Recently, many friends have inquired about CIS-related information. I plan to use this as the theme for this week, concentrating on updating 3 to 5 articles. Today is the first article, starting with an introduction to CIS to help everyone understand its fundamental concepts. The CMOS Image Sensor (CIS) is a semiconductor device based on Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) technology, which functions to convert light signals into digital images. External light sources converge the image onto the photosensitive area of the image sensor through an optical lens. This sensor integrates numerous photon detectors on the surface of the semiconductor chip to convert the energy of photons into electrical signals, which are then amplified, converted by an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter), and processed digitally to ultimately generate a digital image.
The CMOS Image Sensor (CIS) is a semiconductor device based on Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) technology, which functions to convert light signals into digital images. External light sources converge the image onto the photosensitive area of the image sensor through an optical lens. This sensor integrates numerous photon detectors on the surface of the semiconductor chip to convert the energy of photons into electrical signals, which are then amplified, converted by an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter), and processed digitally to ultimately generate a digital image. Working PrinciplePhotoelectric Conversion: Photons strike the photodiode of the CMOS image sensor, exciting electrons and generating charge.Signal Amplification and Conversion: The charge is converted into a voltage signal, amplified by a built-in amplifier, and then converted into a digital signal by an ADC.Digital Signal Processing: The digital signal is processed by an Image Signal Processor (ISP) to remove noise, perform color interpolation, and adjust white balance, ultimately generating high-quality images.To better understand the structure of CIS, we will illustrate using the circuit structure of 4T-APS.4T-APS is a common pixel structure in CMOS image sensors, where each pixel consists of four transistors to enhance image quality and performance. The full name is 4-Transistor Active Pixel Sensor.The following diagram shows the circuit structure of a 4T-APS, which includes a photodiode (PPD: Pinned Photodiode), four transistors (TX, SF, RST, SEL), and a floating diffusion node (FD). In the circuit, PPD is used for converting light signals, TX is for transferring charge, SF is for selecting pixels, RST is for resetting, and SEL is for column selection.
Working PrinciplePhotoelectric Conversion: Photons strike the photodiode of the CMOS image sensor, exciting electrons and generating charge.Signal Amplification and Conversion: The charge is converted into a voltage signal, amplified by a built-in amplifier, and then converted into a digital signal by an ADC.Digital Signal Processing: The digital signal is processed by an Image Signal Processor (ISP) to remove noise, perform color interpolation, and adjust white balance, ultimately generating high-quality images.To better understand the structure of CIS, we will illustrate using the circuit structure of 4T-APS.4T-APS is a common pixel structure in CMOS image sensors, where each pixel consists of four transistors to enhance image quality and performance. The full name is 4-Transistor Active Pixel Sensor.The following diagram shows the circuit structure of a 4T-APS, which includes a photodiode (PPD: Pinned Photodiode), four transistors (TX, SF, RST, SEL), and a floating diffusion node (FD). In the circuit, PPD is used for converting light signals, TX is for transferring charge, SF is for selecting pixels, RST is for resetting, and SEL is for column selection.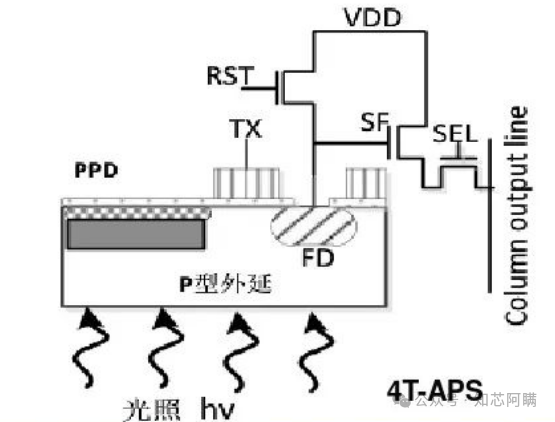 In the above image, you can see many components.These components work together to achieve the photoelectric conversion and signal readout functions of the CMOS image sensor.The following are definitions of related terms:TX stands for Transfer Gate, which in a CMOS image sensor controls the transfer of signal charge from the photodiode to the floating diffusion node.SF:Source Follower is a transistor configuration used to amplify signals from the photodiode in a CMOS image sensor.RST is the reset transistor used to reset the floating diffusion node in the pixels of the CMOS image sensor, preparing for the next charge transfer.SELSelection transistor is used to select specific pixel rows or columns during the readout process of the CMOS image sensor.FD: Floating Diffusion is the area in a CMOS image sensor used to temporarily store the signal charge transferred from the photodiode.TG: Transfer Gate is used to control the transfer of charge in a CMOS image sensor, which is the same component referred to as TX.Structural FeaturesPixel Array: A two-dimensional array composed of numerous pixel units, each responsible for receiving, converting, and storing light signals.
In the above image, you can see many components.These components work together to achieve the photoelectric conversion and signal readout functions of the CMOS image sensor.The following are definitions of related terms:TX stands for Transfer Gate, which in a CMOS image sensor controls the transfer of signal charge from the photodiode to the floating diffusion node.SF:Source Follower is a transistor configuration used to amplify signals from the photodiode in a CMOS image sensor.RST is the reset transistor used to reset the floating diffusion node in the pixels of the CMOS image sensor, preparing for the next charge transfer.SELSelection transistor is used to select specific pixel rows or columns during the readout process of the CMOS image sensor.FD: Floating Diffusion is the area in a CMOS image sensor used to temporarily store the signal charge transferred from the photodiode.TG: Transfer Gate is used to control the transfer of charge in a CMOS image sensor, which is the same component referred to as TX.Structural FeaturesPixel Array: A two-dimensional array composed of numerous pixel units, each responsible for receiving, converting, and storing light signals.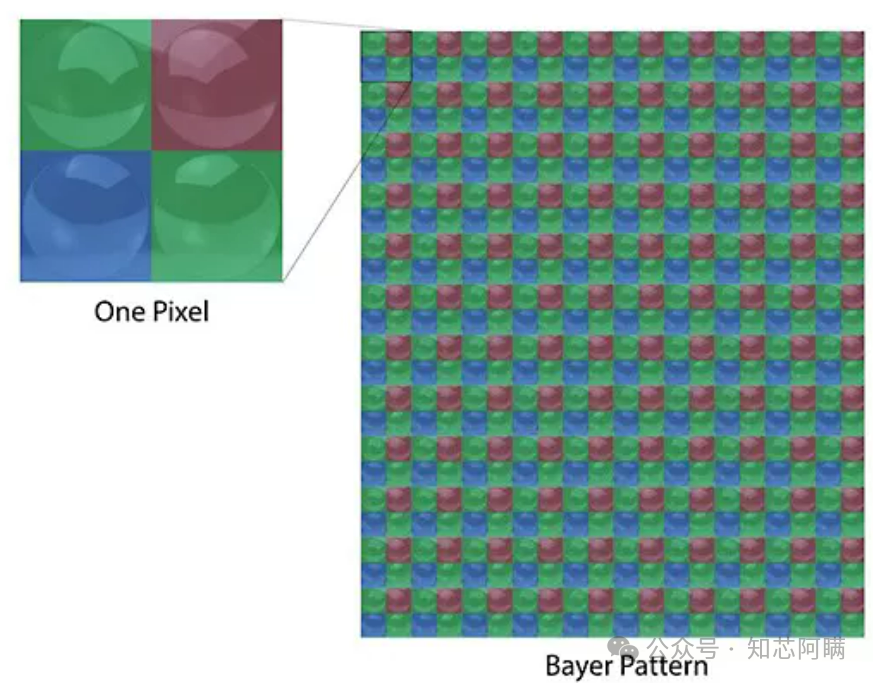 Microlenses and Color Filters: Microlenses are used to focus light, while color filters (such as Bayer filter arrays) are used to separate red, green, and blue light.Control Logic and ADC: Control logic manages the working timing of pixel units, while the ADC converts analog signals into digital signals.
Microlenses and Color Filters: Microlenses are used to focus light, while color filters (such as Bayer filter arrays) are used to separate red, green, and blue light.Control Logic and ADC: Control logic manages the working timing of pixel units, while the ADC converts analog signals into digital signals.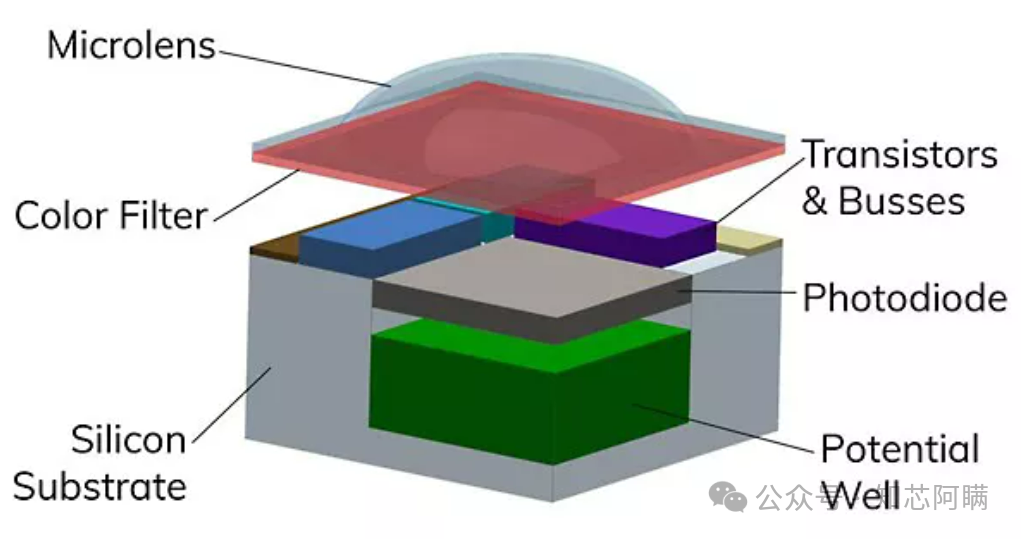 Application Fields
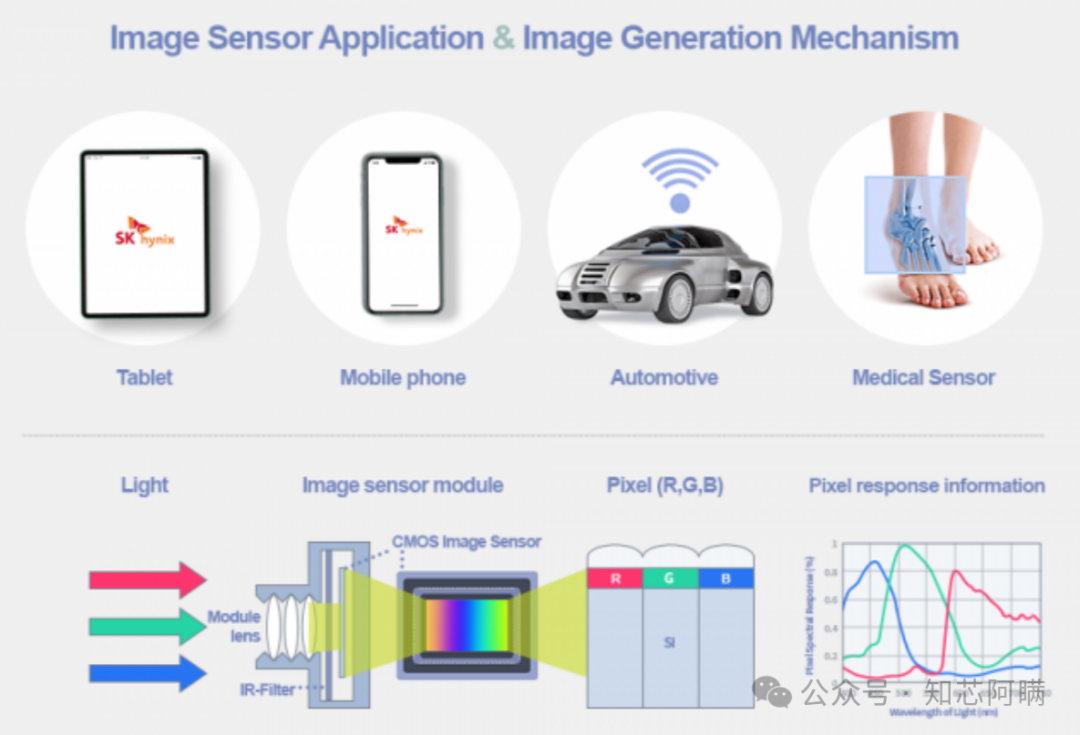
Application Fields
Smartphones: CMOS image sensors are the core components of smartphone cameras, supporting high resolution and multi-camera configurations to meet user demands for photography and video recording.
Automotive Electronics: Used in advanced driver-assistance systems, such as lane departure warning and automatic emergency braking, the number of cameras installed in vehicles is also continuously increasing.
Security Monitoring: Performs excellently in complex environments with low light and high dynamic range, widely used in smart city and safe city projects.
Industrial Vision: Used on production lines for quality inspection and automation control, supporting high-precision and high-speed image acquisition.
Medical Imaging: Has important applications in X-ray imaging, fluorescence imaging, etc., providing high-resolution and low-noise images.
 CCD vs CIS
CCD vs CIS
CIS is often compared with CCD. What are the differences between the two?
CCD: Linear sensor, output directly related to the number of received photons.
CIS: Uses parallel readout technology with pixel-level integrated amplification functions.
In terms of manufacturing costs, CIS is significantly lower than CCD, promoting the popularity of digital cameras.
Performance comparison: CCD and CIS each have their advantages; CIS has advantages in parallel readout and integration, but CCD still holds an irreplaceable position in certain applications.
| Characteristic | CCD | CMOS |
| Signal from pixel | Electron packet | Voltage |
| Signal from chip | Analog Voltage | Bits (digital) |
| Readout noise | low | Lower at equivalent frame rate |
| Fill factor | High | Moderate or low |
| Photo-Response | Moderate to high | Moderate to high |
| Sensitivity | High | Higher |
| Dynamic Range | High | Moderate to high |
| Uniformity | High | Slightly Lower |
| Power consumption | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Shuttering | Fast, efficient | Fast, efficient |
| Speed | Moderate to High | Higher |
| Windowing | Limited | Multiple |
| Anti-blooming | High to none | High, always |
| Image Artefact | Smearing, charge transfer inefficiency | FPN, Motion (ERS), PLS |
| Biasing and Clocking | Multiple, higher voltage | Single, low-voltage |
| System Complexity | High | Low |
| Sensor Complexity | Low | High |
| Relative R&D cost | Lower | Lower or Higher depending on series |
Market Competition Landscape
Global Market: Sony, Samsung, and Omnivision are the top three companies in the global CMOS image sensor market, collectively holding over 70% market share. Additionally, companies like ON Semiconductor, Gpixel, and STMicroelectronics also perform well in specific fields.
Chinese Market: Local companies such as Omnivision, Gpixel, and STMicroelectronics hold significant shares in the domestic market and have made remarkable progress in automotive electronics and security monitoring.
This article references some images and texts from the internet for learning and communication purposes. If there are any copyright issues, please contact me promptly, and I will delete the relevant content immediately.
 ID: ZhiXin A Man
ID: ZhiXin A Man
Discussing fab diversity, savoring silicon-based life
A wealth of learning materials, continuously updated
Willing to collaborate with you all to pursue greatness

If this article is of any help to you, please consider giving a thumbs up, and I would be very grateful.