✦
✧
Introduction
✦
In today’s world where artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly moving towards edge computing, AI is no longer confined to the large computing power of data centers but is increasingly deployed in compact, efficient, and intelligent embedded devices. From autonomous driving and industrial inspection to smart security and robotic control, the performance and stability of these “edge brains” are being put to the test.

Among the many edge AI computing platforms, the NVIDIA Jetson series is undoubtedly one of the most prominent star products. Known for its powerful GPU encoding and decoding capabilities and software ecosystem, it faces competition from emerging platforms like Raspberry Pi, Rockchip RK3588, and Huawei Ascend Atlas, which offer more cost-effective or specialized advantages. So, how do we evaluate the true capabilities of these AI-optimized embedded devices? In this issue, we will conduct a horizontal comparison of four brands across multiple dimensions such as computing power, power consumption, scalability, and ecosystem support.
✦
✧
Key Parameters Introduction
✦
1. AI Computing Power (TOPS)
TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second) indicates how many trillion AI operations can be executed per second, typically at INT8 precision. It represents the upper limit of the device’s neural network inference speed. The higher the value, the more complex or numerous models it can handle.
2. CPU Architecture and Core Count
Includes clock speed and core count. It affects the processing speed of traditional computing tasks, operating system scheduling, and non-neural network tasks.
3. GPU Type and Specifications
Includes the number of CUDA cores (NVIDIA), GPU architecture (such as Volta, Ampere), frequency, etc. It determines the performance of image processing, graphics rendering, and deep learning inference.

4. Memory Capacity and Bandwidth
RAM size and memory bandwidth. It affects whether data can be transmitted quickly, which is particularly critical when running high-resolution images.
5. Power Consumption (W)
The power consumption of the device under high-load inference. It determines whether it can be used in edge or mobile scenarios, such as drones and smart terminals in low-power applications.
6. Price
Includes the price of the development board and the cost of bulk customization.
✦
✧
Comparative Review of AI Embedded Devices
✦
1. Jetson Nano
Jetson Nano is an embedded development platform aimed at entry-level AI applications, with an official price of $99, approximately 600-800 RMB. It features a 128-core NVIDIA Maxwell architecture GPU, supporting up to 472G FLOPS of AI computing performance, suitable for running lightweight models such as MobileNet and YOLOv5-Nano. Its 4-core ARM Cortex-A57 CPU has a maximum clock speed of 1.43GHz, suitable for handling basic tasks.
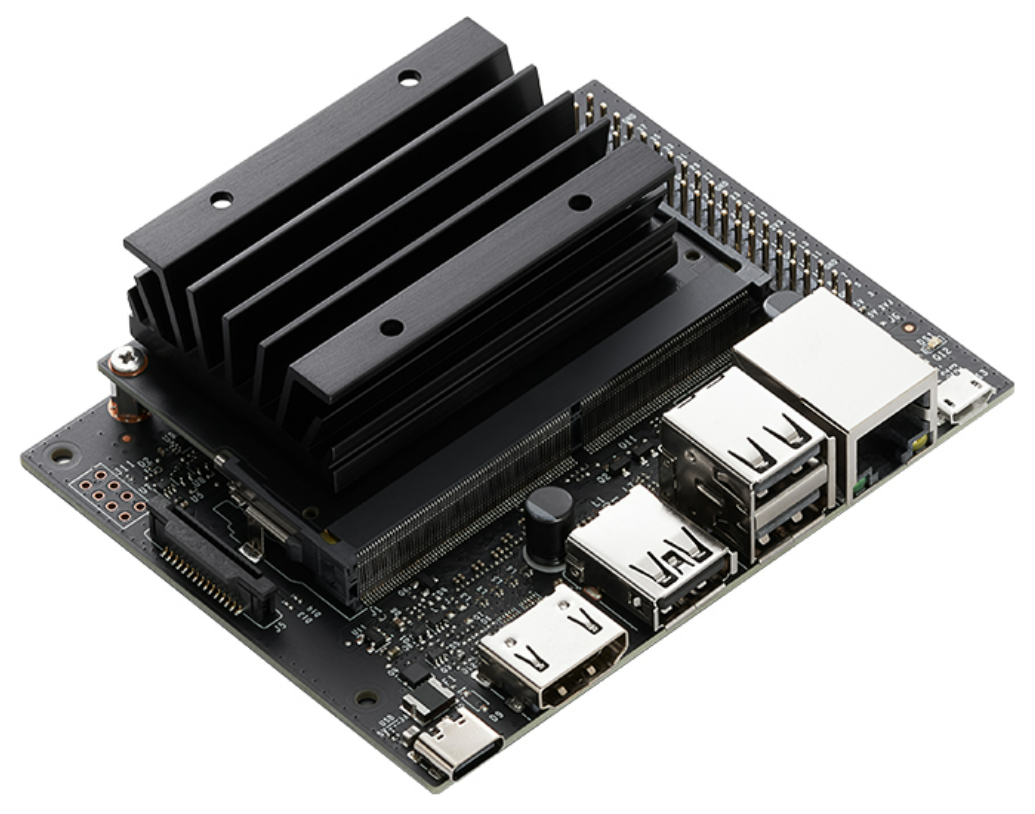

Although it does not have a dedicated deep learning accelerator (NPU), Jetson Nano still offers good cost-effectiveness and development convenience in low-power edge computing scenarios, thanks to its mature CUDA and NVIDIA software ecosystem, making it suitable for AI education, prototyping, and deployment of medium to low complexity inference tasks.
2. Jetson Orin Nano
The Jetson Orin Nano series is positioned for lightweight edge AI inference scenarios, with an official price starting at $199, approximately 1400-2000 RMB. It features an Ampere architecture GPU (up to 1024 cores), without Tensor Cores, with a maximum frequency of 625MHz. The CPU part consists of a 6-core ARM Cortex-A78AE, equipped with LPDDR5 memory, with a maximum memory bandwidth of 68GB/s.

Available in two versions differentiated by memory capacity: 4GB (up to 20 TOPS) and 8GB (up to 40 TOPS), with a maximum power consumption of only 15W, making it very suitable for deployment in power-sensitive scenarios such as smart cameras, service robots, and small drones that require AI inference.
3. Jetson AGX Orin
Jetson AGX Orin is NVIDIA’s flagship product in the current edge computing platform, with an official price starting at $899, approximately 6500-12000 RMB. It features a 2048-core Ampere architecture GPU (including 64 Tensor Cores), with a maximum GPU frequency of 1.3GHz, and inference performance of up to 200 TOPS (INT8). The CPU consists of a 12-core ARM Cortex-A78AE, supporting up to 64GB of LPDDR5 high-speed memory, with a bandwidth of up to 204.8GB/s.
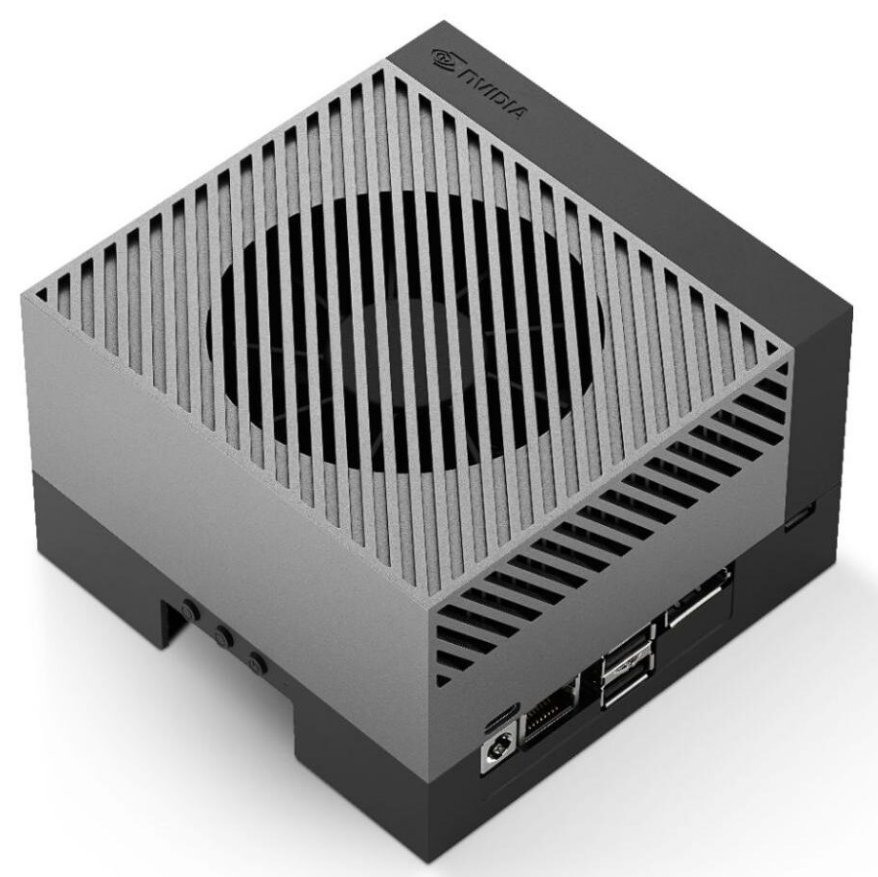

The configurable power consumption range is 15-60W, combining flexibility and high performance. This series is aimed at edge AI scenarios requiring multi-sensor fusion, high concurrency processing, and complex model deployment, such as autonomous driving, industrial robots, medical imaging, and smart cities, making it the preferred platform for data center-level edge intelligent computing power.
4. Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi 5 is the most powerful single-board computer in the Raspberry Pi series to date, with a market price of 500-1000 RMB. It features a 64-bit quad-core Cortex-A76 CPU (up to 2.4GHz), with performance improvements of about 2-3 times compared to Pi 4. It is equipped with a VideoCore VII GPU, supporting OpenGL ES 3.1 and dual 4K display, and introduces PCIe 2.0 interface for NVMe SSD expansion for the first time.
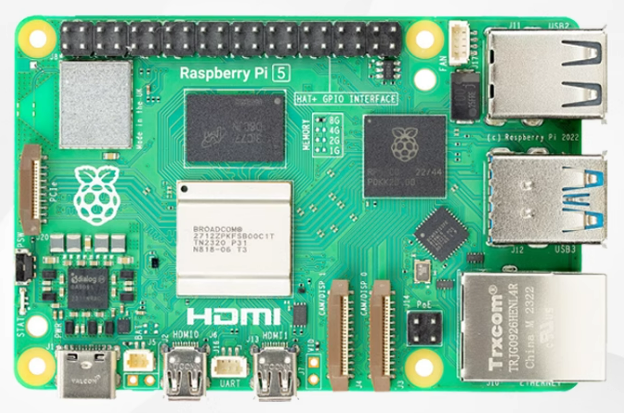
The 8GB kit version includes an original cooling fan, Type-C power supply, pre-installed system card, case, HDMI cable, and microSD card, fully unleashing its performance. It has basic AI acceleration capabilities and supports lightweight inference using frameworks such as OpenCV, ONNX, and TFLite, making it very suitable for edge computing, educational training, and smart home project development.
5. Rockchip RK3588
Rockchip RK3588 is a high-performance domestic AIoT processor, adopting an 8-core CPU architecture with a maximum clock speed of 2.4GHz, built-in ARM Mali-G610 MP4 GPU, and integrated 6 TOPS NPU, supporting various inference formats such as INT8/INT16/FP16, with excellent general computing and neural network inference capabilities.
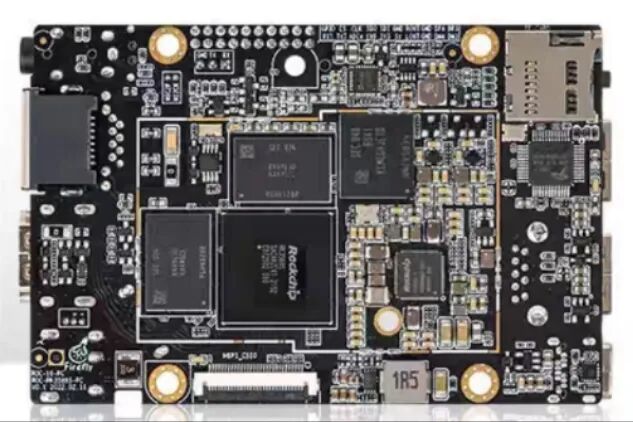

RK3588 supports up to 32GB LPDDR4x/LPDDR5 memory, with rich interfaces such as HDMI 2.1, USB 3.1, PCIe 3.0, supporting 8K video encoding and decoding and multiple 4K image inputs, suitable for edge computing, AI boxes, and smart large screens. The price of the RK3588 motherboard varies based on configuration, with a market price of around 1000-2500 RMB.
6. Huawei Ascend Atlas 200I DK A2
Huawei Ascend Atlas 200 DK A2 is an edge AI development kit based on the self-developed Ascend 310 AI processor, with a market price of around 1300-1800 RMB. It has a maximum inference performance of 16 TOPS (INT8), integrates one Da Vinci architecture AI Core, and is equipped with 8GB LPDDR4x memory, supporting multi-channel HD video encoding and image acceleration processing.
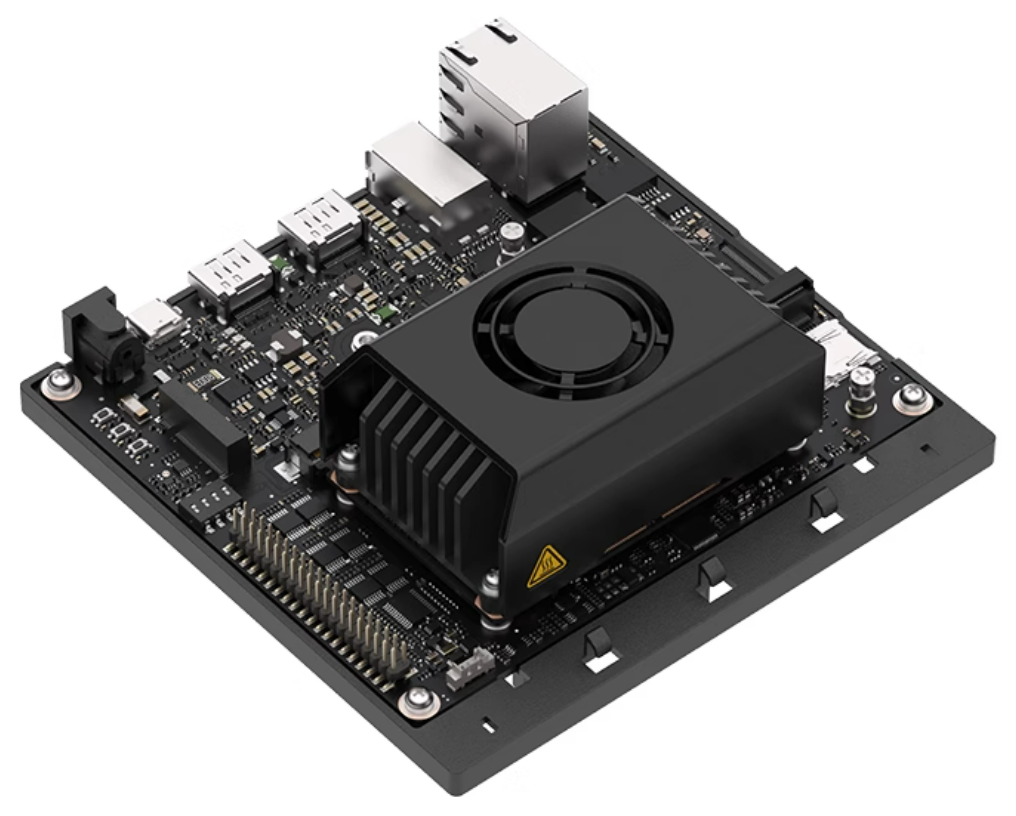
The typical power consumption of the entire board is less than 8W, providing both performance and energy efficiency advantages in lightweight deployment scenarios. In terms of interfaces, it offers rich expansions such as USB, HDMI, and Gigabit Ethernet, suitable for quickly building edge vision solutions. It supports the CANN compiler and MindSpore framework, with a high degree of localization.
✦
✧
Conclusion
✦
In summary, these six mainstream AI embedded development kits each have their advantages: the NVIDIA Jetson series occupies high-end application scenarios with top-notch AI performance and a complete software ecosystem; while the Raspberry Pi 5, although not a dedicated AI chip, remains the top choice for lightweight AI education and maker development due to its excellent general computing capabilities and extensive community support.
| Development BoardName | AIPerformance | GPU | CPU |
| Jetson Nano | 472 GFLOPS | 128-core Maxwell GPU |
Quad-core Cortex-A57 @ 1.43GHz |
| Jetson Orin Nano 8GB | 40 TOPS | 1024-core Ampere GPU |
6-core Cortex-A78AE @ 1.5GHz |
| Jetson AGX Orin 64GB | 200 TOPS | 2048-core Ampere GPU + 64 Tensor Cores |
12-core Cortex-A78AE @ 2.2GHz |
|
Raspberry Pi 5 8GB |
Basic inference support | VideoCore VII GPU |
4-core Cortex-A76 @ 2.4GHz |
| RK3588 | 6 TOPS (INT8) | ARM Mali-G610 MP4 |
4×A76 + 4×A55 @ 2.4GHz |
|
Ascend Atlas 200 DK A2 |
16 TOPS (INT8) | N/A (Da Vinci AI Core) |
Self-developed controller + AI Core |
RK3588, as a domestic SoC, balances image processing and lightweight AI inference, making it a versatile choice for edge computing; while Huawei Ascend Atlas 200 DK A2 demonstrates excellent cost-effectiveness in localization and low-power deployment.
|
Development Board Name |
Memory Specifications |
Power Consumption Range |
Price (RMB) |
| Jetson Nano |
4GB LPDDR4 |
5-10W |
600-800 |
| Jetson Orin Nano 8GB |
8GB LPDDR5 |
7-15W |
1400-2000 |
| Jetson AGX Orin 64GB |
64GB LPDDR5 |
15-60W |
6500-12000 |
|
Raspberry Pi 5 8GB |
8GB LPDDR4x |
5-12W |
500-1000 |
|
RK3588 |
32GB LPDDR5 |
5-15W |
1000-2500 |
|
Ascend Atlas 200 DK A2 |
8GB LPDDR4x |
Less than 8W |
1300-1800 |
The choice of which device to use ultimately depends on your scenario requirements, cost budget, and development cycle, as the best solution is the one that fits your needs!
✦
END
✦