
On December 6, the second day of the Qualcomm Snapdragon Technology Summit, Qualcomm provided a detailed introduction to the Snapdragon 855 mobile platform, which was officially announced the previous day. The new Snapdragon 855 platform not only adopts the latest 7nm process, a completely new CPU architecture design, and a new generation of GPU cores, but also integrates a 5G modem, making it the first commercially available 5G platform. Additionally, in terms of AI, although the Snapdragon 855 still does not feature a dedicated NPU core, it has upgraded to the fourth generation of the multi-core AI Engine.

New 1+3+4 Tri-cluster 8-core CPU Architecture: 45% Performance Improvement
The 7nm process is currently the most advanced semiconductor manufacturing process in mass production. Previously, both the Kirin 980 and Apple A12 utilized TSMC’s 7nm process. The Qualcomm Snapdragon 855 is now the third mobile processor on the market to use TSMC’s 7nm process.
According to data previously released by TSMC, its latest 7nm process can achieve a 20% performance improvement or a 40% reduction in power consumption compared to the previous 10nm process, with a chip density 1.6 times that of 10nm.
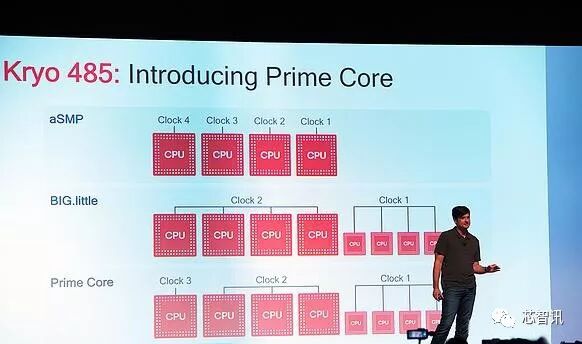
In terms of CPU architecture, the Snapdragon 855 has changed from the previous 4 big cores + 4 small cores big.LITTLE architecture to what Qualcomm calls a Prime Core 1+3+4 tri-cluster 8-core DynamIQ architecture: all based on Qualcomm’s custom Kyro 485 cores, consisting of one high-performance core with a frequency of 2.84GHz, three mid-performance cores with a frequency of 2.42GHz, and four efficiency cores with a frequency of 1.78GHz.
The high-performance core has a 512KB L2 cache (which is double that of the previous generation Snapdragon 845’s Kyro 385 high-performance core), primarily responsible for high-performance computations; the three mid-performance cores are paired with a 256KB L2 cache, while the four efficiency cores are equipped with a 128KB cache, mainly used for handling daily applications.
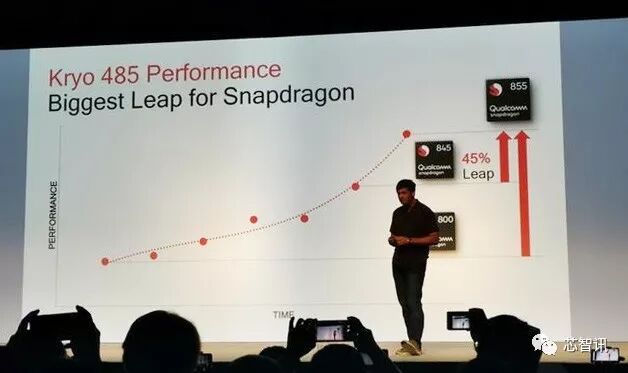
In terms of specific CPU performance, Qualcomm stated that the Snapdragon 855, based on the new Kyro 485 core, has a 45% higher CPU performance compared to the Snapdragon 845, which is based on the Kyro 385 core. Qualcomm also emphasized that the Snapdragon 855 can maintain high performance for extended periods, while competitors may reduce frequency in a short time.
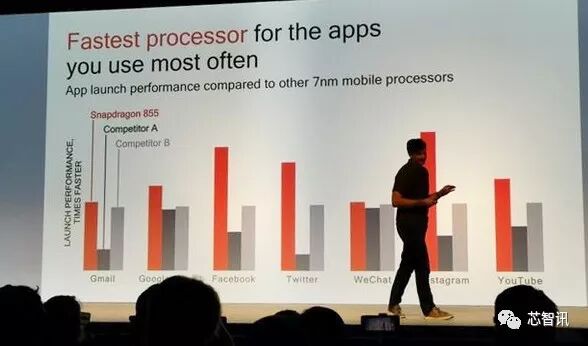
Furthermore, Qualcomm released a comparison of application launch performance against two other competitors’ 7nm chips (Apple A12 and Kirin 980). According to the data released by Qualcomm, the Snapdragon 855 outperforms both competitors in all application performance metrics.
Qualcomm stated that the Snapdragon 855 is the largest CPU upgrade in the company’s history.
GPU Performance Improved by 20%: Significant Enhancements in Gaming and Video Performance
In terms of GPU, the Snapdragon 855 is equipped with the new Adreno 640 GPU, which offers a 20% improvement in graphics performance over the previous generation Adreno 630.

In gaming, the Snapdragon 855 is the first mobile platform to support the new Qualcomm Snapdragon Elite Gaming experience. This experience includes true HDR (over 1 billion colors) cinematic-grade color grading, cinematic-grade tone mapping, demanding physically-based rendering (PBR) technology, and support for Vulkan 1.1 API.
The Vulkan 1.1 API is a low-level graphics API that allows game developers to achieve higher performance from a given mobile device compared to others. Qualcomm stated that Vulkan 1.1 API can save 20% more energy compared to OpenGL ES, while the Adreno 640 also supports 10-bit HDR gaming and PBR technology, which can also bring a 20% performance improvement if developers utilize this technology.
Qualcomm stated that by employing a custom algorithm designed to reduce frame drops by over 90%, even the most demanding games can run smoothly on the Snapdragon 855. Additionally, the Snapdragon 855 can enhance multiplayer gaming experiences by reducing latency.
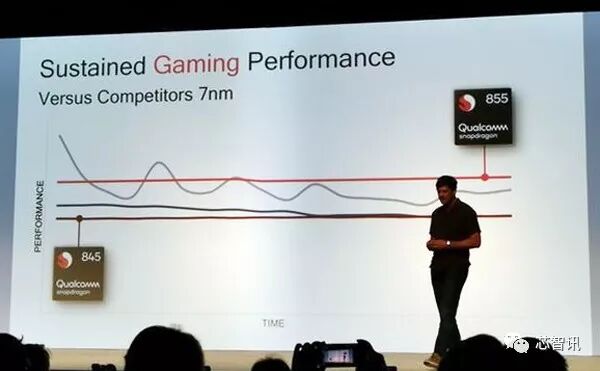
Qualcomm also compared the gaming performance of the Snapdragon 855 with two other competitors’ 7nm mobile chips. From the graphics provided by Qualcomm, it can be seen that during gaming, the Snapdragon 855 can maintain a relatively high performance, while the other two competitors’ 7nm mobile chips, although one can provide high performance initially, begin to decline over time and fall below the Snapdragon 855. The other competitor’s 7nm chip, while initially outperforming the Snapdragon 845, quickly drops to a level comparable to the Snapdragon 845.
In terms of video performance, Qualcomm stated that the Snapdragon 855 will support HDR10+ and Dolby Vision standards, providing brighter and more vivid display effects. Qualcomm claims that the Snapdragon 855 has sufficient performance to handle 120 frames per second HDR video, even 8K resolution 360-degree VR panoramic video.
Additionally, the Snapdragon 855 supports hardware-accelerated H.265 and VP9 video. Qualcomm stated that compared to playing such videos without hardware acceleration, it can save up to 7 times the power, extending battery life.
First Computer Vision ISP: Spectra 380
Currently, major smartphone manufacturers are placing great emphasis on camera functionality, and besides the camera and image sensor, the ISP chip within the mobile SoC is also a key factor affecting photo performance. The Snapdragon 855 has also upgraded to the new generation Spectra 380 ISP chip, providing computer vision (CV) capabilities while reducing power consumption by 4 times.
This CV-ISP includes hardware-based depth sensing, supporting real-time video capture, object classification, and object segmentation at 4K HDR@60fps. This means users can perform real-time blur previews during shooting, allowing for real-time cutting and blurring of backgrounds behind subjects. Qualcomm also demonstrated a special green screen style effect that uses similar technology to completely replace the background behind the live shot.
Qualcomm stated that the Spectra 380 is also the industry’s first ISP to support HDR10+ video capture and the first to support a chip-level triple-camera solution. Additionally, it supports the new HEIF photo format, which can save 50% of storage space. The upcoming Google Android 9 Pie will also add system-level support for HEIF. HEIF also allows smartphones with multiple lenses, such as those with three rear cameras, to store the three images captured by the three cameras as a single photo file.

According to Qualcomm, the Snapdragon 855 supports computer vision-driven portrait mode, while AR/VR functionalities and other computational tasks are directly integrated into the ISP, providing significant speed improvements and power reductions for computationally intensive photography tasks. Qualcomm claims that the new image signal processor can improve battery life by 2-4 times, as it does not require frequent activation of the CPU and GPU.
No NPU, Yet AI Performance Remains Strong
Currently, deploying AI computing on the terminal side has become a trend, prompting many mobile chip manufacturers to integrate dedicated NPU cores for AI computing into their mobile SoCs, such as Apple’s A11/A12 and Huawei’s Kirin 970/980. When the Snapdragon 845 was released last year, some criticized Qualcomm for not following the trend by not including an NPU core in the Snapdragon 845, resulting in a perceived lag in AI capabilities.
However, Qualcomm’s Senior Vice President and General Manager of Mobile Business, Alex Katouzian, stated that although Qualcomm does not have a dedicated neural network engine unit, it has adopted a more flexible machine learning architecture, optimizing cores within a general platform distributed across CPU, GPU, DSP, etc., allowing for flexible invocation of various processing units for different mobile terminals. Qualcomm has been researching AI since the Snapdragon 820, and by the time of the Snapdragon 845, it was already in its third generation, with AI computing performance three times that of the previous generation.
The latest Snapdragon 855 still does not include a dedicated NPU core as some had hoped, but continues to enhance AI support through flexible invocation of existing CPU/GPU/DSP resources, with Qualcomm claiming that the Snapdragon 855 has upgraded to the fourth generation multi-core AI Engine.

Despite the absence of an integrated NPU, Qualcomm claims that the AI computing performance of the Snapdragon 855 is still three times that of the previous generation Snapdragon 845, and even compared to Huawei’s Kirin 980, its AI performance has reached twice that of the latter, with computing power exceeding 70 trillion operations (7+ TOPS).

Specifically, Qualcomm’s fourth-generation AI engine still relies on the new CPU/GPU/DSP. The Adreno 640 GPU has 50% more ALUs (Arithmetic Logic Units) for AI, supporting FP32 and FP16 operations; the new Hexagon 690 DSP has added a new Tensor Accelerator, and the vector extension core (Hexagon Vector eXtensions, HVX) has increased from 2 to 4, which is double that of the Snapdragon 845, and it has also added four-thread scalar cores that support INT16 and INT8 calculations, achieving proprietary, programmable AI acceleration; the Kryo 485 CPU also supports the new dot product operation, supporting FP32 and INT8 calculations.

In terms of specific AI applications, Qualcomm has worked with numerous partners to enable the Snapdragon 855 to support chip-level call noise reduction, 3D facial recognition, portrait mode photography, photo quality optimization, voice assistant activation, and more, providing more AI use cases compared to competitors.
According to Qualcomm, it has been collaborating with Google to optimize the open-source machine learning library TensorFlow for mobile devices. Qualcomm stated that Google’s AI application Google Lens, based on image recognition and OCR technology, will receive significant enhancements from the Snapdragon 855. Google has indicated that it has transferred some key Lens computations directly to the Snapdragon 855, so using the mobile chip will not experience delays or other adverse factors due to reliance on cloud communication.
For example, when using Google Lens for text recognition, users can utilize smartphones equipped with the Snapdragon 855 to more effectively recognize and even translate text in the real world. In addition to text recognition, improvements in TensorFlow on-device will allow the Snapdragon 855 to execute various vision-related tasks faster than before, including AR techniques, such as placing virtual furniture in a room to experiment with different home decor.
Another unique AI application not related to vision is the ability to isolate someone’s voice during a call, allowing you to hear others better in noisy environments. Additionally, Qualcomm demonstrated a feature using a so-called real-time segmentation algorithm to add background blur effects to any photo, including those downloaded directly from the internet, which provides better results than the portrait mode (background blur) effects obtained from iPhone and Pixel devices, as it does not require users to use a special camera mode.

This is primarily due to Qualcomm’s collaboration with an AI company called Nalbi, which is working with Qualcomm to provide impressive new computer vision capabilities, such as real-time hair color changes, allowing users to see a “realistic” effect before deciding to make a real change.
In addition to Nalbi, Qualcomm has also collaborated with numerous AI companies in China, such as SenseTime, Megvii, and iFlytek, to promote AI applications for the Snapdragon 855.

Powerful Network Connectivity: Comprehensive Support for 4G/5G
With the imminent arrival of the 5G era, various chip manufacturers are actively promoting 5G to seize the market opportunity. The Snapdragon 855 released by Qualcomm integrates Qualcomm’s first 5G modem chip, the Snapdragon X50, making it the first commercially available 5G platform.

The Snapdragon X50 modem integrated into the Snapdragon 855 can simultaneously support Sub-6GHz and mmWave frequency bands, providing an average performance improvement of 20 times compared to existing 4G solutions, meeting the high-speed communication needs for ultra-high-definition multiplayer VR gaming, real-time ultra-high-definition video, and autonomous driving.
However, it is important to note that the Snapdragon X50 modem is not backward compatible with 3G/4G networks, so support for 5G requires the Snapdragon 855 to be paired with the external Snapdragon X50 modem, while the Snapdragon 855 supports 3G/4G networks through the integrated Snapdragon X24 modem. The Snapdragon X24 can achieve downlink Cat.20 with a maximum download speed of 2Gbps through 7x20MHz carrier aggregation and 4×4 MIMO; it can achieve uplink Cat.13 with a maximum upload speed of 316Mbps through 3x20MHz carrier aggregation.
Qualcomm stated that it has already engaged in in-depth cooperation on 5G with operators including China Unicom, China Mobile, China Telecom, AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon. Additionally, Qualcomm has collaborated with domestic brands such as Xiaomi, OPPO, OnePlus, and Vivo on 5G.
Overall, Qualcomm has achieved a leading advantage in the commercial progress of 5G, with the already released Snapdragon 855 mobile platform, Snapdragon X50 5G modem series, and the QTM052 mmWave antenna module, which integrates RF transceivers, RF front-end, and antenna components, all helping OEM manufacturers address the exponentially increasing design complexity of 5G terminals that support both sub-6GHz and mmWave frequency bands.
Qualcomm stated that it has already engaged in in-depth cooperation on 5G with operators including China Unicom, China Mobile, China Telecom, AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon. Additionally, Qualcomm has collaborated with domestic brands such as Xiaomi, OPPO, OnePlus, and Vivo on 5G.
Qualcomm’s Senior Vice President and General Manager of Mobile Business, Alex Katouzian, stated: “As operators are set to deploy 5G networks in early 2019, consumers will be the first to experience extraordinary 5G user experiences on devices powered by Snapdragon 855. We are proud to share our technological innovations with the industry and to be the first to bring 5G mobile technology to the world.”

At this Qualcomm Snapdragon Summit, Qualcomm also showcased the first batch of real 5G networks and terminals. Additionally, at the China Mobile Partner Conference held on December 6 in Guangzhou, China Mobile also released the 5G trial terminal “Pioneer No. 1” based on the Snapdragon 855.
OPPO also showcased the OPPO Find X 5G prototype at the China Mobile Partner Conference.
Other
The Snapdragon 855 also provides powerful next-generation Wi-Fi performance through a Wi-Fi 6-ready mobile platform, with a target wake time energy efficiency improvement of up to 67%, while supporting the latest WPA3 security. The Snapdragon 855 also supports Wi-Fi connections in the mmWave frequency band. This industry-first platform based on 802.11ay boosts Wi-Fi speeds to unprecedented 10Gbps and supports low latency comparable to wired networks.

In terms of audio, the Snapdragon 855 has also optimized latency between left and right earbuds while reducing power consumption to extend usage time after each charge, meeting the growing demand for truly wireless products in the headphone market.

Additionally, the Snapdragon 855 is the first mobile platform to support Qualcomm’s 3D Sonic Sensor. Currently, under-display fingerprint recognition has become a standard feature in many flagship smartphones, and there are mainly two methods to achieve this: optical under-display fingerprint and ultrasonic. Qualcomm has always been a proponent of ultrasonic fingerprint recognition. According to Qualcomm, the new 3D Sonic Sensor is different from the screen fingerprint technologies currently in use; the 3D Sonic Sensor can recognize fingerprints and even pores, and oil and dirt will not affect its use. Furthermore, this solution supports thin and stylish product designs while providing higher security and accuracy.
Conclusion:
From the data and information released by Qualcomm, it is clear that the Snapdragon 855 is indeed very powerful, with significant improvements in CPU, GPU, photography, gaming, and XR performance compared to previous generations. Especially in terms of 5G commercialization, Qualcomm Snapdragon 855 has successfully taken the lead and captured the market opportunity. Although the Snapdragon 855 still does not include a dedicated NPU core, its architecture, which flexibly invokes existing CPU/GPU/DSP for AI computations, has achieved a 2x improvement in AI capabilities compared to competitors’ 7nm chips, demonstrating Qualcomm’s deep accumulation in AI. The so-called “fourth-generation AI engine” is not just a gimmick. This is also due to Qualcomm’s years of accumulation in CPU/GPU/DSP research and development (the CPU is custom, while the GPU and DSP are self-developed). However, the true experience of the Snapdragon 855 will need to be tested once the commercial models are mass-produced and launched. It is understood that the Snapdragon 855 mobile platform has already been sampled to customers, and commercial terminals equipped with this platform are expected to start shipping in the first half of 2019. We will see how it performs then.
Author: Chip Intelligence – Wandering Swordsman
Related Articles
Chip performance improved by 5 times, energy consumption reduced by 30 times! Intel aims to use spintronics technology to “revive” Moore’s Law!
Qualcomm to restart acquisition of NXP? Official response released
Gree Electric’s 3 billion support! A-share semiconductor/ODM dual leaders are about to be born, Wingtech Technology aims for a dual 100 billion target
Layoffs of 14,700 and closure of 7 factories! General Motors accelerates transformation to new energy behind the scenes
Analysis of the top ten IC design companies in China in 2018: Who are they?
Stop glorifying Huawei! Signing 640 billion in Germany and 270 billion in the Middle East 5G orders is pure nonsense!
Breaking! Zeng Xuezhong promoted to Vice Chairman and CEO of Spreadtrum, Chu Qing appointed Co-CEO!
In the battle of advanced processes, who can carry Moore’s Law to the end: Intel/TMSC/Samsung?
The US releases the latest 301 investigation report: accusing Chinese VC of taking on the role of technology transfer!
Face recognition algorithm is completely free! ArcSoft aims to be an enabler in the AI field!
The new round of “export controls” from the US has not yet landed, and you are already shocked and scared?
The “help request from an entrepreneur” behind: the grievances between Lexin and Dongguan Yibu!
For industry communication and cooperation, please add WeChat: xintiyan001. For submissions, please send to: [email protected]. Official communication of Chip Intelligence: 221807116