTER)
6. PCB Board (FPC)
7. Connector (CONNECTOR)
8. Peripheral Electronic Components
Below are descriptions of several key components:
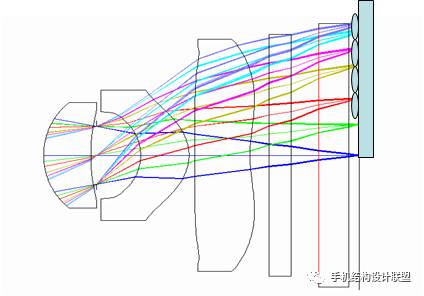
1. Optical Lens (LENS)
The quality of the lens is one of the key factors affecting image quality. It consists of a lens structure made up of several lenses, typically including: 2P, 1G1P, 1G2P, 1G3P, 2G2P, 2G3P, 4P, 5P, etc. P refers to plastic lenses (plastic), mostly aspherical, while G refers to glass lenses (glass), mostly spherical;
Lenses can be classified by focal length into fixed focal length lenses and zoom lenses, etc.
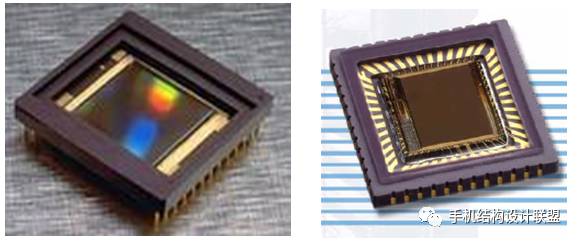
2. Image Sensor (SENSOR)
The image sensor (Sensor) is a type of semiconductor chip that contains hundreds of thousands to millions of photodiodes on its surface. When photodiodes are exposed to light, they generate charge, which is converted into digital signals by an analog-to-digital converter chip.
There are mainly two types of sensors: one is CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) elements; the other is CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) devices.
3. AF Drive Component (Motor)
VCM voice coil motor pushes the lens to move and change the focal length, achieving a clear image.
5. Considerations for Camera Selection
1. During the product definition phase, it is necessary to determine the pixel and size requirements for the camera, as well as whether a flash is needed. Once decided, the possibility of subsequent changes is relatively low.
2. Determine if the sensor model matches based on the smartphone platform (referring to the CPU that connects to the camera module), including whether the interface method is CPU interface, RGB interface, or MIPI interface. High pixel modules usually use RGB interfaces, and MIPI interfaces are becoming popular, but currently, there are not many application processors that support MIPI interfaces. Qualcomm’s MSM7 and 8 series and TI’s OMAP3 series support it.
3. Confirm the imaging direction based on the structural arrangement. The software can adjust the imaging direction by 180 degrees, but adjusting by 90 degrees is more difficult.
4. The supply risk and mass production status of key components such as lenses, motors, and sensors need to be taken into account.


Welcome to join the Design Alliance Technical Exchange Group, scan the QR code below (or add the administrator WeChat ID: mobi_designer)
