1. Domestic AI Industry Expected to Welcome Leapfrog Development
1.1 Overseas AI Industry Thrives
OpenAI released GPT-4 in March 2023, Google launched the Gemini large model in December 2023, and recently introduced Gemini 1.5 pro and the open-source model Gemma, with continuous iterations and upgrades in large model capabilities. With the enhancement of large model capabilities, overseas AI applications are flourishing, with major cloud companies like Microsoft launching Copilot, Bing AI, and Google introducing Workspace and the chatbot Gemini, among many others. According to SensorTower data, in 2023, the annual download volume and in-app purchase revenue of AI applications increased by 60% and 70%, respectively, exceeding 2.1 billion downloads and 1.7 billion USD (with downloads surpassing 300 million in the first half of 2023). NVIDIA mentioned that 40% of its FY24 revenue is expected to come from AI inference. Recently, OpenAI’s Sora and Google’s Genie have been released, significantly advancing AI capabilities in video applications, moving AI towards foundational world models and AGI domains.
From the perspective of the infrastructure supporting AI development, whether from the performance and guidance of hardware manufacturers like NVIDIA, AMD, TSMC, and Supermicro, or from the capital expenditure investments of overseas cloud providers, it confirms the continuous acceleration of the overseas AI industry. NVIDIA’s FY24Q3 and FY24Q4 results consistently exceeded analyst expectations, primarily driven by AI’s boost to data center business. NVIDIA is optimistic about the next quarter’s guidance, expecting FY25Q1 revenue of 24 billion USD, also surpassing the analyst expectation of 21.9 billion USD. Supermicro’s FY24Q2 revenue exceeded expectations, with FY24Q3 expected net sales between 3.7 billion and 4.1 billion USD, far exceeding market expectations, mainly driven by strong demand for AI systems. TSMC expects that AI-related business CAGR will reach 50% in the coming years, raising its long-term AI revenue target, anticipating that by 2027, AI revenue will account for a high double-digit percentage (high teen), up from a previous expectation of a low double-digit percentage (low teen). AMD raised its accelerator scale forecast in December 2023, expecting the overall market size for AI accelerators to reach 400 billion USD by 2027, with a CAGR of 70%, up from a previous estimate of 150 billion USD in August 2023. Overseas cloud providers remain optimistic about AI investment outlook. Google guided that capital expenditures will significantly increase in 2024. Meta guided capital expenditures of 30 to 37 billion USD in 2024, raising the upper limit by 2 billion USD. Microsoft stated that based on investments in cloud and AI infrastructure, the delivery of third-party capacity contracts will be shifted to the next quarter, expecting a significant increase in capital expenditures in the next quarter. Amazon expects its capital expenditures to increase year-on-year in 2024.
1.2 Domestic Large Models Have Basically Achieved Capability Breakthroughs
Domestic manufacturers are also accelerating their R&D pace, successively releasing large model products and continuously iterating updates. Between March and June 2023, manufacturers including Baidu, Tsinghua Zhiyu, Alibaba, iFlytek, and Baichuan Intelligence successively released their large model products, with significant updates released around September and October 2023 to enhance model capabilities. Leading domestic large models have basically achieved capability breakthroughs between October and November 2023, matching or even surpassing some capabilities of ChatGPT, with continuous further iterations and upgrades. With the enhancement of domestic large model capabilities, AI applications are expected to accelerate their landing in 2024.
According to the benchmark evaluation released by the domestic Chinese model evaluation agency SuperCLUE, the capabilities of domestic large model manufacturers are rapidly improving. In May 2023, the overall score of domestic large models was about 20 points lower than GPT-3.5, with the highest scoring domestic model, the Xinghuo Cognitive Model, scoring 53.58, while GPT-3.5 scored 66.18. By November 2023, leading domestic large models had basically surpassed GPT-3.5 in total score, with the gap to GPT-4 Turbo also rapidly narrowing, with Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 scoring 74.02 and Moonshot scoring 72.88, both surpassing GPT-3.5’s score of 59.39, while still being distant from GPT-4’s score of 89.79. The latest evaluation results from SuperCLUE in February 2024 show that the first-tier domestic large models have narrowed the score gap with GPT-4.0 to within 10 points, with Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 scoring 87.75, GLM-4 scoring 86.77, Tongyi Qianwen 2.1 scoring 85.7, Baichuan 3 scoring 82.59, Moonshot (kimichat) scoring 82.37, and iFlytek Xinghuo V3.5 scoring 81.01, while GPT-4.0 Turbo scored 92.71 and GPT-3.5 scored 64.34.
Recently, Kimi supports ultra-long texts of 2 million words, with a surge in user numbers, further optimistic about the capabilities and application prospects of domestic models. On March 18, 2024, the Dark Side of the Moon announced that the Kimi intelligent assistant now supports 2 million words of ultra-long lossless context (when Kimi was first released in October 2023, it could only support 200,000 words of lossless context input), achieving a breakthrough in long text processing capabilities, and product internal testing has begun. Kimi’s monthly active users surged from about 500,000 at the end of 2023 to nearly 3 million, with daily active users on the web increasing from over 120,000 on March 9 to about 350,000 on March 14. On March 21, Kimi reportedly experienced downtime due to a surge in traffic.
1.3 The State Strongly Promotes AI Construction and Application Landing
On February 19, 2024, the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission held a special meeting on the promotion of artificial intelligence in central enterprises. The meeting recognized that accelerating the development of artificial intelligence is an inevitable requirement for state-owned central enterprises to fulfill their functional missions, seize strategic opportunities, cultivate new productive forces, and promote high-quality development. Central enterprises should actively embrace the profound changes brought by artificial intelligence, place the accelerated development of a new generation of artificial intelligence in a more prominent position, continuously strengthen innovation strategies, application demonstrations, and talent aggregation, focus on building artificial intelligence industry clusters, leverage the advantages of large demand scale, comprehensive industrial support, and diverse application scenarios, and take the lead in seizing the opportunities of AI empowering traditional industries, accelerating the construction of a data-driven, human-machine collaborative, cross-border integration, and co-creation sharing intelligent economic form. The meeting emphasized that central enterprises should plan the development of artificial intelligence in the overall work, deeply promote industrial renewal, and accelerate the layout and development of the artificial intelligence industry. They should solidify the development foundation, concentrate major resources in the most needed and advantageous areas, accelerate the construction of a number of intelligent computing power centers, further deepen open cooperation, and better leverage the role of cross-central enterprise collaborative innovation platforms. Carry out AI+ special actions, strengthen demand traction, accelerate empowerment in key industries, build a number of high-quality multimodal datasets, and create an industrial ecosystem empowered by large models from infrastructure, algorithm tools, intelligent platforms to solutions. Ten leading central enterprises signed an initiative to express their intention to actively open artificial intelligence application scenarios to society.
2. Domestic Computing Power Infrastructure Welcomes Development Opportunities
2.1 AI Development Requires Strong Computing Power Infrastructure Support
The data volume and parameter scale used by large language models exhibit “exponential” growth, leading to an explosive increase in demand for intelligent computing power. The parameters of GPT released by OpenAI in 2018 were 117 million, with a pre-training data volume of about 5GB, while GPT-3’s parameters reached 175 billion, with a pre-training data volume of 45TB. Currently, the parameters of large models have further increased to the trillion level and continue to iterate. The computing power demand during the training phase is related to the number of model parameters, the scale of the training dataset, etc. According to calculations from Tianyi Think Tank, based on data from OpenAI’s paper “Scaling Laws for Neural Language Models”, the computing power demand during the training phase = 6 × number of model parameters × training set scale. The GPT-3 model has about 175 billion parameters, with a pre-training data volume of 45TB, equivalent to a training set of about 300 billion tokens, with a total computing power consumption of about 3646 PFLOPS-day. In actual operation, GPU computing power is also needed for communication, data read/write, and other tasks, which will consume even more computing power. For inference-side computing power demand, based on Tianyi Think Tank’s calculations, according to data from OpenAI’s paper, on average, every 1000 tokens correspond to 750 words, with inference-side computing power demand = 2 × number of model parameters × number of tokens. ChatGPT surpassed 1 million users just 5 days after its launch, and within two months, the number of users exceeded 100 million, maintaining weekly active users at the level of 100 million. Assuming a daily active user count of 20 million for ChatGPT, with each user making an average of 10 queries corresponding to 1000 tokens each, the daily dialogue generation computing power demand for the GPT-3 model would be 810 PFLOPS-day, also considering the effective computing power ratio, actual operation would require even greater computing power support.
The development of artificial intelligence will drive rapid growth in computing power scale, thereby stimulating demand for computing power infrastructure. According to data from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, in 2022, the total scale of global computing devices reached 906 EFLOPS, and it is expected that the global computing power scale will grow by over 50% in the next five years. IDC data shows that in 2022, China’s general computing power and intelligent computing power scales reached 54.5 EFLOPS (based on FP64) and 259.9 EFLOPS (based on FP16), respectively, and by 2027, the general computing power and intelligent computing power scales are expected to reach 117.3 EFLOPS and 1117.4 EFLOPS, with estimated compound annual growth rates of 16.6% and 33.9% over the next five years.
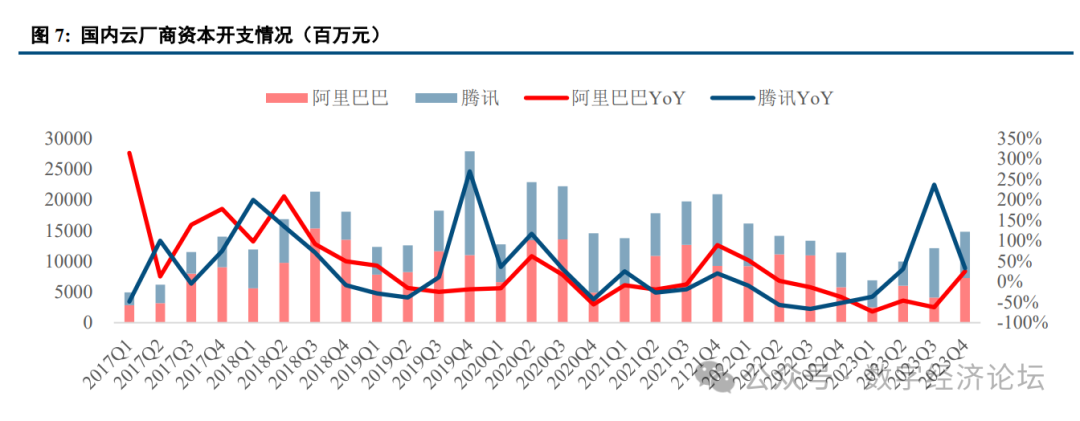
Operators are increasing investment in intelligent computing power infrastructure. China Mobile plans a total capital expenditure of 173 billion yuan in 2024, a year-on-year decrease of 4%, with 47.5 billion yuan allocated for computing power capital expenditure, a year-on-year increase of 21%. China Telecom plans a total capital expenditure of 96 billion yuan in 2024, a year-on-year decrease of 4%, with 37 billion yuan allocated for industrial digitalization capital expenditure, a year-on-year increase of 4%, and 18 billion yuan for cloud/computing power investment. China Unicom plans a total capital expenditure of 65 billion yuan in 2024, a year-on-year decrease of 12%, stating that investment focus will shift from stable networking communication business to high-growth computing and intelligent business. In terms of AI server procurement, in August 2023, China Telecom initiated a centralized procurement for AI computing power servers for 2023-2024, with a total procurement scale of 4175 units, with a total bid price exceeding 8.4 billion yuan. In September 2023, China Mobile initiated a procurement project for new intelligent computing centers (experimental networks) for 2023-2024, procuring AI servers (2454 units), data center switches (204 sets), and their supporting products, with a total price of about 3.3 billion yuan (bids 4-12 total, bids 1-3 failed). In March 2024, China Unicom released a qualification pre-review announcement for the centralized procurement project of AI servers in 2024, covering a total of 2503 AI servers and 688 key networking devices (RoCE switches). At the same time, the three major operators are also actively accelerating the construction of intelligent computing centers and other infrastructures.
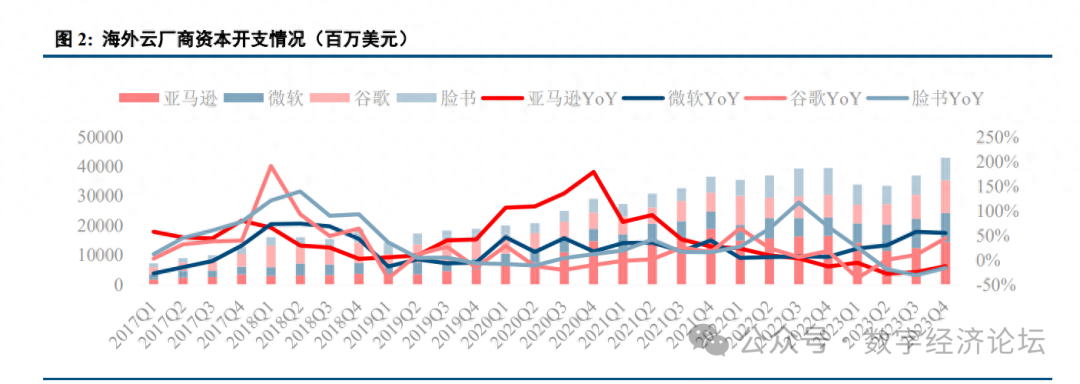
Domestic internet companies are showing signs of recovery in capital expenditure. In 2023, Tencent’s total capital expenditure was 23.893 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 32.6%. Tencent’s capital expenditures for Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4 of 2023 were 4.411 billion, 3.935 billion, 8.005 billion, and 7.524 billion yuan, respectively, with year-on-year changes of -36.7%, +31.1%, +236.8%, and +33.1%. Alibaba’s capital expenditures in the first three quarters of 2023 showed a decline year-on-year, with Q1, Q2, and Q3 capital expenditures of 2.513 billion, 6.007 billion, and 4.112 billion yuan, respectively, with year-on-year changes of -72.7%, -46.0%, and -62.5%. In Q4 2023, capital expenditure turned positive, amounting to 7.286 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 25.8%.
NVIDIA continues to upgrade GPUs, with sustained improvements in computing power. At the GTC in March 2024, NVIDIA released the GB200 super chip, utilizing the Blackwell architecture and TSMC’s 4nm (4NP) process, integrating two independently manufactured dies to form a Blackwell GPU, with two Blackwell GPUs combined with a Grace CPU to become the GB200 superchip. The Blackwell GPU has a total of 208 billion transistors, significantly more than the previous generation H100, which had only 80 billion transistors. A single GB200 NVL72 can support models with up to 27 trillion parameters. NVIDIA stated that previously, training a 1.8 trillion parameter MoE architecture GPT model in 90 days required 8000 Hopper architecture GPUs and 15 megawatts of power. Now, under the Blackwell architecture, the same training can be completed in 90 days with only 2000 GPUs and a quarter of the energy consumption.
2.2 Continued Upgrades of Export Restrictions, Domestic Production Becomes Inevitable Trend
The United States has continuously escalated import restrictions on advanced chips to China. In October 2023, the U.S. issued new semiconductor export restrictions, imposing stricter regulations on chip computing power and performance density, with A100/A800, H100/H200/H800, L4, and L40s not meeting export conditions. In August 2022, the U.S. first implemented large-scale chip export sanctions against China, halting exports of A100 and H100 chips and systems composed of corresponding products. This sanction mainly restricts the export of high-end AI chips with total computing performance (computing power * bit width) ≥ 4800 and interconnect bandwidth ≥ 600GB/s. After the sanctions, NVIDIA redesigned the A800 and H800 “crippled versions” of chips for China, mainly limiting interconnect rates and double-precision computing performance. The upgraded version of the chip ban in October 2023 intensified the crackdown, with performance meeting the following conditions being subject to export controls: (1) total computing power TPP (computing power * bit width) exceeding 4800; (2) TPP exceeding 1600 and PD (TPP/chip area) exceeding 5.92; (3) 2400 ≤ TPP < 4800, and 1.6 ≤ PD < 5.92; (4) 1600 ≤ TPP, and 3.2 ≤ PD < 5.92. Under these requirements, A100/A800, H100/H200/H800, L4, and L40s do not meet export conditions, and NVIDIA can only comprehensively weaken chip computing power, providing China with H20, L20, and L2 chips. Recently, the U.S. government has again escalated semiconductor export control measures. According to information from TiMedia, on March 30, 2024, Beijing time, the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) released new regulations for “implementing additional export controls”, revising the two previous export restrictions established in October 2022 and 2023, comprehensively restricting the sale of NVIDIA, AMD, and more advanced AI chips and semiconductor equipment to China. In this new regulation, BIS deleted and revised some restrictions on the sale of semiconductor products to China from the U.S. and Macau, including that the U.S. will adopt a “presumption of denial policy” for sales to China from Macau and the D:5 country group, and that AI semiconductor products exported to China will be subject to a “case-by-case review” policy, including comprehensive verification of technical levels, customer identities, compliance plans, and other information.
Domestic self-reliance in computing power is an inevitable trend. Previously, China had a high dependence on NVIDIA chips, with NVIDIA accounting for 85% of shipments in the AI accelerator market in 2022, while domestic chips such as Huawei, Baidu Kunlun, Cambricon, and Suiruan accounted for 10%, 2%, 1%, and 1%, respectively. IDC data shows that in the first half of 2023, the market size of China’s accelerator chips exceeded 500,000 units. From a technical perspective, GPU cards occupy 90% of the market share, while from a brand perspective, domestic AI chip brands shipped over 50,000 units, accounting for about 10% of the entire market. Currently, as export restrictions continue to escalate, the trend and intensity of artificial intelligence development in China will not change; on the contrary, we need to pay more attention to the development of artificial intelligence. The U.S. restrictions on advanced chips to China may further promote the pace of high-level technological self-reliance in our country. It is expected that the proportion of domestic production will significantly increase in the future. In the short term, due to the gap in supply and demand for domestic computing power chips, overseas chips including H20 are also expected to further supplement the domestic computing power industry. The H20 chip does not have outstanding advantages in single-card performance but utilizes NVLINK technology to enhance cluster performance.
2.3 Current Domestic Chip Performance May Be Close to A100, or Better than H20
Currently, domestic GPU manufacturers such as Huawei HiSilicon, Cambricon, Pingtouge, Biren Technology, Baidu Kunlun, Suiruan Technology, and Haiguang have all launched computing power chips for training and inference scenarios, continuously iterating and upgrading, with performance steadily improving. In terms of ecosystem, domestic GPU manufacturers have also launched software development kits supporting mainstream frameworks like TensorFlow and Pytorch, and have established development platforms based on their own software to attract more developers to build a complete ecosystem. The performance of leading domestic chips may be close to A100 or better than H20. For example, at FP16 precision, Huawei Ascend 910 has a computing power of 256 TFLOPS, slightly lower than A100’s 312 TFLOPS, but significantly higher than H20’s 148 TFLOPS, while H100’s 1513 TFLOPS shows a larger gap. Additionally, Pingtouge’s Lingang 800 exceeds A100 in INT8 precision, and Biren Technology’s BR100 exceeds A100 in FP32 precision. In terms of peak computing power per chip, domestic chips have already met the conditions for large-scale use. With the enhancement of domestic chip capabilities, the development of the domestic computing power industry will further accelerate.
3. Overview of the Domestic Computing Power Industry Chain
3.1 Servers: AI Growth, Domestic Computing Power Chip Development May Change the Landscape
General servers are relatively weak, while AI servers are experiencing high growth. Affected by the ongoing economic downturn, high inflation, reduced corporate capital expenditures, and inventory destocking, the overall shipment volume of the server market in 2023 did not meet expectations. IDC data shows that in the third quarter of 2023, global server sales amounted to 31.56 billion USD, a year-on-year increase of 0.5%; shipment volume was 3.066 million units, a year-on-year decrease of 22.8%; it is expected that the global server market size will slightly grow to 128.471 billion USD in 2023, with a growth rate of 4.26%; the annual growth rates for the next four years are expected to be 11.8%, 10.2%, 9.7%, and 8.9%, respectively, with the market size expected to reach 189.139 billion USD by 2027. Trendforce data indicates that China’s server demand is expected to decline by 9.7% year-on-year in 2023. The general server market is further compressed due to the explosive demand for AI and the global shift of spending towards AI. IDC data shows that in the first half of 2023, both the global general server market and CPU market size experienced declines, with the CPU market in the second quarter down 13.4% year-on-year. AI servers are experiencing high growth. IDC expects the global AI hardware market (servers) to grow from 19.5 billion USD in 2022 to 34.7 billion USD in 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 17.3%. IDC expects the Chinese AI server market size to reach 9.1 billion USD in 2023, a year-on-year increase of 82.5%, and to reach 13.4 billion USD by 2027, with a five-year compound growth rate of 21.8%.
The increase in the proportion of AI servers and the rise in domestic production rates may change the competitive landscape among domestic server manufacturers. Previously, manufacturers like Inspur and H3C held a high market share in the server competition landscape. In 2022, the market share of China’s server market was led by Inspur, H3C, Super Fusion, Ning Chang, and ZTE, with shares of 28%, 17%, 10%, 6%, and 5%, respectively. In the AI server market in 2022, Inspur, H3C, Ning Chang, Anqing, Kun Qian, and Huawei ranked in the top six, with shares of 47%, 11%, 9%, 7%, 6%, and 6%, respectively. As the proportion of domestic AI chips increases, the supplier landscape for AI servers may change. Currently, Ascend is relatively leading among domestic GPUs, and manufacturers deeply involved in supplying Huawei Ascend computing power servers are expected to benefit more, specifically referring to the bidding candidates from China Telecom and China Mobile. In the future, with the launch of new GPU products from other domestic manufacturers and the enrichment of inference scenarios, the domestic GPU ecosystem is also expected to become more diverse, potentially leading to new changes. Under the trend of domestic production, the landscape of the general server market may also change. In domestic CPU servers, X86 solutions currently include Haiguang, Zhaoxin, and Lianqi, mainly led by Haiguang; ARM solutions include Huawei Kunpeng and Feiteng. In the PC server procurement by China Mobile from 2021 to 2022, servers using Haiguang chips accounted for 20.90%, while those using Kunpeng chips accounted for 20.53%, with a total domestic server share exceeding 41.43%. Recently, in the 2024 PC server procurement project by China Mobile, the number of bids for ARM servers compared to X86 servers reached 1.71:1, with ARM server share surpassing X86.
3.2 Switches: Ethernet High-Speed Products Gradually Mature, High-End Products Expected to Achieve Rapid Growth
AI deployment requires greater network capacity, and data center switch bandwidth is currently growing at a rate of doubling every two years. In August 2022, Broadcom released Tomahawk 5, with switch bandwidth increased to 51.2T, serdes rates reaching 100Gb/sec, and single-channel rates reaching up to 800G, supporting 800G and 1.6T network deployments. The next generation of switches will upgrade bandwidth to 102.4T, further laying the foundation for 1.6T and 3.2T networks.
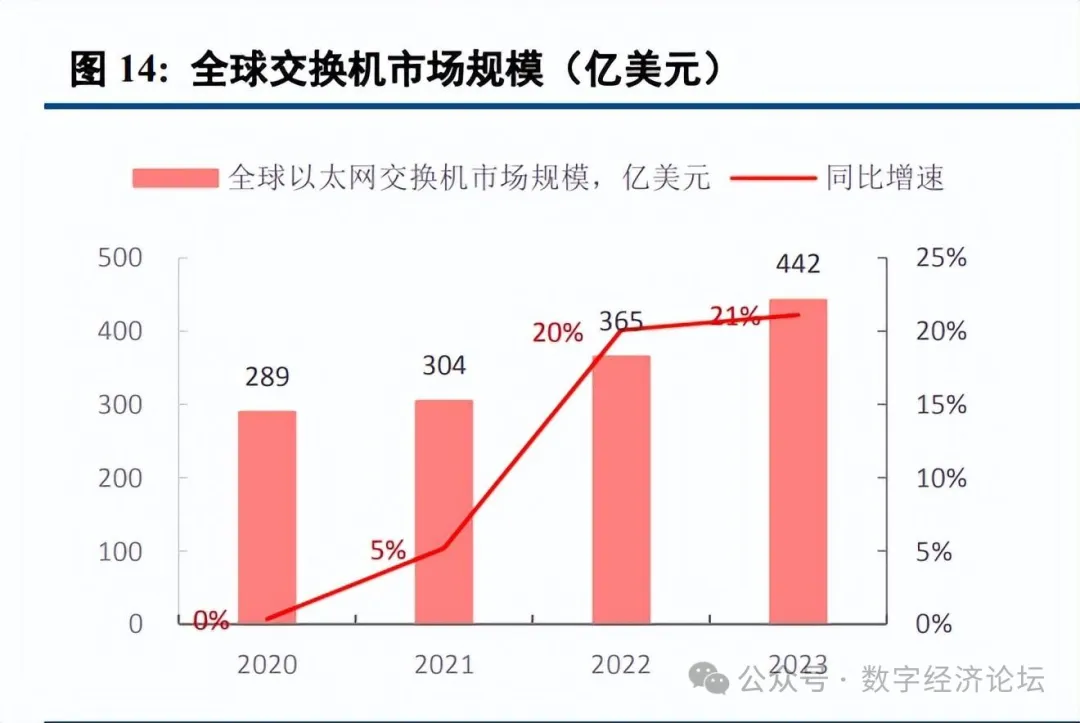
Benefiting from the drive of AI development, demand for high-end switches is rapidly increasing. According to IDC data, global Ethernet switch revenue reached 44.2 billion USD in 2023, a year-on-year increase of 20.1%, with the data center segment’s market revenue increasing by 13.6% year-on-year, accounting for 41.5% of total market revenue. In 2023, the revenue of 200/400 GbE switches in the data center segment increased by 68.9% year-on-year. Industrial Internet’s 2023 annual report indicates that 800G high-speed switches have undergone NPI, and mass production is expected to begin in 2024, contributing to revenue. It is anticipated that 2024 will be an important year for 800 Gbps port deployment, with the penetration rate of 400 Gbps/800 Gbps ports expected to exceed 40% by 2027. In China, due to weak demand from government and enterprise sectors and a shortage of high-end AI computing power chips, IDC data shows that in 2023, China’s Ethernet switch revenue decreased by 4% year-on-year (with a scale of nearly 5 billion USD in 2022), but in the fourth quarter of 2023, it grew by 9.1% year-on-year. With the construction of domestic computing power, the penetration of high-end switches in China is expected to accelerate, driving overall demand.
InfiniBand’s current share is increasing. AI high-performance computing scenarios further raise the requirements for network performance. One of the most important features of InfiniBand is the use of the RDMA protocol (Remote Direct Memory Access), which allows for low latency. Compared to traditional TCP/IP network protocols, RDMA enables applications to directly read and write data with the network card without the intervention of the operating system kernel, significantly reducing data transmission latency. InfiniBand technology is based on end-to-end flow control for network data packet transmission, ensuring that messages are sent without congestion, thus greatly reducing the risk of network performance degradation caused by packet loss. Additionally, InfiniBand introduces SHARP technology (Scalable Hierarchical Aggregation and Reduction Protocol), allowing the system to perform calculations within the switch while forwarding data, thereby reducing the number of data transmissions between computing nodes and significantly improving computational efficiency. InfiniBand, as a network communication standard for high-performance computing, has advantages in high throughput and low latency, enabling high-speed interconnects between computers, computers and storage, and storage. InfiniBand currently achieves transmission speeds of up to 400Gb/s. According to the technology development roadmap, IBTA plans to launch XDR products in 2024, with four-channel corresponding rates of 800Gb/s and eight-channel corresponding rates of 1600Gb/s, with GDR products expected to be released two years later, with four-channel rates reaching 1600Gb/s. Currently, the main players in the IB market are Nvidia (acquired Mellanox) and Intel (acquired Qlogic). Thanks to superior performance and Nvidia’s integrated sales strategy, InfiniBand currently leads the AI market.
Ethernet is also continuously improving performance to support high-performance computing scenarios. Ethernet also has related RDMA technology standards, especially with the emergence and maturity of RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet), RDMA has been widely applied in data centers based on Ethernet. IBTA released the RoCE protocol technology standard in 2010 and the RoCEv2 protocol technology standard in 2014. After years of development, RoCE has gained routing capabilities and has shown significant performance improvements. In November 2022, Broadcom and Arista announced an open end-to-end network solution optimized for RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE). In May 2023, Nvidia launched NVIDIA Spectrum-X, with switch bandwidth of 51.2T, enhancing the performance of NVIDIA collective communication libraries through RoCE. However, RDMA was originally designed to connect smaller-scale nodes, and its design inherently requires high performance and low latency from the network, especially that the network cannot lose packets; otherwise, performance degradation will be significant, which poses greater challenges to the underlying network hardware and also limits the scale of RDMA networks. Additionally, RDMA achieves high bandwidth and low latency through hardware, placing a low load on the CPU, but the use and management of hardware are relatively complex. In the face of AI high-performance computing scenarios, the global establishment of the Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC) and China Mobile’s promotion of fully scheduled Ethernet (GSE) further enhance Ethernet transmission performance. In July 2023, hardware vendors such as Broadcom, AMD, Cisco, Intel, Arista, Eviden, HP, and large-scale cloud vendors like Meta and Microsoft jointly established UEC to develop open “Ultra Ethernet” solutions across the physical layer, link layer, transport layer, and software, creating high-performance Ethernet for new forms of transmission layer processing, achieving Ethernet performance improvements even in non-lossless networks, making it more flexible than RDMA. In August 2023, China Mobile Research Institute, together with over 30 partners, launched the “Fully Scheduled Ethernet (GSE) Promotion Plan”, breaking through traditional lossless Ethernet performance bottlenecks based on packet-by-packet Ethernet forwarding and global scheduling mechanisms. In September 2023, China Mobile Research Institute and partners released the industry’s first prototype of “Fully Scheduled Ethernet (GSE)”. Overall, Ethernet’s support for high-performance computing scenarios has gradually been validated.
CPO, silicon photonics, and other technologies will be used in high-end switches. Co-packaged optics (CPO) is recognized as one of the mainstream product forms for future higher-speed optical communication, significantly reducing the power consumption and cost of switches. As switch bandwidth upgrades from the initial 640G to 51.2T, the total power consumption of switches has increased significantly by about 22 times due to the continuous upgrade of Serdes rates and the increasing number of components, while CPO technology can effectively reduce the power consumption of Serdes. Therefore, in the era of switches with bandwidth of 51.2T and above, CPO is expected to achieve breakthroughs. Silicon photonic chips are the best product form for the optical engine in CPO switches and are expected to be widely used in the future. Overseas companies like Broadcom, Intel, and Meta have layouts in CPO switch products. In June 2023, H3C launched the 51.2T 800G CPO silicon photonic data center switch, integrating CPO silicon photonic technology, liquid cooling design, and intelligent lossless technologies to meet the needs of intelligent computing networks for high throughput, low latency, and green energy efficiency. Its solution based on RoCE for all business scenarios in data centers has also gradually been commercialized. Ruijie Networks has also launched 51.2T silicon photonic NPO switches and 25.6T silicon photonic NPO switches.
The increase in the scale of domestic AI server deployments, the continuous iteration of domestic GPU chips, and the maturity of high-speed Ethernet switch solutions will benefit domestic switch manufacturers’ participation in domestic computing power construction. Orders related to 400G and 800G switches from domestic manufacturers are expected to achieve rapid growth. Switches have technical barriers, and domestic manufacturers have launched high-end products to meet AI demands. Globally, in the Ethernet switch field, Cisco holds the first share, followed by Arista, Huawei, and HPE. In the domestic market, according to IDC data, in Q1 2023, H3C (34.5%), Huawei (30.9%), and Ruijie (14.9%) ranked as the top three in China. Currently, many domestic switch manufacturers have launched 51.2T switches, with Ruijie launching a 51.2T silicon photonic NPO liquid-cooled switch in March 2022, H3C launching a 51.2T 800G CPO silicon photonic data center switch (H3C S9827 series) in June 2023, and Inspur launching a flagship 51.2T high-performance switch (SC8670EL-128QH) in November 2023. Internet companies are increasing their self-research efforts, which may lead to new changes in the landscape. Alibaba, Tencent, and ByteDance all released their self-developed 51.2T white-box switches in 2023 and announced large-scale commercialization, namely Alibaba’s “White Tiger”, Tencent’s TCS9500, and ByteDance’s B5020. The strong entry of internet companies may bring new changes in market share.
Ethernet switching devices consist of Ethernet switch chips, CPUs, PHYs, PCBs, and interface/port subsystems, and the demand for high-speed switches will directly drive the demand for high-speed switch chips. The global Ethernet switch chip market is mainly dominated by Broadcom, Marvell, Qualcomm, Huawei, Realtek, Nvidia, and Intel, with Cisco and Huawei primarily using their own chips. In the domestic switch market, Broadcom, Marvell, Realtek, Huawei, and Shengke Communication are the main participants. According to Shengke Communication’s prospectus, in 2020, the market share of the commercial Ethernet switch chip market in China, based on sales value, was dominated by the top three suppliers, accounting for 97.8% of the market share, with Broadcom, Marvell, and Realtek ranking first, second, and third with market shares of 61.7%, 20.0%, and 16.1%, respectively, while Shengke Communication ranked fourth with a market share of 1.6%. Domestic manufacturers still lag behind overseas in the high-speed switch chip field, but under the trend of domestic production, they are accelerating their catch-up efforts. Shengke Communication mentioned in its prospectus that it plans to launch the Arctic series in 2024, with a maximum switching capacity of 25.6Tbps, supporting a maximum port rate of 800G, targeting ultra-large-scale data centers, with switching capacity basically reaching the level of leading competitors.
3.3 Optical Modules: Expected Significant Growth in Domestic Demand for 400G and Other Optical Modules in 2024
Since 2022, the optical module market in North America’s traditional cloud computing sector has begun upgrading to 800G speeds, with a significant increase in shipments of 800G optical modules expected in 2024. From the historical development of the traditional data communication market, the optical module speed has already upgraded to 800G, corresponding to a single Serdes rate of 100G for electrical ports, and a single optical path rate reaching 50G Baud (the rate of EML), achieving 100G speed after PAM4 modulation. Shipments of 800G optical modules began in small batches at the end of 2022, with demand in 2023 mainly coming from Google and NVIDIA (including self-use and external sales). A significant increase in 800G shipments is expected in 2024.
1.6T optical modules are expected to begin small batch shipments in the second half of 2024 and are expected to see significant growth in 2025, while it is recommended to focus on the penetration process of new technologies such as silicon photonics and thin-film lithium niobate. The demand for bandwidth in AI is limitless; the larger the bandwidth, the lower the cost per bit transmitted, the lower the power consumption, and the smaller the size. The upgrade of optical module speeds to 1.6T is currently based on a 100Gbps rate for electrical ports, while the optical ports will gradually upgrade from 100G to 200G. Thanks to the high cost-performance ratio of the network, the 1.6T optical module is expected to accelerate its application, with small batch shipments expected in the second half of 2024 and significant growth anticipated in 2025. From the perspective of downstream customers, NVIDIA, Google, and Amazon are likely to be the main demanders of 1.6T optical modules.
Domestic optical modules are slightly lagging behind overseas in terms of the latest generational development, with a significant increase in demand for 400G expected in 2024, and some leading CSPs are procuring 800G products. Currently, NVIDIA’s A100 GPU primarily uses 200G optical modules, while the H100 GPU primarily uses 800G optical modules. Each A100 GPU is paired with a Mellanox HDR 200Gb/s InfiniBand network card, while each H100 GPU is paired with a Mellanox NDR 400Gb/s InfiniBand network card. In the design of NVIDIA’s H100 SuperPOD, 800G optical modules are used, where one 800G optical module can replace two 400G optical modules, and at the electrical port, eight SerDes channels can be integrated, corresponding one-to-one with eight 100G channels at the optical port. Therefore, under this design, the channel density of the switch is increased, and the physical size is significantly reduced. Domestic GPUs and network cards are often connected via PCIe, and the PCIe connection method largely determines the use of optical modules. According to information from Huawei Ascend’s official website, the Ascend Atlas 300T A2 training card uses a PCIe x16 Gen5.0 interface, with a network using a 1*200GE QSFP-DD interface. Domestic systems can also adopt the method of using one 400G optical module to replace two 200G optical modules to enhance channel density. Additionally, the PCIe x16 Gen5.0 interface network can also use 400G optical modules for non-blocking connections. With the growth in domestic AI server shipments, it is expected to also drive the volume of related optical module segments.
3.4 Liquid Cooling: Industry Trend is Clear, Entering the Scale Deployment Stage in 2024
Liquid cooling is a trend that has become relatively clear. As GPU computing power increases, chips need to complete more calculations in a shorter time, inevitably leading to increased chip energy consumption, which will continuously raise the requirements for chip cooling. According to predictions from Shuanghong, by 2026, AI chips are expected to consume over 2000W. Liquid cooling is expected to become the main method for server cooling, with NVIDIA’s latest generation Blackwell compute node adopting a liquid-cooled MGX design. Liquid cooling solutions are divided into cold plate liquid cooling, immersion (single-phase, two-phase), etc. Currently, from the perspective of industry maturity and cost, cold plate liquid cooling solutions are dominant and are expected to become the main solution for liquid cooling of high-performance chips. At the same time, relevant manufacturers in the industry are continuously researching and developing to further enhance cooling efficiency, deployment convenience, and cost-effectiveness through liquid upgrades, architectural designs, and solution combinations to meet the continuously increasing chip power consumption and cooling demands.
From the perspective of the industry chain, cold plate liquid cooling is mainly divided into components such as cold plates, pipelines, quick connectors, etc., within the server, as well as CDU, manifold, etc., for cooling distribution, and the air cooling part that supplements heat dissipation. The internal components of the server are mainly procured by server manufacturers, while some chip manufacturers have certain bargaining power in the supply chain. The cooling distribution systems related to CDU and manifold are mainly procured by downstream customers such as internet companies, operators, data center manufacturers, or integrators, and modular equipment providers. Different manufacturers participate in different segments, and the overall business potential also varies.
Recently, overseas cooling supply chain companies related to computing power have also actively laid out liquid cooling. Supermicro stated that by June 2024, the liquid-cooled rack capacity of Supermicro will reach 1500 units per month, with a total rack capacity of 5000 units, with liquid cooling accounting for 30%. Shuanghong predicts that by the fourth quarter of 2024, the demand for liquid cooling and air cooling will reach a 50% to 50% ratio. Qihong AVC expects that in 2024, due to the growth in demand for AI servers, the demand for cooling will increase, and the upgrade of cooling products is expected to accelerate, with liquid cooling products expected to begin small-scale shipments in the second half of 2024, with explosive growth anticipated in 2025. Viavi plans to expand the production scale of liquid cooling solutions by more than 40 times by the end of 2024. CoolerMaster released an all-in-one liquid-cooled host Cooling X and a mini liquid-cooled host Sneaker X in November 2023, and announced its strategic blueprint in early 2024, promoting the layout of the technology ecosystem from the perspective of excellent cooling technology and technology DIY services.
Domestic operators are rapidly advancing, with the penetration rate of liquid cooling in new AI server tenders already reaching a large share. In June 2023, the three major operators jointly released the “Telecom Operators Liquid Cooling Technology White Paper”, proposing that 2023 be the technology verification phase, with the three major operators conducting technology verification to lead the formation of standards for decoupling liquid cooling cabinets and servers, with mainstream manufacturers completing the development of decoupled liquid cooling products; 2024 will be the scale testing phase, with 10% of new projects adopting liquid cooling technology; and from 2025 onwards, large-scale applications will be carried out, with over 50% of data center projects applying liquid cooling technology, achieving comprehensive leadership in technology, ecology, and application. In August 2023, in the centralized procurement project for AI computing power servers (2023-2024) by China Telecom, the proportion of liquid cooling in the G-series training servers procured was already considerable. In September 2023, in the procurement of new intelligent computing centers (experimental networks) initiated by China Mobile (only counting bids 4-12, bids 1-3 failed), a total of 1658 AI training servers were procured (of which 1500 were liquid-cooled, accounting for 90%), and a total of 80 AI inference servers were procured (of which 64 were liquid-cooled, accounting for 80%). Liquid cooling is entering the scale deployment stage, with the domestic industry space exceeding 20 billion yuan and expected to further increase. It is expected that liquid cooling will enter the scale deployment stage in 2024, and we believe that with the verification of solution maturity brought by large-scale applications and the decrease in costs, coupled with the substantial implementation of PUE regulatory requirements, liquid cooling is expected to further penetrate the general server market. In the short to medium term, cold plate liquid cooling solutions are mainstream, and through assumptions regarding AI server shipments, general server shipments, single KW cost, and liquid cooling penetration rates, we estimate that the overall scale is expected to exceed 20 billion yuan. As AI develops, the volume of servers is expected to increase significantly, and the industry scale is expected to further open up.
Domestic listed companies are also actively laying out liquid cooling, with different manufacturers participating in different segments, leading to differences in market space, direct customers, and capability requirements. The internal components of servers, such as cold plates and connectors, are mainly sold to server manufacturers, while some GPU chip manufacturers also have certain bargaining power. These products are precision machined parts, emphasizing thermal design capabilities, production manufacturing capabilities, and cost control capabilities. CDU, manifold, and other cooling distribution systems are mainly sold to end customers, third-party data center manufacturers, integrators, and whole cabinet-level product providers, emphasizing the overall system design capabilities of the cooling cycle.
3.5 Connectors/Wiring Harnesses: AI Drives Connector Systems to Upgrade to 112G/224G
Communication connectors are key devices for transmitting current and signals, mainly used in various communication equipment such as servers, 5G communication base stations, data centers, Ethernet, and high-end storage devices. Connector products in the communication field are mostly customized products, using electrical connectors, RF connectors, optical connectors, etc. For example, in server scenarios, connectors used include DDR connectors for storage modules, mezzanine connectors for data transmission modules, high-current connectors for power modules, optical connectors for optical transmission modules, and high-speed backplane connectors for signal transmission modules. According to connection type, there are internal and external I/O connectors: external I/O connectors mainly include Type-A, Type-C, RJ45, SFP, QSFP, D-SUB, etc.; internal connectors mainly include PCIe, DDR, Mini-SAS, Mini-SAS HD, Gen Z, Slim SAS, and high-speed backplane connectors.
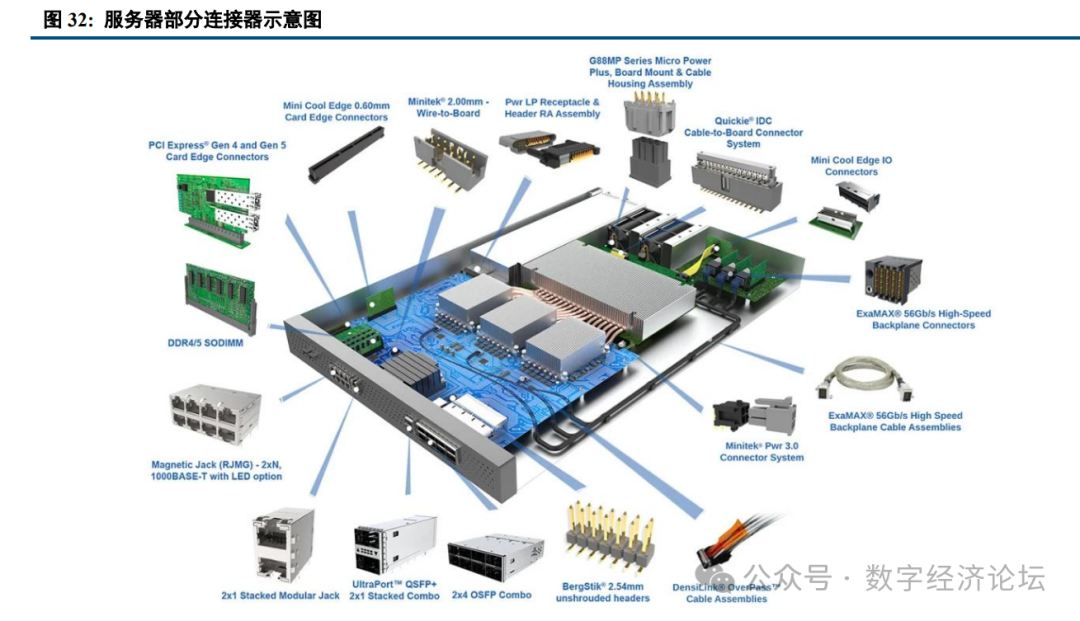
With the development of AI and the continuous improvement of GPU performance, the architecture of related data center connection systems is also continuously upgrading to high speeds, iterating from 10Gbps-40Gbps to 56Gbps, 112Gbps, and 224Gbps. Currently, overseas has developed to a data transmission rate of 224 Gbps to meet the demands of artificial intelligence and 1.6T networks for high-speed connections. Common signal transmission is divided into single-ended signals and differential signals, with differential signals consisting of two single-ended signals. When the transmitter transmits a differential signal, it splits the single-ended signal into two signals with equal amplitude and opposite phase, which the receiver recognizes and converts back into a single-ended signal. The receiver subtracts the two single-ended signals, resulting in a signal amplitude that is double that of a single signal. Due to their strong anti-interference capabilities, differential signals are widely used in high-speed signal transmission. During the process of connector rate enhancement, higher requirements are placed on PCB routing complexity, PCB materials and layers, heat dissipation, crosstalk, and insertion loss at micro-spacing, significantly increasing the technical difficulty. For example, in terms of differential impedance, differential impedance is strongly related to rise time; the shorter the rise time, the greater the impedance fluctuation, making it harder to control impedance; rise time is inversely proportional to bandwidth, and for products with higher rates, impedance fluctuations will be greater, and matching difficulty will significantly increase. High-speed backplane connectors are mainly used for data connections between single boards and backplanes, transmitting high-speed differential signals or single-ended signals. Huawei’s AI training cluster Atlas 900AI adopts a cable backplane connector architecture, achieving interconnection between servers and between servers and access layer switches. Currently, traditional backplane architectures (where all boards are plugged into the same side of the backplane, completing direct interactions between boards through traces on passive copper backplanes) have long traces and high losses, unable to meet bandwidth and capacity bottlenecks. The orthogonal architecture is expected to penetrate in the future, where the main control board, line board, interface board, and other components are in an orthogonal hardware structure with the switching network board, directly connected through orthogonal connectors, further minimizing the trace distance from the line board to the switching network.
High-speed I/O connectors are mainly used for data transmission between switches and between switches and servers. Previously, SFP28/SFP56, QSFP28/QSFP56, and other I/O connectors were mainly used for connections. The 56Gbps QSFP-DD I/O module can achieve a 400G port capacity. With the increase in transmission rates, high-speed I/O connectors are also upgrading to 112G and 224G rates. Using 64×224Gbps QSFP-DD or 64×224Gbps OSFP forms can support chips with specifications of 512×224Gbps=102.4T, with a single port capacity of 1.6Tbps (224Gbps×8). Using 32×OSFP-XD forms can support chips with specifications of 512×224Gbps=102.4T, with a single port capacity of 3.2Tbps (224Gbps×16); using 64×OSFP-XD forms can support chips with specifications of 1024×112Gbps=204.8T, with a single port capacity of 3.2Tbps (224Gbps×16).
The performance of copper interconnects is gradually improving, and active copper cables (ACC) and active electrical cables (AEC) may replace some passive copper direct-attach cables (DAC). Considering that with the increase in bandwidth and rates, the effective transmission distance of electrical signals will significantly shorten, we believe that the penetration rate of optical solutions will increase in the future. Electrical signals transmitted in copper wires experience losses, and as communication bandwidth increases, skin effect leads to increased transmission losses in copper wires and PCB traces, increased connector head losses, and increased packaging trace losses, thus significantly shortening the effective transmission distance. According to the goals published by IEEE P802.3df, the distance for electrical signal transmission at a single-channel rate of 100Gbps is 2m. For the transmission distance of electrical signals at a single-channel rate of 200Gbps, Google’s report has demonstrated the feasibility of reaching 1m, while Intel believes it can reach 1m with good materials. As rates continue to increase, we believe that the penetration rate of optical solutions will increase, while in the short term, the power consumption and cost issues of optical solutions will be addressed by new technologies or products, but the underlying solutions will still be optical.
Currently, in the 224Gbps connection system, overseas manufacturers are still leading. Top global manufacturers such as Amphenol, Molex, and TI have launched relatively complete 224G connection system solutions. Domestic manufacturers are slightly lagging behind overseas in terms of overall network-side deployment upgrades, and the upgrade of connection systems will also be slightly delayed compared to overseas. Currently, domestic manufacturers’ products are still mainly at 56Gbps, with breakthroughs in 112Gbps and 224Gbps products in some areas.
3.6 PCBs: AI Drives High-Speed PCB Upgrades, Benefiting Leading Shares and Profitability Improvements
The development of AI drives strong demand for large-size, high-layer, high-level HDI, and high-frequency high-speed PCB products in AI servers, HPC, switches, and storage infrastructure systems, raising higher requirements for their technical levels and quality, thus driving PCB demand growth. AI servers: New PCB demand related to GPUs, upgrades of CPU platform PCBs, and increased usage and grade requirements in storage, backplane, and other segments. 1) New PCBs required for GPUs with high performance requirements. According to DIGITIMES information, the PCBs used for NVIDIA A100, H100, and other GPU products generally have a high number of layers, typically ranging from 16 to 24 layers. According to Yahoo News, NVIDIA’s new GB200 design integrates OAM/UBB, using M8-level CCL and 20-layer HDI, with the estimated PCB value per GPU increasing by about 10% compared to ordinary B-series AI servers and by about 30-40% compared to H-series. 2) The CPU platform is accelerating its upgrade to PCIe5.0 and continues to iterate, driving upgrades of CPU platform PCBs. The CPU platform previously underwent upgrades every 2-3 years to meet the increasing requirements for data transmission rates and operating frequencies in new application scenarios. Broadcom stated that the speed of PCIe upgrades is accelerating. As Intel’s server CPU platform gradually upgrades from PCIe3.0 to 4.0 and 5.0, the transmission rate can be increased to 32Gbps, with signal application frequencies reaching up to 16GHz, placing stricter requirements and standards on signal integrity during transmission. This trend drives materials towards high-frequency/ultra-low loss/very low loss levels and strengthens cooperation with upstream copper foil suppliers to jointly develop new solutions with lower roughness and cost advantages, further enhancing product electrical performance design requirements while reducing PCB costs. Generally, the mainstream PCB materials are 8-16 layers, corresponding to PCIe3.0 generally being 8-12 layers, 4.0 being 12-16 layers, while 5.0 platforms are above 16 layers.
High-speed switches: As the speed of switches increases, the material grade of their PCBs also further increases, with stricter control over insertion loss requirements. The transmission rates of high-speed signals have increased from 50G to 100G and then to 200G, with the loss of the transmission system increasing from below 10dB to over 20dB, significantly increasing the complexity of PCB interconnections. According to Panasonic’s official website information from January 2022, it has developed low transmission loss MEGTRON 8 multilayer circuit board materials for high-speed communication network devices, supporting 800G Ethernet switches.
The upstream of the PCB industry mainly consists of raw materials such as copper foil, copper foil substrates, fiberglass cloth, and resin. The downstream application fields of the PCB industry are numerous, with a broad overall market scale. From a global market perspective, according to Prismark data, the global PCB output value in 2022 was approximately 81.741 billion USD, with China’s output value around 44.150 billion USD. In 2021, the global output value of copper-clad laminates reached 18.807 billion USD, with China’s output value reaching 13.905 billion USD. From the downstream perspective, the computer, communication, consumer electronics, and automotive electronics sectors account for a high proportion, with Prismark data indicating that in 2021, computers (including PCs, servers/storage, and other computers), advanced communications (including mobile phones, wired infrastructure, and wireless infrastructure), consumer electronics, and automotive electronics accounted for approximately 35%, 32%, 15%, and 10%, respectively. In terms of production capacity, globally, the PCB industry is mainly distributed in East Asia and Europe and the United States, and in recent years, global PCB production capacity has gradually shifted to China, which has become the largest region for PCB production in the world, currently accounting for over 50% of global PCB output, although most of it is still in the mid-to-low end, and domestic manufacturers have accelerated the layout of high-end production lines in recent years.
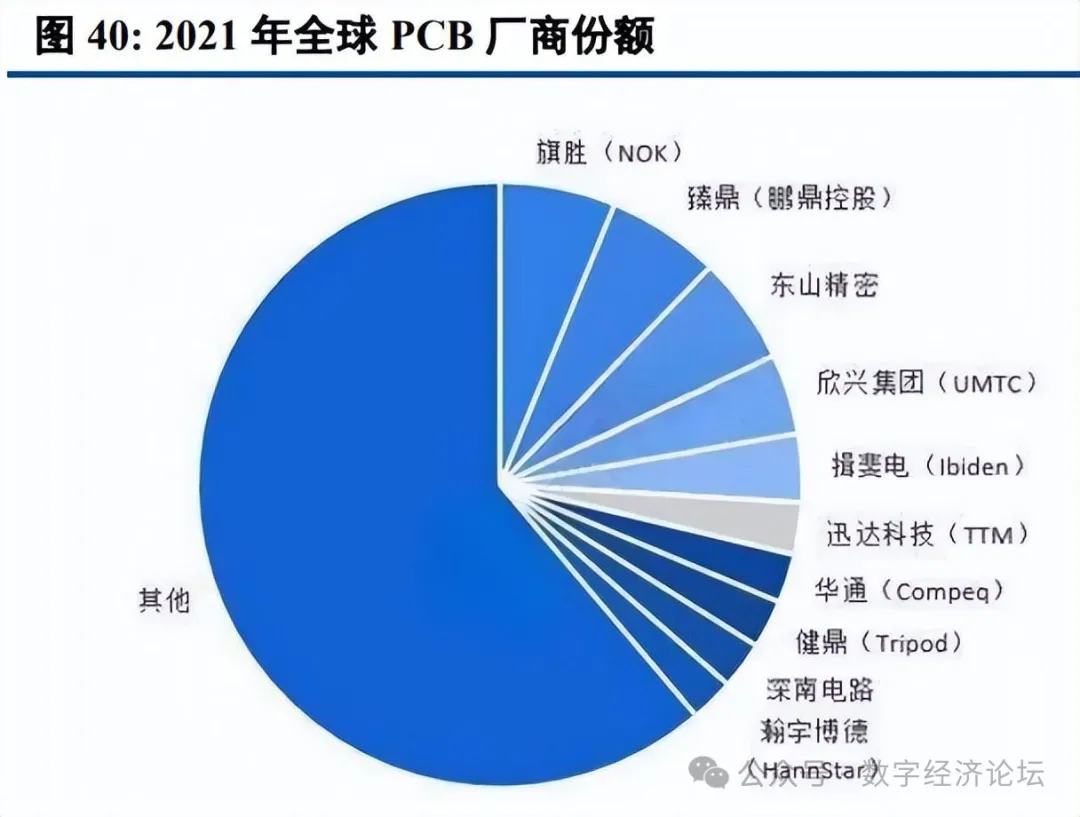
The performance requirements for high-speed PCB products have significantly increased, which will benefit leading manufacturers in terms of market share and profitability improvements. Facing the opportunities presented by AI, leading domestic PCB manufacturers and copper-clad laminate manufacturers are also accelerating their layouts. Currently, some manufacturers have already made good progress and are expected to continue benefiting from AI development.
3.7 IDC Construction: Focus on Intelligent Computing Center Construction and Existing Renovation Opportunities
The integration of computing power technology and artificial intelligence drives the construction of intelligent computing centers, accelerating deployment in China. According to data from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, by the end of 2022, China’s total computing power scale reached 180 EFLOPS, a year-on-year increase of nearly 30%, with intelligent computing power accounting for about 22.8%, a year-on-year increase of 41.4%. The number of operational data center racks exceeded 6.5 million standard racks, with 25 intelligent computing centers in operation and over 20 under construction. By the end of June 2023, China’s computing power scale reached 197 EFLOPS, a year-on-year increase of 30%, with intelligent computing power accounting for 25%, a year-on-year increase of 45%. According to incomplete statistics from IDC, by the end of 2023, there were 129 projects nationwide with the label “intelligent computing center”, with 83 projects disclosing their scale, totaling over 77,000 P, with 49,000 P under construction. According to IDC data, the compound annual growth rate of China’s intelligent computing power scale from 2023 to 2027 is expected to be 33.9%. Third-party data center manufacturers deeply involved in the construction of intelligent computing centers and related power equipment, cooling systems, and other data center infrastructure segments are expected to benefit. In the cost of building data center supporting facilities, power equipment accounts for about 55%-60% (of which diesel generator sets account for about 20-25%, UPS accounts for about 15-20%, and other power equipment accounts for about 20%), cooling equipment accounts for about 15%-20%, civil construction and decoration account for about 20%, and bandwidth and network account for about 5%-10%.
As the low-carbon and green transformation of data centers progresses, there is significant room for renovation. The demand for energy-saving renovations mainly comes from operators, third-party IDC service providers, and financial entities. According to the “China Data Center Industry Development White Paper (2023)” by China Telecom’s Digital Infrastructure Research Institute, the market space for data center energy-saving renovations is expected to exceed 34 billion yuan from 2023 to 2025. Renovations mainly focus on air conditioning, power supply, cabinet relocation, and data center renovations, with air conditioning renovations accounting for over 70%.
Source: Future Think Tank
