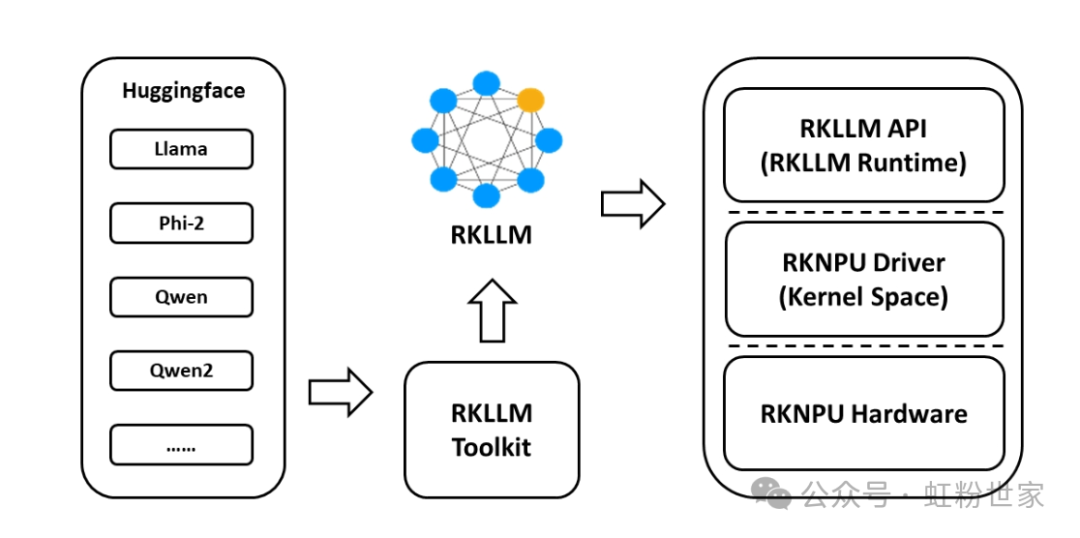
The example of function call invocation is as follows:
POST /v1/chat/completions HTTP/1.1
Host: api.openai.com
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
Content-Type: application/json
{
"model": "gpt-4",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What is the weather like in Beijing today?"}],
"tools": [ // Define the tool list
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get weather information for a specified city",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string", "description": "City name"},
"date": {"type": "string", "format": "date", "description": "Query date"}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}
}
],
"tool_choice": "auto" // Control whether the model automatically calls tools (optional values: auto/none/specified tool name)
}In https://github.com/airockchip/rknn-llm example flask_server.py
if not "stream" in data.keys() or data["stream"] == False:
# Process the received data here.
messages = data['messages']
print("Received messages:", messages)
for index, message in enumerate(messages):
input_prompt = message['content']
rkllm_output = ""
# Create a thread for model inference.
model_thread = threading.Thread(target=rkllm_model.run, args=(input_prompt,))
model_thread.start()
# Wait for the model to finish running and periodically check the inference thread of the model.
model_thread_finished = False
while not model_thread_finished:
while len(global_text) > 0:
rkllm_output += global_text.pop(0)
time.sleep(0.005)
model_thread.join(timeout=0.005)
model_thread_finished = not model_thread.is_alive()
rkllm_responses["choices"].append(
{"index": index,
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": rkllm_output,
},
"logprobs": None,
"finish_reason": "stop"
}
)
return jsonify(rkllm_responses), 200
else:
messages = data['messages']
print("Received messages:", messages)
for index, message in enumerate(messages):
input_prompt = message['content']
rkllm_output = ""
def generate():
model_thread = threading.Thread(target=rkllm_model.run, args=(input_prompt,))
model_thread.start()
model_thread_finished = False
while not model_thread_finished:
while len(global_text) > 0:
rkllm_output = global_text.pop(0)
rkllm_responses["choices"].append(
{"index": index,
"delta": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": rkllm_output,
},
"logprobs": None,
"finish_reason": "stop" if global_state == 1 else None,
}
)
yield f"{json.dumps(rkllm_responses)}\n\n"
model_thread.join(timeout=0.005)
model_thread_finished = not model_thread.is_alive()
return Response(generate(), content_type='text/plain')
else:
return jsonify({'status': 'error', 'message': 'Invalid JSON data!'}), 400
finally:
lock.release()
is_blocking = FalseThere is no handling of the request field for tools. Therefore, the actual implementation of the function call feature according to the OpenAI interface is ineffective.Taking Qwen2.5 as an example
Generally, the input and output of large language models are in string format. However, the Function Call feature breaks this convention, allowing the model to keenly identify specific function call needs during the dialogue process and respond with the required parameters in a structured data format. In the Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct model, the Function Call consists of the following key parts:
- messages: This part records the historical information of the dialogue, including the messages sent by the user, the prompts given by the system, and the content of the assistant’s replies.
- tools: This part provides information about the functions available for the model to call, detailing the function names, specific formats of parameters, and other key details.
In the Qwen2.5 backend, all messages and tools are applied to a fixed template to enable the model to correctly parse and execute the Function Call.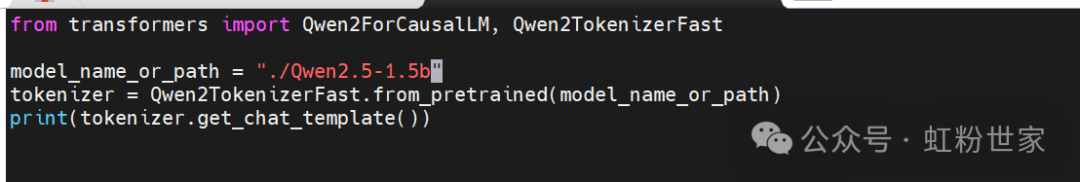
{%- if tools %} {{- '<|im_start|>system\n' }} {%- if messages[0]['role'] == 'system' %} {{- messages[0]['content'] }} {%- else %} {{- 'You are Qwen, created by Alibaba Cloud. You are a helpful assistant.' }} {%- endif %} {{- "\n\n# Tools\n\nYou may call one or more functions to assist with the user query.\n\nYou are provided with function signatures within <tools></tools> XML tags:\n<tools>" }} {%- for tool in tools %} {{- "\n" }} {{- tool | tojson }} {%- endfor %} {{- "\n</tools>\n\nFor each function call, return a json object with function name and arguments within <tool_call></tool_call> XML tags:\n<tool_call>\n{\"name\": <function-name>, \"arguments\": <args-json-object>}\n</tool_call><|im_end|>\n" }}{%- else %} {%- if messages[0]['role'] == 'system' %} {{- '<|im_start|>system\n' + messages[0]['content'] + '<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- else %} {{- '<|im_start|>system\nYou are Qwen, created by Alibaba Cloud. You are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- endif %}{%- endif %}{%- for message in messages %} {%- if (message.role == "user") or (message.role == "system" and not loop.first) or (message.role == "assistant" and not message.tool_calls) %} {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role + '\n' + message.content + '<|im_end|>' + '\n' }} {%- elif message.role == "assistant" %} {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role }} {%- if message.content %} {{- '\n' + message.content }} {%- endif %} {%- for tool_call in message.tool_calls %} {%- if tool_call.function is defined %} {%- set tool_call = tool_call.function %} {%- endif %} {{- '\n<tool_call>\n{\"name\": " }} {{- tool_call.name }} {{- '", "arguments": ' }} {{- tool_call.arguments | tojson }} {{- '}\n</tool_call>' }} {%- endfor %} {{- '<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- elif message.role == "tool" %} {%- if (loop.index0 == 0) or (messages[loop.index0 - 1].role != "tool") %} {{- '<|im_start|>user' }} {%- endif %} {{- '\n<tool_response>\n' }} {{- message.content }} {{- '\n</tool_response>' }} {%- if loop.last or (messages[loop.index0 + 1].role != "tool") %} {{- '<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- endif %} {%- endif %}{%- endfor %}{%- if add_generation_prompt %} {{- '<|im_start|>assistant\n' }}{%- endif %}
When messages and tools are applied to this template
messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}, {"role": "user", "content": "What is the weather like in Beijing today?"}]
tools= [ # Define the tool list
{ "type": "function", "function": { "name": "get_weather", "description": "Get weather information for a specified city", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "city": {"type": "string", "description": "City name"}, "date": {"type": "string", "format": "date", "description": "Query date"} }, "required": ["city"] } } } ]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tools=tools, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False)
print(text)
Execution result:
<|im_start|>systemYou are a helpful assistant.
# Tools
You may call one or more functions to assist with the user query.
You are provided with function signatures within <tools></tools> XML tags:<tools>{"type": "function", "function": {"name": "get_weather", "description": "Get weather information for a specified city", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"city": {"type": "string", "description": "City name"}, "date": {"type": "string", "format": "date", "description": "Query date"}}, "required": ["city"]}}}</tools>
For each function call, return a json object with function name and arguments within <tool_call></tool_call> XML tags:<tool_call>{"name": <function-name>, "arguments": <args-json-object>}</tool_call><|im_end|><|im_start|>userWhat is the weather like in Beijing today?<|im_end|><|im_start|>assistant
Therefore, in flask_server.py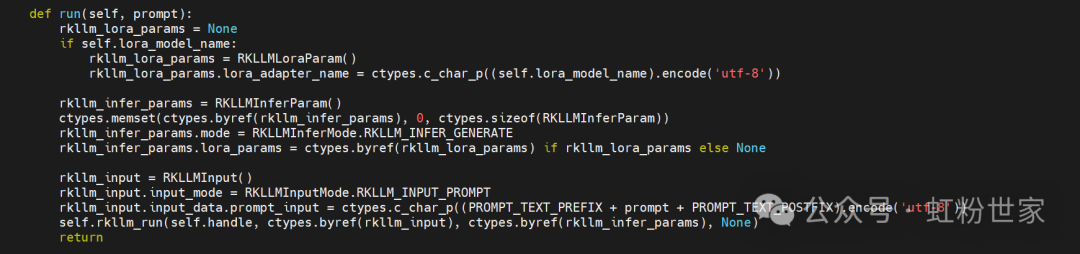 Refer to the above to supplement the tools-related information into prompt_input.When determining that there is a tools field, add the following content when concatenating prompt_input.
Refer to the above to supplement the tools-related information into prompt_input.When determining that there is a tools field, add the following content when concatenating prompt_input.
PROMPT_TOOLS_TEXT='''# Tools
You may call one or more functions to assist with the user query.
You are provided with function signatures within <tools></tools> XML tags:
<tools>{"type": "function", "function": {"name": "get_weather", "description": "Get weather information for a specified city", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"city": {"type": "string", "description": "City name"}, "date": {"type": "string", "format": "date", "description": "Query date"}}, "required": ["city"]}}}</tools>
For each function call, return a json object with function name and arguments within <tool_call></tool_call> XML tags:
<tool_call>{"name": <function-name>, "arguments": <args-json-object>}</tool_call>'''Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct effectively calls external tools through structured templates and XML formatted function calls. The template structure is clear: it uses <|im_start|> and <|im_end|> to distinctly separate dialogue content. Tool calls are explicit: using defined available functions and returning function calls within the <tool_call></tool_call> structure. It is easy to extend: multiple tools can be easily added to support complex application scenarios. This Function Call mechanism provides great flexibility for LLMs in practical applications, enabling them to efficiently execute function calls and obtain external information across various tasks.