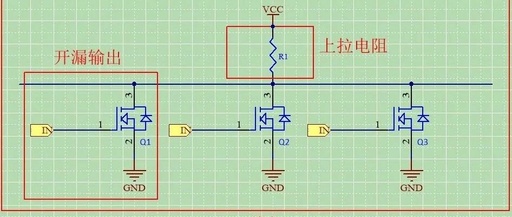
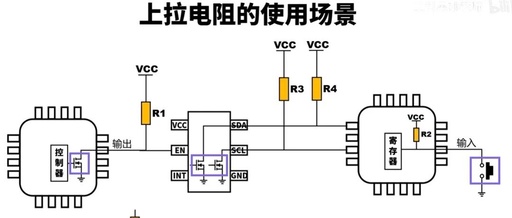
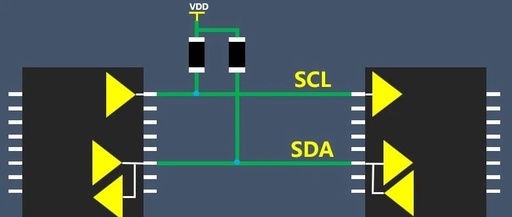
Why Use Open-Drain Output and Pull-Up Resistors in I2C?
Why do we need pull-up resistors in I2C? Because it uses open-drain output. Why is it open-drain output? The I2C protocol supports multiple master devices and multiple slave devices on a single bus. If push-pull output is used instead of open-drain output, it could lead to short circuits between master devices. Therefore, the bus generally … Read more