
Abstract:
In automation control systems, PLCs are responsible for processing and executing various logical operations and control tasks. However, in practical applications, we often add an intermediate relay to the output terminals of the PLC for two main reasons.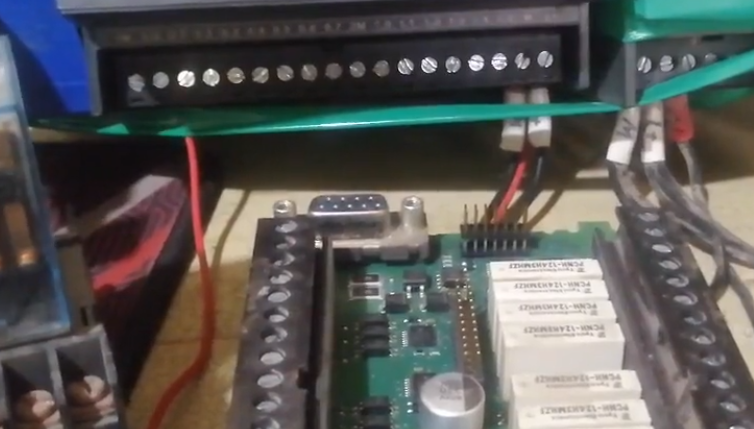 First Reason: It is impossible to use without an intermediate relay
First Reason: It is impossible to use without an intermediate relay
First, let’s explore the first reason: In certain cases, if an intermediate relay is not added, the output terminal of the PLC may be completely unusable. This is because the output module of the PLC is often designed only to drive smaller loads, such as small solenoids or contactors.
If the PLC directly drives a large load, such as a large motor or high-power equipment, it may overload the output module or even burn it out. The intermediate relay plays a “buffer” role here. It can withstand larger currents and voltages, thus being able to drive larger loads. When the PLC outputs a signal to the intermediate relay, the intermediate relay then drives the large load, ensuring the safe operation of the PLC.
- For example: Suppose we need to control a 220V AC motor, while the PLC’s output port can only provide a 24V DC signal. In this case, if the PLC’s output is directly connected to the motor, the motor will not operate correctly.
- Analysis: The intermediate relay can convert the PLC’s low-voltage DC signal into a high-voltage AC signal, thus meeting the load requirements. By using an intermediate relay, we can isolate the PLC’s output signal from the load, protecting the PLC’s output port from high voltage and high current.
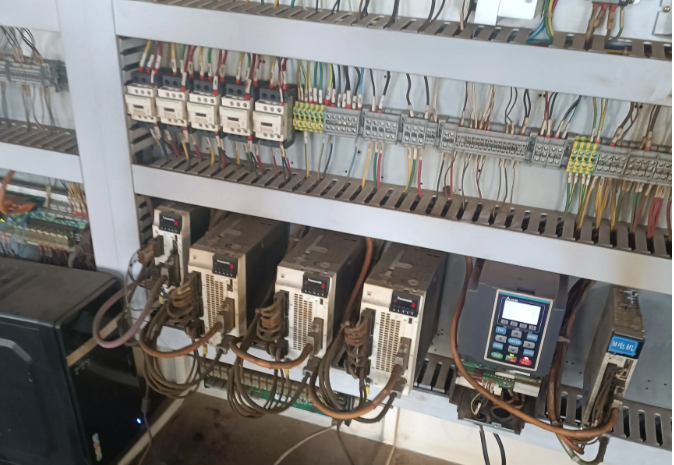

Second Reason:From the perspective of operational safety and later maintenanceNext, let’s analyze the second reason: From the perspective of safety and later maintenance. In industrial environments, the safety of equipment is crucial. By adding an intermediate relay to the PLC output terminal, we can increase a layer of safety protection. For example, when a fault occurs in the equipment, the intermediate relay can act as an isolator, separating the faulty part from the other parts to prevent the fault from escalating. Additionally, if the equipment needs maintenance or parts replacement, the intermediate relay can facilitate circuit disconnection, making maintenance work safer and more convenient.
- For example: In an industrial control system, the PLC needs to control the opening and closing of multiple solenoids. If the PLC’s output is directly connected to the solenoids, once a solenoid fails, it may cause the entire system to fail.
- Analysis: By using an intermediate relay, we can isolate the solenoids from the PLC. Even if a solenoid fails, it will only affect the intermediate relay and not directly impact the PLC. This facilitates later maintenance and fault troubleshooting.
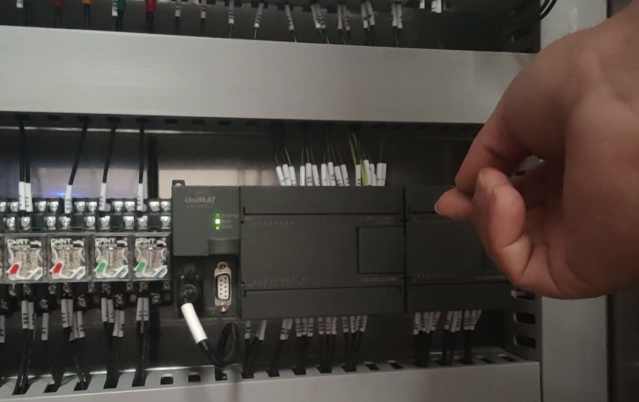

To better illustrate these two reasons, let’s further explain with a specific example. Suppose we have an automated production line where the motor needs to be controlled by the PLC to start and stop. Due to the large power of the motor, if it is directly driven by the PLC output terminal, it may overload the PLC output module. In this case, we can add an intermediate relay to the PLC output terminal. When the PLC outputs a signal to the intermediate relay, the intermediate relay will connect the power supply, thereby driving the motor to rotate. This ensures both the safe operation of the PLC and more stable and reliable control of the motor.Furthermore, from the perspective of safety and maintenance, if a fault occurs in the motor during production and causes excessive current, the intermediate relay can provide overcurrent protection, automatically disconnecting the circuit to prevent greater damage to the production line. At the same time, during later maintenance, the intermediate relay can conveniently control the starting and stopping of the motor, making maintenance work more convenient and efficient.In summary, the reasons for adding an intermediate relay to the PLC output terminal are mainly twofold: first, to drive large loads and avoid overloading the PLC output module; second, to enhance safety and facilitate later maintenance, adding a layer of protection and making maintenance work easier. In practical applications, selecting the appropriate intermediate relay and load matching method based on specific needs can ensure the stable and safe operation of the system.
Classic PLC Cases and Source Code
Scan to receive classic PLC cases and source code