How Are Circuit Boards Made? Equipment Needed in Production
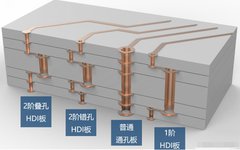
How are circuit boards made? The production process of PCB boards can be roughly divided into: Printed circuit board—inner layer circuitry—lamination—drilling—plating through holes (first copper)—outer layer circuitry (second copper)—solder mask green paint—text printing—contact processing—shaping and cutting—final inspection and packaging. So there are many devices involved; what equipment does PCB need? Generally, the production of PCB … Read more