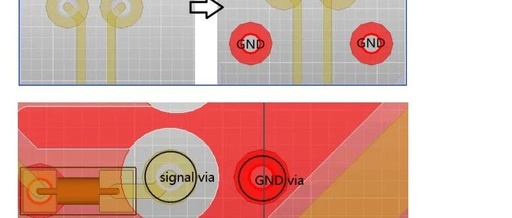
I2C Bus Design
1. First, let’s discuss open-drain output and push-pull output First, watch the video explanation: The following video is from Guo Tianxiang Push-Pull Output Structure and Principle: A push-pull output circuit consists of two complementary transistors (usually an NPN transistor and a PNP transistor). In this structure, when the input is high, the upper transistor (like … Read more