 Authors: Zhang Jing1, Geng Liang1, Wang Xudong2 (1. Henan Provincial Toll Highway Management Center; 2. Henan Provincial Highway Network Monitoring Communication Toll Service Co., Ltd.)Abstract: This article explores the development direction of electromechanical operation and maintenance (O&M) from the perspective of improving comprehensive efficiency, focusing on the application and management aspects. It emphasizes the intelligent upgrade of infrastructure, the intelligent transformation of operational management, the intelligent innovation of data applications, and the intelligent transformation of business models, in conjunction with new generation information technologies. The aim is to provide references for the implementation of electromechanical O&M work on highways. As China’s transportation development enters a new stage of intelligence, the continuous development and gradual application of information technologies such as cloud computing, big data, 5G, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things will inevitably promote the deep integration of advanced information technology with transportation, accelerating the transition of the transportation industry from informatization to intelligence. In 2019, the construction of ETC gantries on highways was fully completed, establishing a hardware foundation covering the entire road network. The logical layout and moderately advanced equipment configuration have brought massive data resources to the entire highway network, laying the foundation for establishing a ubiquitous IoT perception system and accelerating the transformation of the electromechanical O&M industry. Meanwhile, the comprehensive implementation of the new highway toll model after the removal of provincial toll stations has also posed new impacts and requirements for electromechanical O&M in the new ETC era. Therefore, this article discusses the new model of electromechanical O&M on highways.
Authors: Zhang Jing1, Geng Liang1, Wang Xudong2 (1. Henan Provincial Toll Highway Management Center; 2. Henan Provincial Highway Network Monitoring Communication Toll Service Co., Ltd.)Abstract: This article explores the development direction of electromechanical operation and maintenance (O&M) from the perspective of improving comprehensive efficiency, focusing on the application and management aspects. It emphasizes the intelligent upgrade of infrastructure, the intelligent transformation of operational management, the intelligent innovation of data applications, and the intelligent transformation of business models, in conjunction with new generation information technologies. The aim is to provide references for the implementation of electromechanical O&M work on highways. As China’s transportation development enters a new stage of intelligence, the continuous development and gradual application of information technologies such as cloud computing, big data, 5G, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things will inevitably promote the deep integration of advanced information technology with transportation, accelerating the transition of the transportation industry from informatization to intelligence. In 2019, the construction of ETC gantries on highways was fully completed, establishing a hardware foundation covering the entire road network. The logical layout and moderately advanced equipment configuration have brought massive data resources to the entire highway network, laying the foundation for establishing a ubiquitous IoT perception system and accelerating the transformation of the electromechanical O&M industry. Meanwhile, the comprehensive implementation of the new highway toll model after the removal of provincial toll stations has also posed new impacts and requirements for electromechanical O&M in the new ETC era. Therefore, this article discusses the new model of electromechanical O&M on highways.
1
New Requirements for Electromechanical O&M Models in the New ETC Era
Currently, ETC is gradually replacing manual toll collection as the main method of highway tolling. The stability of the electromechanical system’s operation directly affects the toll revenue of the road sections, highlighting the importance of electromechanical O&M work. At present, the maintenance workload of outdoor equipment is increasing, the types are diversifying, and the technological level is becoming more advanced, which raises higher requirements for the professional skills of electromechanical O&M personnel. After the completion of the ETC gantries, the Ministry of Transport issued a series of regulations that set higher requirements for response and repair times for various faults. Currently, many provinces have issued relevant documents linking the operational status of electromechanical equipment directly to toll standards. In the new ETC era, the traditional highway electromechanical O&M model can no longer meet the new demands for intensive, intelligent, and refined maintenance, nor can it keep pace with the new trends in the industry. It needs to evolve towards a proactive, safe, intelligent, and efficient new maintenance model to meet the refined management needs of highway operations. Technological innovation provides unlimited possibilities for industry development and is profoundly changing the way practitioners think. With the continuous improvement of informatization levels and the significant increase in the demand for data resource sharing across various fields, various applications developed based on massive data are about to experience explosive growth. Data empowerment will serve as a new lever to enhance highway O&M capabilities, improve intelligent management, elevate data-assisted decision-making levels, promote scientific maintenance expansion, and advance the development of smart transportation.
2
Evolution of Electromechanical O&M Models on Highways
The operational status of electromechanical equipment can be divided into three stages based on technological development: post-failure repair, pre-failure maintenance, and predictive inspection. The core difference among these three operational states lies in the supporting systems behind them, transitioning from manual judgment in post-failure repair to machine judgment in predictive inspection. This leap at the technical level is fundamentally about the collection and empowerment of equipment status data. In conjunction with the new demands for electromechanical O&M in the new ETC era, in addition to the systematic upgrade of the O&M platform, corresponding institutional reforms, including personnel training and management, changes in the structure and scheduling of O&M teams, and management of spare parts, are also important factors to consider. In the face of new challenges for electromechanical O&M work after the removal of toll stations, changing the traditional passive perception, remote emergency response, and experience-based maintenance methods has become an inevitable trend. According to national guiding documents such as the “Digital Transportation Development Plan Outline,” “Outline for Building a Strong Transportation Nation,” and “Recent Action Plan for Intelligent Transportation Development,” it is essential to seize the opportunity of developing the digital economy and building smart transportation in Henan Province, establish the concept of “demand-driven technology, innovation-driven development,” use big data as technical support, and drive innovation boldly. The focus should be on promoting the rapid enhancement of the intelligent O&M system and capabilities of highways through four development goals: intelligent upgrade of infrastructure, intelligent transformation of operational management, intelligent innovation of data applications, and intelligent transformation of business models, ultimately achieving the intelligent development of electromechanical O&M.
3
Data Empowerment for New Models of Electromechanical O&M on Highways
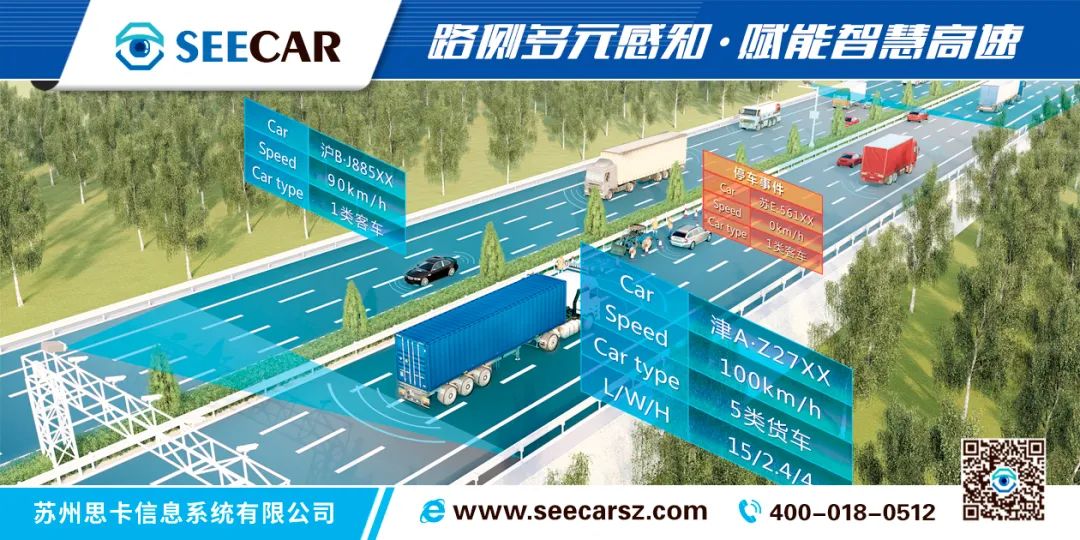
(1) Intelligent Upgrade of Infrastructure 1. Utilize a data middle platform to construct two data closed loops—creating a sustainable development dual engine for intelligent O&M. Establishing an “intelligent, precise, and proactive” operational mechanism for equipment and facilities must rely on a powerful data governance system that aggregates various O&M data scattered across different systems and regions in real-time, forming massive data resources. As the digital infrastructure for future highway O&M, the construction of the data governance system should break away from the previous concepts of directly supplying data warehouses and platforms. It should not overly pursue scale and comprehensiveness, but rather emphasize the intermediate links, focusing on the ability to process and output data. The goal is to maximize the value of highway O&M data resources, using the concept of a “data middle platform” to govern and utilize data, planning small scenarios based on all scenarios, continuously connecting the two closed-loop processes of data and business, and gradually outlining the core capabilities of big data as “real-time, full-volume, and full-network.” A data closed loop refers to the process of continuously providing effective information to various business systems based on metadata, which is then analyzed, summarized, and fed back to the data middle platform, enabling secondary consumption of data resources. Through secondary data backend applications, the front-end system analysis capabilities are continuously optimized, breaking down platform boundaries, organically integrating various business systems, and generating new data assets, thus realizing the process from data to value. From the perspective of the O&M business closed loop, relying on the ubiquitous perception capabilities of highway O&M, fully utilizing various business-related systems and devices, and under the drive of big data and artificial intelligence, real-time acquisition of various equipment’s refined operational status parameters and various O&M events can be achieved, forming a three-dimensional perception capability for equipment, road networks, and events. Supported by the algorithm models provided by the O&M data middle platform, the linkage of judgment, dispatching, and processing can be completed based on situational predictions and event analyses, forming a more complete optimization of the business closed loop. By building a data foundation through the concept of a data middle platform, fully leveraging the core value of the two closed loops, the highway network will ultimately possess the capability of data mining based on deep learning, enabling self-perception, self-learning, and self-correction, allowing the equipment within the highway network to operate stably and orderly, thereby enhancing the overall management level and operational capabilities of highway O&M. 2. Transformation of existing electromechanical equipment—optimizing the configuration of electromechanical systems in the new era. (1) Through the integration of network communication system transformations, create a network backbone with high reliability, high expandability, and high compatibility; (2) Through the modular upgrade of existing electromechanical equipment, relying on embedded and modular sensors combined with IoT gateways, achieve the collection of operational status detection data for electromechanical equipment; (3) By increasing the number of road monitoring systems and enhancing the quality of road video, provide good and stable power supply for monitoring systems by increasing municipal power supply cables, laying a solid foundation for the future realization of a low-cost, full-domain perception system based on image AI recognition. 3. Application of new electromechanical equipment—continuously synchronizing with technological development directions. (1) Gradually promote the application of panoramic camera high-frequency lookout technology at toll stations to achieve real-time analysis of toll station traffic and congestion situations and provide early warnings for low-credit vehicles; (2) On the basis of achieving full coverage of monitoring in service areas, increase analysis and environmental perception devices to continuously improve service levels and create intelligent service areas. 4. Deployment of next-generation sensors—continuously enhancing road network status perception capabilities. (1) Based on technological development and comprehensive cost considerations, deploy millimeter-wave radar, laser radar, etc., to further enhance road traffic status perception capabilities, providing business support for vehicle-road collaboration and autonomous driving technologies; (2) Collaborate with maintenance departments to deploy IoT sensors with key parameter measurement functions at key road sections, bridges, and tunnels. 5. Establish roadside edge computing servers—creating a new intelligent architecture for edge-cloud collaboration. By connecting all devices on the road to small servers set up in the ETC gantry machine rooms, the potential of edge and end computing can be released. Edge computing will continuously provide effective data to the data middle platform and cloud, achieving the goals of saving bandwidth resources, optimizing device path structures, and reducing effective data output time, providing low-latency and high-reliability services, and assisting in the future application of vehicle-road collaboration and autonomous driving technologies.(2) Intelligent Transformation of Operational Management 1. Restructure job placements to enhance professional capabilities. Traditional electromechanical O&M organizational structures generally refer to road administration management models, dividing responsibilities by road sections and forming electromechanical O&M teams to inspect and maintain the three major systems of their respective sections. Some electromechanical O&M teams are only responsible for maintaining toll and monitoring systems, while communication systems are entirely entrusted to professional agencies, and high-voltage parts of the power supply system can be managed by local power departments. Based on the various characteristics and demands of electromechanical O&M in the new ETC era, new electromechanical O&M organizations will face systemic and holistic restructuring. The execution, combat effectiveness, and organizational capabilities of O&M teams need to be further stimulated. Refined job division, comprehensive personnel placement, and high-level talent cultivation will be key development directions for future electromechanical O&M. Refined job division: From the perspective of promoting high-quality development and in conjunction with the changes in electromechanical O&M content in the new ETC era, it is necessary to shift electromechanical O&M management from extensive to refined, deeply dividing O&M work to create multi-skilled business teams with different responsibilities for the same position. Comprehensive personnel placement: Based on the characteristics of numerous ETC gantry points and long lines, further segment the road sections to improve emergency response and enhance equipment control. According to job divisions, reasonably allocate 2-3 personnel to form small electromechanical O&M teams, deploying them in stations, areas, and posts to ensure full coverage and readiness for quick response. High-level talent cultivation: First, focus on high precision and sophistication, cultivating O&M personnel to further explore work methods, striving to become technical experts and O&M elites, thereby solidifying the foundation for development. Second, consider long-term trends in the talent introduction and cultivation process, emphasizing the recruitment and training of versatile comprehensive talents, building a professional, multi-skilled, and efficient talent reserve system that can quickly adapt to modern comprehensive transportation development requirements. 2. Improve work efficiency and reform institutional models. To ensure the implementation of intelligent O&M system reforms, consider establishing a centralized O&M center to promote the flat development of the O&M system. Using the centralized O&M center as a hub, through practical applications of the O&M data middle platform, deeply mine O&M data information, establish and improve predictive warning mechanisms and intelligent dispatching mechanisms for O&M, and promote shared management of spare parts, facilitating the intelligent, collaborative, and efficient operation of the two-level O&M system, effectively improving O&M efficiency. 3. Enhance O&M effectiveness and refine assessment mechanisms. Utilizing a big data assessment platform, introduce a new O&M work assessment mechanism based on refined operational information data, integrating multi-dimensional information such as the severity of equipment faults, accuracy of fault judgments, stability of equipment after maintenance, workload, and response time, forming an automatic evaluation system from grassroots organizations to O&M personnel, achieving data-driven evaluation of O&M effectiveness, guiding and encouraging grassroots O&M teams to conduct proactive inspections, discover issues, and handle them immediately. 4. Enhance collaborative response capabilities and achieve cloud-based data assessment. (1) Based on big data, create profiles of O&M personnel. Using big data concepts, collect comprehensive business information of O&M personnel to create profiles, analyzing past operational data including maintenance content, repair times, single fault recovery rates, and overall business coordination capabilities, scoring their operational capabilities across various systems, and linking this to performance assessments and title evaluations. In O&M work, personnel profiles will be applied to the dispatching mechanism, laying a solid decision-making foundation for transitioning from fixed scheduling to optimal scheduling. (2) Establish an automatic fault assessment and classification system. Through a comprehensive perception system for equipment status, call upon historical maintenance data and O&M knowledge bases from the data middle platform to conduct automated cloud analysis of sudden situations and classify them. Combining with personnel profiles, fault events and information will be accurately pushed to qualified O&M personnel, forming temporary response teams to assist repair personnel in quickly resolving issues. (3) Build an expert assistance system within the industry. Construct a database of technical personnel from design and construction units and equipment manufacturers, linking key personnel information throughout the entire process from manufacturer development and maintenance to project design and construction, providing support for O&M personnel’s accurate judgment, setting up equipment usage information push functions, breaking down communication barriers, and establishing a rapid coordination mechanism for resolving difficult equipment issues.(3) Intelligent Innovation in Data Applications 1. Comprehensive perception system for equipment status. Through various sensors, monitor real-time and historical operational status data of equipment environments, electrical performance, and equipment performance. Employ data mining techniques and deep learning methods to conduct correlation analysis on status parameters, manufacturer-provided thresholds, and equipment maintenance history, uncovering common characteristics among early operational data of various electromechanical equipment faults. Establish deep neural network models to discover valuable status information and patterns in equipment monitoring data from massive datasets. Utilizing reinforcement learning, the decision-making process can be adaptively adjusted, allowing deep neural networks to improve the accuracy of predicting equipment health status through equipment detection data. By analyzing the status data of the entire network, potential issues in highway operations can be corrected in real-time, achieving unified perception through multiple channels, presenting a macro view of equipment operations and micro status, constructing a health indicator system for equipment, calculating and updating various indicators every few minutes, and comparing them with historical data to promptly identify potential hazards, providing data support for predictive maintenance and the scientific formulation of O&M plans. 2. Full lifecycle management system for electromechanical equipment. Manage the entire lifecycle of equipment from selection, installation, operation, maintenance, repair, transformation, and replacement to scrapping, based on in-use equipment, forming a system from basic units of equipment composition to relational data. In addition to entering basic equipment information and historical spatial positioning information, link various operational data, maintenance records, and maintenance costs generated throughout the equipment’s lifecycle to the management system dynamically, forming a ledger. Through economic, reliability, and management cost analyses, assist in formulating maintenance strategies, refining the frequency and content of equipment repairs, and maximizing equipment lifespan while aiding in the formulation of equipment asset replacement strategies. 3. Comprehensive platform scheduling system for O&M. First, globally optimize the allocation of O&M resources. The comprehensive platform scheduling system at the O&M center will design intelligent scheduling algorithm models based on personnel profiles, human resource distribution, fault content, fault locations, and warehouse positions, automatically pushing relevant work order information to the best O&M candidates, ultimately achieving scientific allocation and efficient use of highway O&M resources, making O&M work more efficient and resource-saving. Second, reconstruct the fault resolution process. Relying on the comprehensive perception system for equipment status, classify and process equipment O&M issues at different levels, breaking through the fully automated digital process from hardware perception, intelligent dispatching, O&M operations, business collaboration, warehouse scheduling to effect evaluation. Comprehensive use of technologies such as Beidou positioning, high-precision maps, video monitoring, VR individual equipment, and handheld terminals to facilitate human-machine interaction, constructing an O&M scheduling system that is knowable, perceptible, intuitive, and user-friendly, achieving digital empowerment and digital twin for O&M business.(4) Intelligent Transformation of Business Models 1. Transition from manual reporting of issues to proactive warning. Apply artificial intelligence and deep learning technologies in the field of intelligent discovery of equipment issues, enriching the channels for discovering equipment problems, and creating a fault warning mechanism. Expand the previous single channel of manual reporting and regular inspections to include multiple channels for discovering fault issues, such as AI analysis, automated system inspections, and one-click mobile reporting, achieving a shift from passive handling of faults to proactive warnings. 2. Transition from delayed handling of issues to immediate resolution. First, quickly perceive and discover faults, optimizing the dispatch of widely covered O&M personnel through the O&M personnel comprehensive platform scheduling system to achieve rapid response to faults. Second, through the accumulation of equipment repair data and the sedimentation of O&M experience, continuously optimize and improve the maintenance knowledge base of the data middle platform, providing assistance and repair guidance to frontline maintenance personnel, rapidly enhancing their business capabilities and completing quick resolution of equipment faults. 3. Transition from human experience to data-assisted judgment in O&M strategies. Through the construction of the data middle platform and supporting organizational mechanisms, promote the integration and utilization of O&M data and resources, build an O&M data algorithm analysis platform, enhance the data mining and analysis capabilities of operational management units, and provide analytical ideas for addressing equipment O&M challenges, gradually achieving data-based operational management decisions and equipment O&M models, and establishing a modern management system for O&M.
4
Electromechanical O&M Promoting New Developments in Intelligent Highways
With the gradual application of new technologies such as big data, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, 5G, and the Internet of Things in the highway sector, how to govern and utilize data and achieve high-quality development for operational management units through data empowerment will become the new mission of electromechanical O&M in the new era. Current issues include: first, difficulties in integrating transportation data resources; second, insufficient demand for big data applications in transportation; and third, a lack of big data application products. For enterprises’ internal O&M businesses, based on their understanding of the professional field and the accumulation of skills and experience, specific technical paths are relatively easy to explore. However, it still requires 5-8 years of data accumulation from the equipment lifecycle or even technological cycles to form a highly reliable automated monitoring and maintenance system for electromechanical equipment. In providing decision-making and public services, not only is the integration of massive data required, but also the need for professional perspectives to judge key data. Currently, theories in the field of artificial intelligence, such as deep neural network algorithms, are still in the “black box” stage. Even if accurate predictions can be made, the internal data logic of the conclusions cannot be understood, making it difficult to derive specific solutions to problems. Based on the current level of foundational theories in digital technology and the characteristics of the development era, innovative concepts and precise diagnostics must shift from the traditional emphasis on large systems and platforms to a top-down design approach, focusing on developing a platform architecture based on integration and expansion, continuously enriching big data applications oriented towards solving practical problems, and forming a steady advancement of intelligent development from the value excavation of transportation big data to widespread application. The focus should be on quickly constructing a series of “small but excellent” applications based on simple needs at various business points, rapidly completing algorithm iterations and upgrades through the powerful computing power of cloud platforms, allowing effective data to feedback into the data middle platform, forming a data closed loop. On one hand, new complex applications can be generated from the secondary produced data, and on the other hand, while constructing various applications, the accumulation of data from all aspects can be completed, so that when breakthroughs in artificial intelligence technology occur, the accumulated data can quickly release productivity and accelerate the application of new technologies. In summary, to achieve efficient utilization of data and rapid iteration of systems and applications, returning transportation to its essential needs of safety, comfort, and smoothness, three major development directions for new electromechanical O&M applications are proposed:(1) Promote Sharing of Transportation Big Data Platforms and Application of New Technologies 1. Improve traffic situation prediction models through data sharing. Break down data barriers in the new environment of data sharing, continuously strengthen data integration with urban brains in various cities, and connect traffic flow, vehicle type structure, and other situations around urban highway toll stations to the data middle platform. Utilizing the powerful computing power of cloud platforms, improve the prediction models for traffic situations on urban peripheral highways. 2. More accurate road traffic predictions and toll revenue forecasts. Starting from major road sections that significantly impact network traffic changes, link adjacent cities one by one based on the prediction effects of urban highway traffic situation models, enhancing the accuracy of road traffic predictions from points to lines and then to areas, gradually achieving a technological leap from comprehensive perception of traffic conditions to precise prediction of traffic situations, and through long-term data accumulation, achieving more accurate road traffic predictions and toll revenue forecasts.(2) Enhance Road Condition Assessment Capabilities to Improve Safety Levels In terms of traffic facilities, improve the ability to assess the health status and service levels of traffic facilities, thereby providing auxiliary decision-making information for formulating scientific and reasonable construction and maintenance plans. In terms of traffic management, develop applications for early warning of traffic safety risks, analyzing congestion causes, and optimizing traffic timing, assisting in achieving refined traffic control services.(3) Explore the Application of Road Testing Equipment to Enhance Service Capabilities Provide comprehensive support for vehicle operation and supervision through data management and decision-making. 1. Based on the ETC gantry system, pilot new OBU applications to timely push information about upcoming road conditions, assisting in guiding travel; 2. Promote data sharing to real-time push road operation status, aiding the development of internet enterprises and providing multi-faceted travel services; 3. Build Beidou ground enhancement stations and explore roadside facilities based on 5G to further enhance vehicle positioning accuracy and expand vehicle networking applications.
5
Conclusion
Compared to the previously narrow scope of electromechanical O&M work, under the new circumstances, electromechanical O&M will inevitably first integrate with new information technologies. Therefore, addressing the business’s own needs must be the primary task, innovating digital empowerment and applications, and continuously promoting the intelligent development of electromechanical O&M. The digital collection system for equipment is the cornerstone of data empowerment for high-quality development of enterprises. The electromechanical O&M industry is a backbone force in constructing intelligent management systems, intelligent decision-making systems, and the goal of all-weather autonomous driving in the development of smart highways. In the long run, it will inevitably drive changes in the highway industry. Therefore, it is necessary to re-examine and optimize the electromechanical O&M model from a new technical perspective, starting from management needs, empowering industry development with data, and continuously contributing to the development of intelligent transportation in China.(Original text published in the 10th issue of “China Transportation Informatization” in 2020)WeChat Editor | Hu Lihua
Editor-in-Chief | Liu Ruijian
