👆 View More Directory👆
👆 View More Directory👆
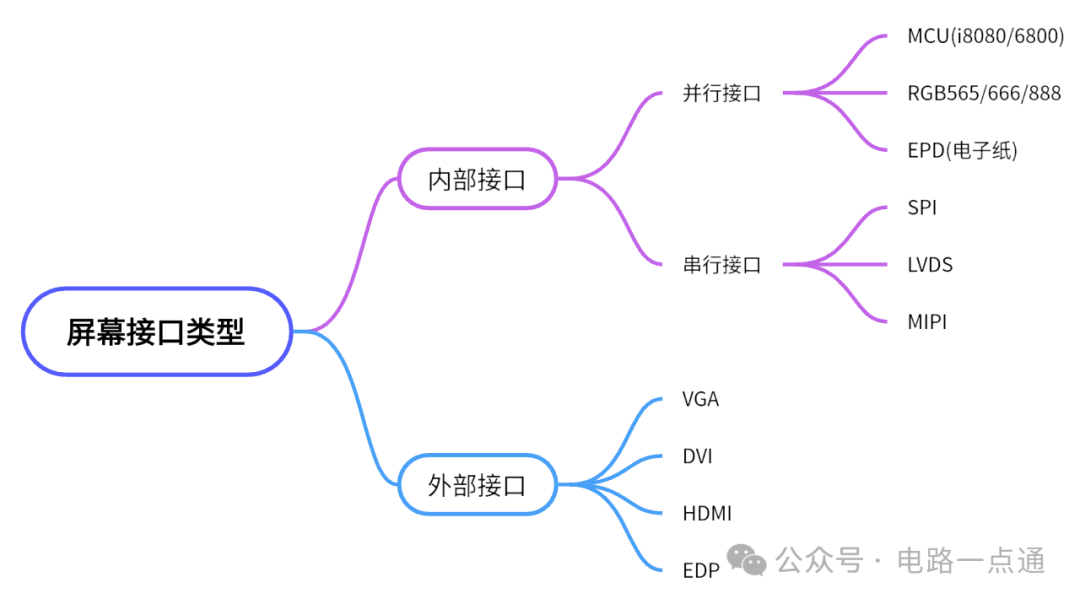
1. Internal Interfaces (Onboard Interfaces for Embedded Systems)
1. Parallel Interfaces
(1) MCU Interface
-
The standard term for the MCU interface (Microcontroller Interface) is the 8080 bus standard proposed by Intel, so it is commonly referred to as the I8080 interface or 8080 interface. Its name originates from its early applications primarily in the microcontroller (MCU) field, such as embedded systems and mid-range mobile phones.
-
Two Modes of MCU Interface The MCU interface includes two timing modes:
- 8080 Mode (Intel Standard): Control signals are
<span><span>CS</span></span>,<span><span>RS</span></span>,<span><span>RD</span></span>,<span><span>WR</span></span>, transmitting data through parallel data lines, and is the most widely used. - 6800 Mode (Motorola Standard): Control signals are
<span><span>CS</span></span>,<span><span>RS</span></span>,<span><span>E</span></span>(latch signal), with timing different from 8080, and is now rarely used. -
Other Aliases
The 8080 interface has various other names, such as:
- DBI (Data Bus Interface): Data bus interface;
- MPU Interface: Microprocessor interface;
- CPU Interface: Emphasizing direct connection to the processor.
-
Difference from RGB Interface
- MCU Interface: Relies on the screen’s built-in GRAM (Graphics RAM), requiring commands to write data, suitable for small screens (e.g., 2.8~4.3 inches) and low refresh rate scenarios (e.g., static images), commonly using
<span><span>CS</span></span>,<span><span>RS</span></span>,<span><span>RD</span></span>,<span><span>WR signals</span></span>. (e.g., screens from ZLG and Firefly development boards) - RGB Interface: Directly provides graphics memory from system memory (e.g., some SoC/MCU chips integrate DDR2/DDR3/PSRAM/nor FLASH). Transmits pixel data through synchronization signals (e.g.,
<span><span>HSYNC</span></span>,<span><span>VSYNC</span></span>), suitable for large screens and high refresh rate scenarios (e.g., video playback).
(2) RGB Interface (DPI Interface)
- Definition: Directly transmits pixel RGB data, without GRAM, with graphics memory provided by system memory.
- Characteristics:
- Control signals:
<span><span>HSYNC</span></span>(line sync),<span><span>VSYNC</span></span>(frame sync),<span><span>DOTCLK</span></span>(pixel clock). - Data width: 16/18/24 bits, supports high-speed refresh (suitable for video).
- Applications: Medium-sized screens (2~10 inches), such as smart meters, in-car central control, tablets.
| Comparison Item | RGB565 | RGB666 | RGB888 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bit Depth | 16 bits (5 bits red, 6 bits green, 5 bits blue) | 18 bits (6 bits each for red, green, blue) | 24 bits (8 bits each for red, green, blue) |
| Color Count | 65,536 colors | 262,144 colors | 16,777,216 colors |
| Color Accuracy and Performance | Fewer colors, complex color transitions and subtle color differences are prone to distortion | Higher color accuracy than RGB565, transitions are more natural, but still some color loss | Rich color performance, smooth transitions, can perfectly restore true colors |
| Data Storage and Transmission | 2 bytes per pixel, small data volume, occupies fewer resources | 2.25 bytes per pixel, moderate data volume | 3 bytes per pixel, large data volume, high storage and transmission requirements |
| Application Scenarios | Embedded devices, low-resolution displays | Scenarios with certain color requirements, need to balance storage and processing costs | Computer monitors, HD TVs, digital cameras, professional image and video processing software, etc. |
2. Serial Interfaces
(1) SPI Interface
- Characteristics: 3/4 wire serial transmission, low speed, supports only small screens (≤2 inches).
- Applications: Segment LCDs, small-sized OLEDs (e.g., wristband screens).
Three-wire SPI (SCK, SDIO, SS), four-wire (SCK, MISO, MOSI, SS).
(2) MIPI-DSI Interface
- Definition: A high-speed serial interface standard in the mobile industry, transmitting differential signals.
- Characteristics:
- Fewer pins (e.g., D0P/D0N differential pair), strong anti-interference, supports high resolution (720P~2K).
- Bidirectional communication, supports power-saving mode.
- Applications: Mobile phones, tablets, small-sized laptops.
1. Note the distinction:
| Upper Layer Protocol (Application Layer) | Physical Layer | |
| Display |
MIPI DSI (Display Serial Interface) |
MIPI D-PHY |
| Camera |
MIPI CSI (Camera Serial Interface) |
MIPI C-PHY |
2. What is a MIPI Lane, and what is the difference between 1 Lane MIPI and 4 Lane MIPI?
A lane can be understood as a data transmission channel. MIPI’s 1 lane, 2 lane, and 4 lane represent 1 data channel, 2 data channels, and 4 data channels respectively; the more channels, the stronger the data transmission capability, and each must also be paired with a differential clock.
| Number of Lanes | Bandwidth | Number of Pins | Cost | Power Consumption | Applicable Scenarios | Number of Differential Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Lane | Low | Few | Low | Low | Small, low-resolution screens | 2 pairs |
| 2 Lane | Medium | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Medium-sized, medium-resolution screens | 3 pairs |
| 4 Lane | High | Many | High | High | High-resolution, high-frame-rate screens | 5 pairs |
(3) LVDS Interface
- Definition: Low Voltage Differential Signal interface, encodes RGB data into differential signals for transmission.
- Characteristics:
- Long transmission distance (over 10 meters), strong anti-interference, suitable for large screens.
- Requires dedicated chips to convert TTL/RGB signals.
- Applications: In-car screens, industrial displays, large-sized tablets.
2. External Interfaces (Universal Standard Interfaces for Device Interconnection)
1. VGA (D-Sub)
- Definition: An analog signal interface that transmits RGB primary colors and line/frame sync signals.
- Characteristics: Strong compatibility but prone to interference, gradually being replaced by digital interfaces.
- Applications: Old computers, projectors.
2. DVI
- Definition: A digital interface, divided into DVI-D (pure digital) and DVI-I (compatible with analog).
- Characteristics: Supports HD (1080P), no signal conversion loss.
- Applications: Computer monitors, graphics cards.
3. HDMI
- Definition: High-Definition Multimedia Interface, transmits audio and video simultaneously.
- Characteristics:
- High bandwidth (HDMI 2.1 reaches 48Gbps), supports 4K/8K, HDR.
- Supports HDCP copyright protection.
- Applications: TVs, set-top boxes, game consoles.
4. EDP
- Definition: Embedded DisplayPort, high-speed serial interface.
- Characteristics: Fewer pins, high bandwidth, supports 2K/4K large screens.
- Applications: Laptops, monitors, all-in-ones.
Supplement:EDP interface is different from EPD (commonly refers to Electronic Paper Display, Electronic Paper Display) which are two completely different concepts.
3. Interface Comparison and Selection Recommendations
| Interface Type | Transmission Method | Graphics Memory Location | Typical Size | Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCU/8080 | Parallel | Built-in GRAM | 2~4.3 inches | Microcontrollers, low-end devices |
| RGB | Parallel | System Memory | 2~10 inches | Smart hardware, in-car central control |
| MIPI-DSI | Serial Differential | System Memory | 3~10 inches | Mobile phones, tablets |
| LVDS | Serial Differential | System Memory | Over 7 inches | In-car, industrial displays |
| HDMI/DVI | External Standard | Host Memory | Over 10 inches | TVs, external computer monitors |
Conclusion
- Small Screens (≤4.3 inches): Prefer MCU/8080 Interface (e.g., screens driven by STM32).
- Medium Screens (2~10 inches): RGB Interface is cost-effective, for high speed choose MIPI-DSI. (e.g., ITE, Sigmastar, etc.)
- Large Screens (>7 inches): LVDS or EDP, for long-distance transmission prefer LVDS.
- External Connections: HDMI is mainstream, use VGA for older devices.
Disclaimer
Note: This article only represents the author’s views, readers should verify its authenticity and legality. If you find any errors in the content or it infringes your rights, please contact (WeChat haizililiang), and this public account will promptly modify or delete it.
Recommended by Yidian Tong
- Electrical CircuitResource Collection
- 👉 Automotive Resources Collection
- Electrical Engineering, Industrial Automation (PLC), Microcontroller, etc. Resources
Join the family⭕ to discuss and reply: Communication
Support with “three points” action! Share💬 Like👍 View❤️