Description
Deploying YOLOv8 on Wildfire RK3588, we use yolov8s.pt (downloaded from the YOLOv8 official website) as an example.
1. pt->onnx
Do not use the official YOLOv8 code; instead, use the Rockchip YOLOv8 code, available at
https://github.com/airockchip/ultralytics_yolov8
After downloading the code, execute the model conversion with the following code:
from ultralytics import YOLO
model = YOLO('yolov8s.pt')
model.export(format="rknn")
Output content:
YOLOv8s summary (fused): 168 layers, 11,156,544 parameters, 0 gradients, 28.6 GFLOPs
PyTorch: starting from 'yolov8s.pt' with input shape (1, 3, 640, 640) BCHW and output shape(s) ((1, 64, 80, 80), (1, 80, 80, 80), (1, 1, 80, 80), (1, 64, 40, 40), (1, 80, 40, 40), (1, 1, 40, 40), (1, 64, 20, 20), (1, 80, 20, 20), (1, 1, 20, 20)) (21.5 MB)
RKNN: starting export with torch 2.2.2...
RKNN: feed yolov8s.onnx to RKNN-Toolkit or RKNN-Toolkit2 to generate RKNN model.
Refer https://github.com/airockchip/rknn_model_zoo/tree/main/models/CV/object_detection/yolo
RKNN: export success ✅ 1.8s, saved as 'yolov8s.onnx' (42.6 MB)
Export complete (5.6s)
Results saved to C:\Work\ultralytics_yolov8-main\ultralytics_yolov8-main\tests
Predict: yolo predict task=detect model=yolov8s.onnx imgsz=640
Validate: yolo val task=detect model=yolov8s.onnx imgsz=640 data=coco.yaml
Visualize: https://netron.app
Process finished with exit code 0
Use Netron to view yolov8s.onnx, the result is shown in the figure below:

2. Setting up the ONNX to RKNN model environment
a. Create a Python 3.8 virtual environment using conda
b. Navigate to the rknn_toolkit2\packages folder
c. Install rknn_toolkit2 with the following code:
pip install rknn_toolkit2-1.5.0+1fa95b5c-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
3. ONNX to RKNN conversion, code as follows
import os
import cv2
from rknn.api import RKNN
import numpy as np
IMG_FOLDER = "dataset-1"
RESULT_PATH = './dataset-2'
CLASSES = ["person", "bicycle", "car","motorbike ","aeroplane ","bus ","train","truck ","boat","traffic light",
"fire hydrant","stop sign ","parking meter","bench","bird","cat","dog ","horse ","sheep","cow","elephant",
"bear","zebra ","giraffe","backpack","umbrella","handbag","tie","suitcase","frisbee","skis","snowboard","sports ball","kite",
"baseball bat","baseball glove","skateboard","surfboard","tennis racket","bottle","wine glass","cup","fork","knife ",
"spoon","bowl","banana","apple","sandwich","orange","broccoli","carrot","hot dog","pizza ","donut","cake","chair","sofa",
"pottedplant","bed","diningtable","toilet ","tvmonitor","laptop ","mouse ","remote ","keyboard ","cell phone","microwave ",
"oven ","toaster","sink","refrigerator ","book","clock","vase","scissors ","teddy bear ","hair drier", "toothbrush "]
OBJ_THRESH = 0.45
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
MODEL_SIZE = (640, 640)
color_palette = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(CLASSES), 3))
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def letter_box(im, new_shape, pad_color=(0, 0, 0), info_need=False):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
ratio = r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=pad_color) # add border
if info_need is True:
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
else:
return im
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
"""Filter boxes with object threshold."
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
candidate, class_num = box_class_probs.shape
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score * box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
scores = (class_max_score * box_confidences)[_class_pos]
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.
# Returns
keep: ndarray, index of effective boxes.
"""
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def softmax(x, axis=None):
x = x - x.max(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
y = np.exp(x)
return y / y.sum(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
def dfl(position):
# Distribution Focal Loss (DFL)
n, c, h, w = position.shape
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
y = position.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
y = softmax(y, 2)
acc_metrix = np.array(range(mc), dtype=float).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
y = (y * acc_metrix).sum(2)
return y
def box_process(position):
grid_h, grid_w = position.shape[2:4]
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, grid_w), np.arange(0, grid_h))
col = col.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
row = row.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=1)
stride = np.array([MODEL_SIZE[1] // grid_h, MODEL_SIZE[0] // grid_w]).reshape(1, 2, 1, 1)
position = dfl(position)
box_xy = grid + 0.5 - position[:, 0:2, :, :]
box_xy2 = grid + 0.5 + position[:, 2:4, :, :]
xyxy = np.concatenate((box_xy * stride, box_xy2 * stride), axis=1)
return xyxy
def post_process(input_data):
boxes, scores, classes_conf = [], [], []
defualt_branch = 3
pair_per_branch = len(input_data) // defualt_branch
# Python ignores score_sum output
for i in range(defualt_branch):
boxes.append(box_process(input_data[pair_per_branch * i]))
classes_conf.append(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1])
scores.append(np.ones_like(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1][:, :1, :, :], dtype=np.float32))
def sp_flatten(_in):
ch = _in.shape[1]
_in = _in.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
return _in.reshape(-1, ch)
boxes = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in boxes]
classes_conf = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in classes_conf]
scores = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in scores]
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
# filter according to threshold
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
# nms
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if len(keep) != 0:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw_detections(img, left, top, right, bottom, score, class_id):
"""
Draws bounding boxes and labels on the input image based on the detected objects.
Args:
img: The input image to draw detections on.
box: Detected bounding box.
score: Corresponding detection score.
class_id: Class ID for the detected object.
Returns:
None
"""
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
color = color_palette[class_id]
# Draw the bounding box on the image
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color, 2)
# Create the label text with class name and score
label = f"{CLASSES[class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
# Calculate the dimensions of the label text
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
# Calculate the position of the label text
label_x = left
label_y = top - 10 if top - 10 > label_height else top + 10
# Draw a filled rectangle as the background for the label text
cv2.rectangle(img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color,
cv2.FILLED)
# Draw the label text on the image
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
img_h, img_w = image.shape[:2]
# Calculate scaling factors for bounding box coordinates
x_factor = img_w / MODEL_SIZE[0]
y_factor = img_h / MODEL_SIZE[1]
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = [int(_b) for _b in box]
left = int(x1 * x_factor)
top = int(y1 * y_factor) - 10
right = int(x2 * x_factor)
bottom = int(y2 * y_factor) + 10
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(left, top, right, bottom))
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
draw_detections(image, left, top, right, bottom, score, cl)
# cv2.rectangle(image, (left, top), (right, bottom), color, 2)
# cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
# (left, top - 6),
# cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
# 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Determine the target device
target = 'RK3588'
# Create RKNN object
rknn = RKNN()
# Configure RKNN model
print('--> config model')
rknn.config(
mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]],
std_values=[[255, 255, 255]],
target_platform=target,
)
print('done')
# Load .onnx model
print('--> loading model')
ret = rknn.load_onnx(model="./yolov8s.onnx")
if ret != 0:
print("load model failed!")
rknn.release()
exit(ret)
print('done')
# Build RKNN model
print('--> building model')
ret = rknn.build(do_quantization=False, dataset="./dataset.txt")
if ret != 0:
print("build model failed!")
rknn.release()
exit(ret)
print('done')
# Export RKNN model
print('-->export RKNN model')
ret = rknn.export_rknn('./yolov8s.rknn')
if ret != 0:
print('export RKNN model failed')
rknn.release()
exit(ret)
# Initialize runtime environment
print('--> Init runtime environment')
# run on RK356x/RK3588 with Debian OS, do not need specify target.
#ret = rknn.init_runtime(target='rk3588', device_id='48c122b87375ccbc')
# If using a computer for simulation testing
ret = rknn.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# Data processing
img_list = os.listdir(IMG_FOLDER)
for i in range(len(img_list)):
img_name = img_list[i]
img_path = os.path.join(IMG_FOLDER, img_name)
if not os.path.exists(img_path):
print("{} is not found", img_name)
continue
img_src = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img_src is None:
print("File does not exist\n")
# Due to rga init with (0,0,0), we using pad_color (0,0,0) instead of (114, 114, 114)
pad_color = (0, 0, 0)
img = letter_box(im=img_src.copy(), new_shape=(MODEL_SIZE[1], MODEL_SIZE[0]), pad_color=(0, 0, 0))
# img = cv2.resize(img_src, (640, 512), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) # direct resize
input = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
outputs = rknn.inference([input])
boxes, classes, scores = post_process(outputs)
img_p = img_src.copy()
if boxes is not None:
draw(img_p, boxes, scores, classes)
# Save results
if not os.path.exists(RESULT_PATH):
os.mkdir(RESULT_PATH)
result_path = os.path.join(RESULT_PATH, img_name)
cv2.imwrite(result_path, img_p)
print('Detection result saved to {}'.format(result_path))
pass
rknn.release()
Use Netron to view yolov8s.rknn, the result is shown in the figure below:
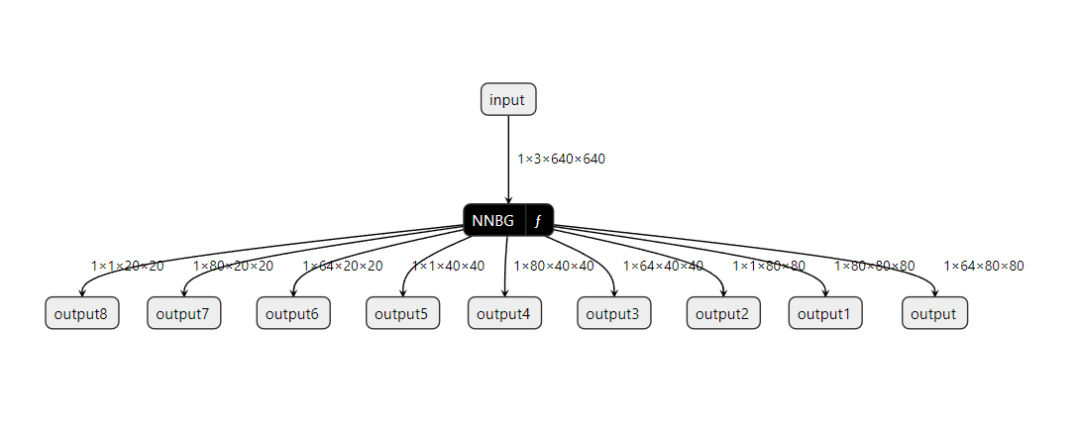
4. Deployment and Execution
Test code:
import os
import cv2
import sys
import time
import numpy as np
from copy import copy
# from rknn.api import RKNN
from rknnlite.api import RKNNLite
OBJ_THRESH = 0.25
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
IMG_SIZE = (640, 640)
target = "rk3588"
device_id = ""
rknn_model_path = ""
img_path = ""
# CLASSES = ("ding_ning_shuan_se", "gu_you", "gu_mo_chuan_kong","gu_mo_gai_hua ","mei_jun ","yan_xing_shi_zhen ","yan_zheng","you_er ","zhen_jun","zheng_chang_er" )
CLASSES = ("person", "bicycle", "car","motorbike ","aeroplane ","bus ","train","truck ","boat","traffic light",
"fire hydrant","stop sign ","parking meter","bench","bird","cat","dog ","horse ","sheep","cow","elephant",
"bear","zebra ","giraffe","backpack","umbrella","handbag","tie","suitcase","frisbee","skis","snowboard","sports ball","kite",
"baseball bat","baseball glove","skateboard","surfboard","tennis racket","bottle","wine glass","cup","fork","knife ",
"spoon","bowl","banana","apple","sandwich","orange","broccoli","carrot","hot dog","pizza ","donut","cake","chair","sofa",
"pottedplant","bed","diningtable","toilet ","tvmonitor","laptop ","mouse ","remote ","keyboard ","cell phone","microwave ",
"oven ","toaster","sink","refrigerator ","book","clock","vase","scissors ","teddy bear ","hair drier", "toothbrush "]
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
"""Filter boxes with object threshold."
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
candidate, class_num = box_class_probs.shape
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score* box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
scores = (class_max_score* box_confidences)[_class_pos]
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.
# Returns
keep: ndarray, index of effective boxes.
"""
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
# def dfl(position):
# # Distribution Focal Loss (DFL)
# import torch
# x = torch.tensor(position)
# n,c,h,w = x.shape
# p_num = 4
# mc = c//p_num
# y = x.reshape(n,p_num,mc,h,w)
# y = y.softmax(2)
# acc_metrix = torch.tensor(range(mc)).float().reshape(1,1,mc,1,1)
# y = (y*acc_metrix).sum(2)
# return y.numpy()
def dfl(postion):
n, c, h, w = postion.shape
print(postion.shape)
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
y = postion.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
y = softmax(y, 2)
acc_metrix = np.arange(mc).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
y = (y * acc_metrix).sum(2)
return y
def softmax(data, dim):
max = np.max(data, axis=dim, keepdims=True).repeat(data.shape[dim], axis=dim)
exps = np.exp(data - max)
return exps / np.sum(exps, axis=dim, keepdims=True)
def box_process(position):
grid_h, grid_w = position.shape[2:4]
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, grid_w), np.arange(0, grid_h))
col = col.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
row = row.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=1)
stride = np.array([IMG_SIZE[1]//grid_h, IMG_SIZE[0]//grid_w]).reshape(1,2,1,1)
position = dfl(position)
box_xy = grid +0.5 -position[:,0:2,:,:]
box_xy2 = grid +0.5 +position[:,2:4,:,:]
xyxy = np.concatenate((box_xy*stride, box_xy2*stride), axis=1)
return xyxy
def post_process(input_data):
boxes, scores, classes_conf = [], [], []
defualt_branch=3
pair_per_branch = len(input_data)//defualt_branch
# Python ignores score_sum output
for i in range(defualt_branch):
print(pair_per_branch*i)
boxes.append(box_process(input_data[pair_per_branch*i]))
classes_conf.append(input_data[pair_per_branch*i+1])
scores.append(np.ones_like(input_data[pair_per_branch*i+1][:,:1,:,:], dtype=np.float32))
def sp_flatten(_in):
ch = _in.shape[1]
_in = _in.transpose(0,2,3,1)
return _in.reshape(-1, ch)
boxes = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in boxes]
classes_conf = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in classes_conf]
scores = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in scores]
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
# filter according to threshold
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
# nms
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if len(keep) != 0:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = [int(_b) for _b in box]
print("%s @ (%d %d %d %d) %.3f" % (CLASSES[cl], top, left, right, bottom, score))
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
(top, left - 6), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2, cv2.LINE_AA)
def letter_box(im, new_shape, color=(0, 0, 0)):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
ratio = r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
def get_real_box(src_shape, box, dw, dh, ratio):
bbox = copy(box)
# unletter_box result
bbox[:,0] -= dw
bbox[:,0] /= ratio
bbox[:,0] = np.clip(bbox[:,0], 0, src_shape[1])
bbox[:,1] -= dh
bbox[:,1] /= ratio
bbox[:,1] = np.clip(bbox[:,1], 0, src_shape[0])
bbox[:,2] -= dw
bbox[:,2] /= ratio
bbox[:,2] = np.clip(bbox[:,2], 0, src_shape[1])
bbox[:,3] -= dh
bbox[:,3] /= ratio
bbox[:,3] = np.clip(bbox[:,3], 0, src_shape[0])
return bbox
if __name__ == '__main__':
rknn = RKNNLite()
# rknn.list_devices()
# Load rknn model
rknn.load_rknn("yolov8s.rknn")
# Set runtime environment, target defaults to rk3588
ret = rknn.init_runtime()
# Input image
img_src = cv2.imread("zidane.jpg")
src_shape = img_src.shape[:2]
img, ratio, (dw, dh) = letter_box(img_src, IMG_SIZE)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
print(img.shape)
#img = cv2.resize(img_src, IMG_SIZE)
# input=np.expand_dims(img,axis=0)
# print(input.shape)
# Inference run
print('--> Running model')
outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[img])
# outputs = rknn.inference([input])
print('done')
# Post-processing
boxes, classes, scores = post_process(outputs)
img_p = img_src.copy()
if boxes is not None:
draw(img_p, get_real_box(src_shape, boxes, dw, dh, ratio), scores, classes)
cv2.imwrite("result.jpg", img_p)
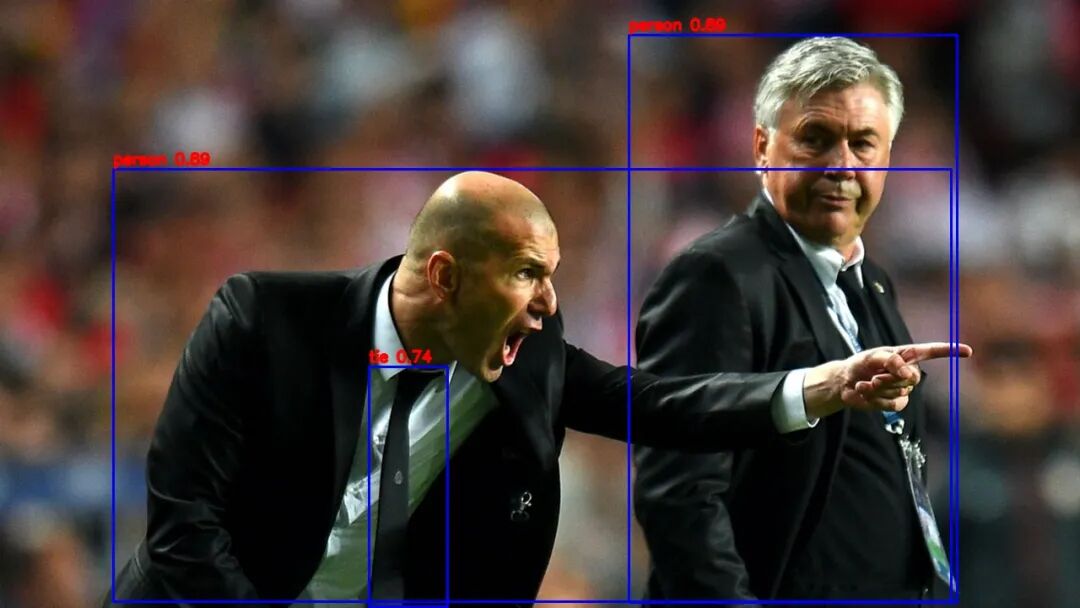
The result of running result.jpg is shown in the figure below:
