Metal is applied to exposed pads using an organic coating, known as surface treatment. The surface finish protects copper pads from scratches and oxidation while facilitating soldering in a reflow oven. Although there are various types of surface treatments, ENIG and ENEPIG are two common types. Manufacturers typically use them for ceramicPCBs, flexible boards, and rigid-flex PCBs to provide high reliability. Compared to OSP, HASL, immersion tin, etc., ENIG and ENEPIG offer better surface finish.

How to Choose Surface Finish?
So far, manufacturers have used more widely accepted surface treatments such as OSP or organic solderability preservatives, HASL or hot air solder leveling, immersion tin, immersion gold, ENIG and ENEPIG. Each of these surface treatments has its advantages and disadvantages, making it necessary to choose the one that best fits the application. Choosing a surface finish requires consideration of factors such as cost, application environment, fine-pitch components, the use of leaded or lead-free solder, operating frequency, shelf life, drop resistance, impact resistance, volume and throughput, and thermal resistance.
As PCBs trend towards microvias and finer traces, and the drawbacks of HASL and OSP become more pronounced, such as flatness and flux removal issues, the demand for surface treatments like ENIG continues to grow. Additionally, ENEPIG is an improvement over black pads, which are a major weakness of ENIG.

What is ENIG Surface Treatment?
ENIG, or Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold, is also known as chemical gold or immersion gold in the electronics industry. This type of surface treatment provides two layers of metal—gold and nickel—which manufacturers deposit sequentially on the surface of the PCB pads. This surface finish is a selective surface finish, meaning that certain specific pads may have an ENIG surface finish while others may have different types, such as OSP, HAL, HASL or immersion tin. Manufacturers perform the ENIG surface treatment in several steps:
Copper Activation
PCB manufacturers first activate the copper layer through cleaning. This helps remove dust and oxide residues from the surface. They also wet the surface to remove any gas or air trapped in the vias. The next step is to micro-etch the surface with peroxide or sulfuric acid. Some manufacturers also use pre-dip catalysts to remove oxide residues.
Electroless Nickel Plating
The next step in the process is to coat the activated copper surface with a layer of nickel. This nickel layer acts as a barrier or inhibitor, preventing the copper surface from reacting with any other elements.
Immersion Gold
This is the final step of the process. Manufacturers immerse the PCB in a mixture that oxidizes the nickel surface, generating nickel ions and reducing gold from the mixture. The reduced gold forms a metallic coating that protects the nickel surface. The thickness of the gold layer must meet specifications.
Advantages of ENIG Surface Treatment
ENIG coatings have many advantages, primarily:
● Surface flatness—especially useful for fine-pitch components like BGA and other small form factor components.
● Suitable for press-fit components—provides good connections for electrical testing.
● Suitable for wire bonding and edge connector connections.
● Cheaper compared to ENEPIG.
Disadvantages of ENIG Surface Treatment
ENIG coatings also have some disadvantages:
● Black pad—result of uncontrolled nickel and gold plating processes.
● Variable coating thickness—caused by uncontrolled nickel and gold plating processes.
● Low wettability—during soldering.

What is ENEPIG Surface Treatment?
ENEPIG stands for Electroless Nickel Electroless Palladium Immersion Gold. This type of metallic coating on the surface of PCB pads consists of three layers—nickel, palladium, and gold—which manufacturers deposit layer by layer. In addition to protecting the copper surface from corrosion and oxidation, this type of surface treatment is suitable for high-density SMT designs. Manufacturers first activate the copper surface, then deposit a layer of electroless nickel, followed by a layer of electroless palladium, and finally a layer of immersion gold. The process is somewhat similar to the one they follow in the ENIG process. The ENEPIG process was developed by adding a palladium layer to the ENIG technology.
The addition of the palladium coating improves the protection of the PCB surface. The palladium layer prevents nickel degradation and interaction with the gold coating. The chemical reduction during the electroless process forms thin layers of nickel and palladium. Finally, the gold layer can protect the palladium from elemental influences.
Advantages of ENEPIG Surface Treatment
● Reduces quality issues caused by the presence of palladium, such as black pads.
● Excellent solderability and high reflow soldering stages.
● Provides highly reliable wire bonding capabilities.
● Supports high-density vias.
● Meets a wide range of miniaturization standards.
● Suitable for thin PCBs.
Disadvantages of ENEPIG Surface Treatment
● More expensive than ENIG.
● Thicker palladium layer reduces the efficiency of SMT soldering.
● Longer wetting time.

Similarities Between ENIG and ENEPIG Surface Treatments
Although these are two different types of surface treatments, they also share some common features. Both ENIG and ENEPIG surface treatments utilize electroless nickel and immersion gold. Both provide straight, flat soldering surfaces, making it easier to solder small components on the PCB surface. Additionally, both surface treatments are lead-free and are environmentally friendly alternatives for PCB products.
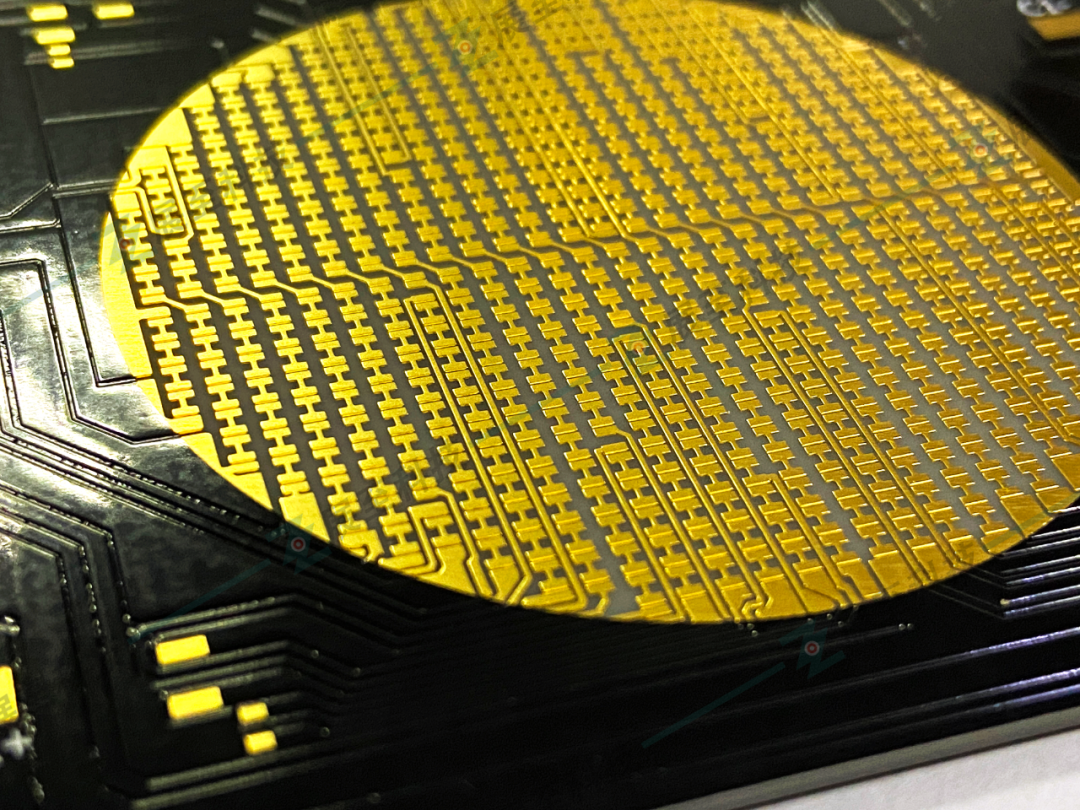
Both ENIG and ENEPIG provide excellent electrical performance and thermal diffusion properties. Using ENIG or ENEPIG coatings on the PCB pad surface requires following similar procedures. For example, both processes start with copper activation, followed by the electroless nickel coating. The final layer for both surface treatments is immersion gold.

Differences Between ENIG and ENEPIG Surface Treatments
The main difference between the two surface treatments is the presence of the palladium layer in ENEPIG. This palladium layer has high oxidation resistance, enhancing the electrical performance of the surface finish. However, the additional palladium layer increases the cost of the ENEPIG surface treatment compared to ENIG.
Additionally, due to low reliability of solder joints, the ENIG surface finish can be inconsistent for gold wire bonding. Furthermore, additional procedures are required to prevent nickel corrosion in ENIG. For such issues, ENIG surface treatment is best suited for low-end electronic products.

Considerations for Choosing ENIG or ENEPIG
1.Application
Choosing the best surface finish depends on the application and use case. For example, if the application requires the PCB to operate in high-temperature environments, it is best to use ENIG. This is because the ENIG surface treatment can withstand high temperatures.
2.Cost
This is an important factor to consider. For example, if you are looking for a low-cost surface finish, ENIG can meet your requirements. Since ENEPIG has an additional palladium layer, it increases the cost. However, ENEPIG is cheaper than solid gold coatings.
3.Flatness
Many traditional surface finishes are not smooth and flat enough. This makes it difficult to install very small SMT components with tiny form factors. For fine-pitch components like BGA, uneven surfaces can also pose problems. However, both ENIG and ENEPIG surface finishes are very smooth and form thin, uniform layers on the pads.
4.Wire Bonding
ENEPIG provides the best option for wire bonding due to its strong wire bonding capabilities.
5.Touch Interfaces
ENEPIG can handle touch interfaces without any issues.
6.RoHS Compliance
Many traditional surface treatments contain harmful substances and therefore do not comply with RoHS requirements. Both ENIG and ENEPIG fully comply with RoHS requirements and are lead-free.
7.Shelf Life
The shelf life of the circuit board is a critical factor. The shelf life of ENIG and ENEPIG surface treatments can last up to a year.

Conclusion:
ENIG and ENEPIG modern surface treatments are highly reliable. They are very suitable for high-quality ceramic circuit boards. Since PCBs do not contain lead or any harmful substances, they comply with RoHS requirements. Furthermore, both surface treatments provide very flat and level surfaces for SMT assembly. However, ENEPIG can meet any additional specifications required for PCBs using various SMT packages. ENEPIG is often used in PCBs required by the military, aerospace, and medical industries.
This article is sourced from the WeChat public account “Zhan Zhi Technology”
Copyright belongs to the original author
ABOUT CERADIR
“CERADIR™ Advanced Ceramics Online”—a vertical service platform for the advanced ceramics industry, dedicated to providing users with one-stop B2B solutions, professionally serving global advanced ceramics supply chain upstream and downstream factories, traders, and service providers, developed as a B2B industry platform to attract global suppliers and buyers.
 Share
Share Like
Like View
View