In 2025, the global competition in quantum technology has entered a heated phase. When Google’s quantum chip announced a thousand-fold breakthrough in error correction capabilities, Chinese research teams declared to the world with the dual breakthroughs of the “Zuchongzhi No. 3” superconducting quantum computer and the “Jiuzhang No. 4” photonic quantum computer: China has transformed from a “follower” in quantum computing to a “co-runner,” and even achieved “leadership” in certain fields. This silent revolution in computing power is reshaping the global technology landscape.
1. Technical Breakthrough: Multi-Route Progress to Build a Chinese Solution
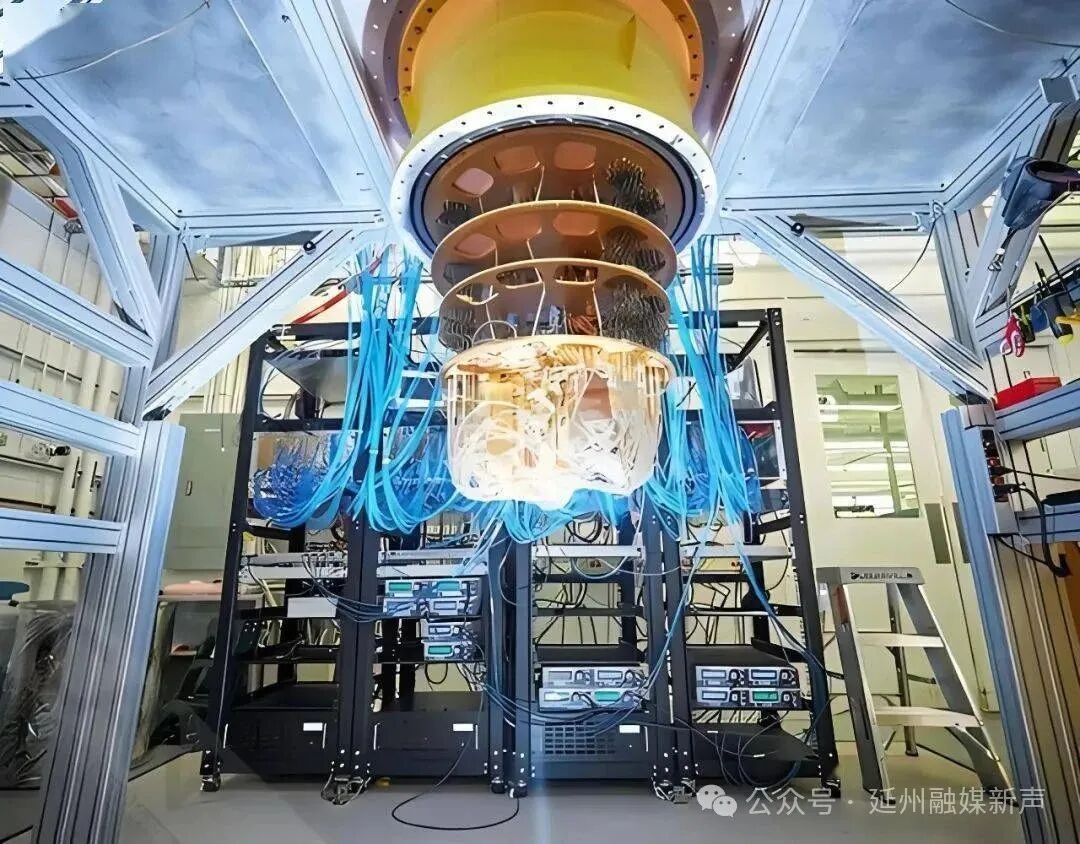

In the field of superconducting quantum computing, the Chinese Academy of Sciences team has achieved a 105-qubit “Zuchongzhi No. 3” system, whose surface code logical qubit error correction performance has reached an internationally leading level, with an error rate reduced by 40% compared to the previous generation product. More notably, the third-generation autonomous superconducting quantum computer “Benyuan Wukong” has achieved mass production of quantum chips for the first time, with a monthly production capacity exceeding 10 chips. This breakthrough signifies that China’s superconducting quantum computing has officially entered the stage of engineering application, providing reliable computing power support for financial modeling, drug development, and other fields.
In the field of photonic quantum computing, Chinese teams have also delivered impressive results. The “Jiuzhang No. 4” photonic quantum computer completed a Gaussian boson sampling experiment with 2000 photons, achieving a problem-solving speed 10^32 times faster than classical supercomputers, consolidating China’s global advantage in photonic quantum computing. The coherent photonic quantum computer independently developed by Beijing Boson Quantum Technology Co., Ltd. achieved a computational breakthrough of 10 million times in the second quarter of 2025, with SDK calls exceeding 21 million times, setting a new service record for domestic quantum computing companies.
This dual-track breakthrough of “superconducting + photonic quantum” is not accidental. Chinese research teams have also made significant progress in the field of semiconductor quantum dot technology, with the Shenyang Institute of Materials of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developing ultra-low loss tantalum nitride films that can extend the coherence time of superconducting qubits by 30%. This strategy of parallel development across multiple technical routes not only disperses R&D risks but also provides customized solutions for different application scenarios.
2. Industrial Leap: The Critical Point from Laboratory to Commercialization

In the Hefei Quantum Industrial Park, the world’s first quantum computing industrial alliance is promoting an innovative closed loop of “hardware-software-scenarios.” The compatibility testing of the Benyuan Sinan quantum programming framework with IBM Qiskit has achieved breakthroughs, marking the beginning of China’s quantum software ecosystem integrating into the international mainstream system. More notably, Alibaba Cloud’s quantum computing platform has connected to over 100,000 classical computers globally, providing “quantum-classical hybrid cloud” services, reducing the threshold for quantum computing from billion-level equipment investment to on-demand cloud services.
The financial sector has become the first battlefield for the commercialization of quantum computing. Fidelity Investments has optimized asset allocation through quantum algorithms, increasing annualized returns by 18%; JPMorgan has optimized investment portfolios using quantum algorithms, improving risk assessment efficiency by 60%. In the biopharmaceutical field, Pfizer and IBM collaborated to analyze the spike protein of the COVID-19 virus using quantum simulation, completing in 3 days a task that would traditionally take months; CATL utilized quantum computing to simulate battery material structures, shortening the R&D cycle by 60%. These cases confirm the feasibility of quantum computing transitioning from the laboratory to industrialization.
Breakthroughs in logistics optimization are even more practically significant. JD Logistics optimized delivery routes using quantum annealing technology, reducing transportation costs by 18% and carbon emissions by 19%; SF Express collaborated with Benyuan Quantum to improve path planning efficiency by 30 times. The implementation of these application scenarios marks the deep integration of quantum computing into the real economy.
3. Global Competition: Building a New Order in Quantum Technology
As the United States established a $500 million special fund through the “Quantum Computing Cybersecurity Act,” China’s “Three-Year Action Plan for the Development of the Quantum Information Industry” is promoting the establishment of more than 10 quantum technology industrial parks. This policy-level game reflects the strategic height of global competition in quantum technology. The European Union has launched the “Quantum Internet Alliance” plan, deploying quantum memory at six nodes; meanwhile, China has built over 10,000 kilometers of quantum communication backbone networks, covering multiple provinces nationwide.
In the field of technical standards, China has taken the lead in formulating international standards such as the “Technical Requirements for Quantum Key Distribution Networks,” breaking the technological monopoly of Europe and the United States. The interoperability testing framework for the BB84 protocol and CV-QKD protocol completed by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) also features the participation of Chinese research teams. This transition from “following technology” to “setting standards” marks the beginning of China’s quantum technology influencing global rules.
The capital market’s enthusiasm for quantum technology shows a difference between the East and West. While Rigetti secured $320 million in Series D funding, the Chinese quantum communication company Wentian Quantum completed 1.5 billion yuan in Pre-IPO financing, with a valuation exceeding 20 billion yuan. This shift in capital flow reflects the market’s optimism about the prospects of China’s quantum industry and suggests that the global center of quantum technology may shift eastward.
4. Challenges and Future: Three Paths to Quantum Advantage
Despite the breakthroughs in China’s quantum chip industry, engineering still faces challenges such as improving yield rates and cost control. Core technologies like quantum error correction codes and low-temperature control have been conquered, but achieving system integration of millions of qubits still requires breakthroughs. More urgently, the construction of a quantum software ecosystem is needed, as the current quantum algorithm library only covers 12% of industrial scenarios, and the adaptation costs for developers are high.
In the next five years, the development of China’s quantum technology needs to focus on three major directions: first, breaking through technologies such as topological qubits to promote exponential growth in quantum volume; second, expanding new fields such as quantum Monte Carlo simulations in application scenarios to form a market worth hundreds of billions; third, improving supporting tools such as quantum programming languages to establish an open and inclusive quantum ecosystem.
As Microsoft announced that its “four-dimensional topological quantum error correction code” technology would reduce error rates by a thousand times, Chinese research teams are responding to challenges with the “thousand-bit measurement and control system” and the “quantum computing industrial alliance.” The ultimate goal of this computing power revolution is not only to create more powerful computers but also to build a new computing paradigm. In this process, China is expected to leverage policy-driven, industry collaboration, and open innovation to occupy a commanding height in the global competition of quantum technology, contributing Eastern wisdom to the expansion of human understanding of the world.