01SD Card
SD Card is the abbreviation for Secure Digital Card, which translates directly to “secure digital card.” It is a proprietary non-volatile storage card format developed by the SD Association for portable devices. Due to its small size, fast data transfer speed, and hot-swappable features, it is widely used in portable devices.
The standard was introduced in August 1999 by SanDisk, Matsushita Electric, and Toshiba as an improvement over the MultiMediaCard (MMC), and has since become an industry standard. These three companies formed the SD-3C LLC, which licenses and enforces the intellectual property related to SD storage cards and SD host and accessory products.
The two companies also established a non-profit organization, the SD Association (SDA), in January 2000 to promote and create SD card standards. The SDA now has about 1,000 member companies. The SDA uses multiple trademark logos owned and licensed by SD-3C to enforce compliance with its specifications and ensure user compatibility.
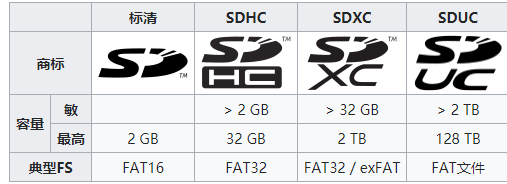
SD Card Capacity
Secure Digital includes five series of cards that offer three different sizes. These five series are the original standard capacity (SDSC), high capacity (SDHC), extended capacity (SDXC), ultra capacity (SDUC), and SDIO, which combines input/output functions with data storage. The three form factors are standard size, micro size, and mini size.
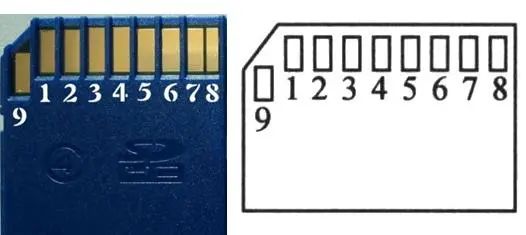
SD Card Appearance
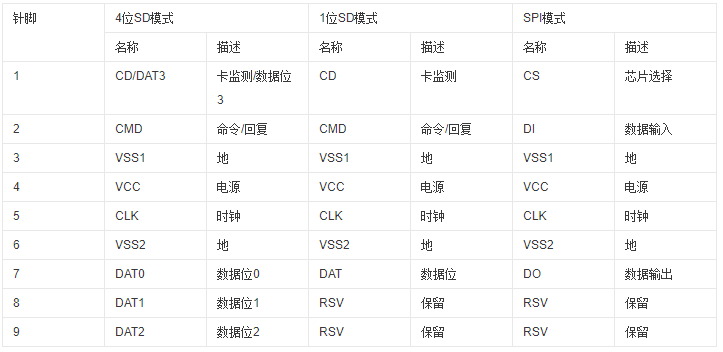
Drive Modes
SD cards have two drive modes: SPI mode and SDIO mode. They use different interface signals. In SPI mode, only four signal lines of the SD card are used, namely CS, DI, SCLK, and DO (which are the chip select, data input, clock, and data output of the SD card).
Transfer Modes
SD cards support three transfer modes: SPI mode (independent serial input and output), 1-bit SD mode (independent command and data channels with a unique transfer format), and 4-bit SD mode (using additional pins and some reconfigured pins. It supports four-bit wide parallel transfer).
Pin definitions for the three modes of SD cards:
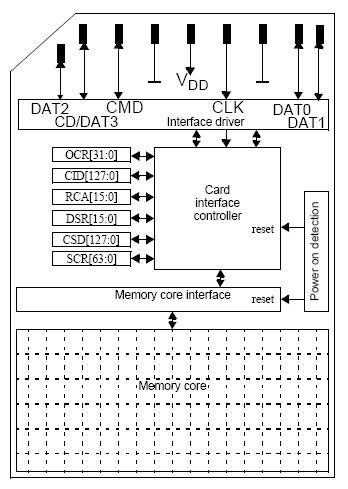
The internal structure and pins of the SD card are shown in the following diagram:
Write Protection Switch
On the right side of the SD card, there is usually a switch, which is the write protection switch. When the write protection switch is turned down, the SD card will be write-protected, and data can only be read. When the write protection switch is in the up position, data can be overwritten. Since this protection switch is optional, some brands of SD cards do not have this protection switch.

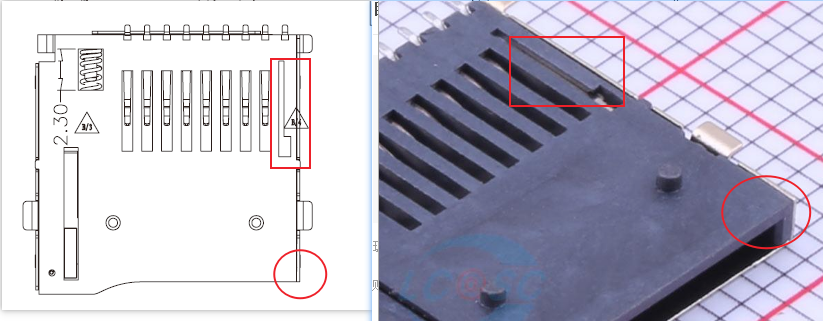
Schematic Diagram
Although the standard SD card has nine pins, the schematic diagram of the SD card slot is not the same as the SD card!! Therefore, the schematic diagram generally has 11 pins or more.

Generally, pin 10 is used to detect whether the card is inserted, pin 11 is for detecting card write protection, and other pins are used to secure the card slot. In simple applications, these two pins can actually be ignored, which is why the number of pins in the schematic diagram of the SD card varies.
Typical Circuit Connection
SDIO connection mode
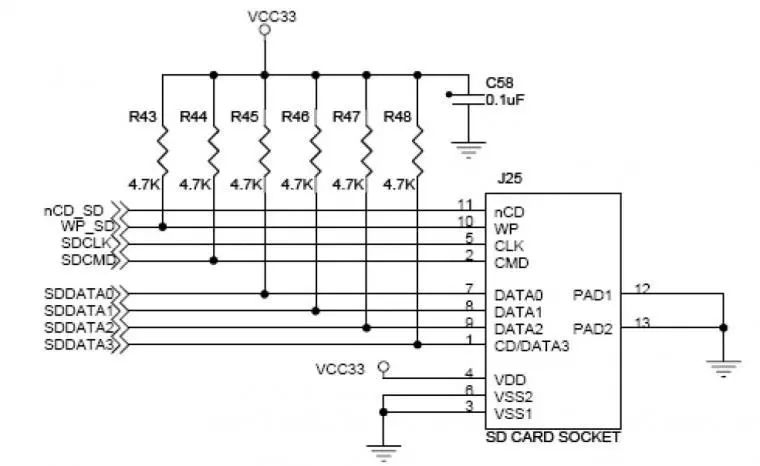
SPI connection mode
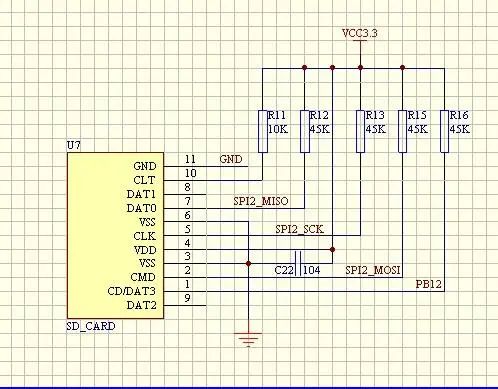
02TF Card
Micro SD Card, originally named Trans-flash Card (TF Card), was officially renamed Micro SD Card in 2004, invented by SanDisk. Micro SD Card is an extremely small flash memory card, with a format derived from SanDisk’s creation. Originally, this memory card was called T-Flash, later renamed TransFlash; it was renamed Micro SD because it was adopted by the SD Association (SDA).

Its dimensions are 15mm x 11mm x 1mm, roughly the size of a fingernail, making it the smallest memory card currently available. It can also be used in an SD card slot via an SD adapter. Currently, Micro SD cards offer capacities of 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1G, 2G, 4G, 8G, 16G, 32G, 64G, and 128G (During the MWC 2014, SanDisk broke the tradition of a maximum storage capacity of 64GB by officially releasing a Micro SD XC storage card with a capacity of up to 128GB).
Micro SD is smaller and can be converted for use as an SD card. The circuit and pins of the TF card are the same as those of the SD card.
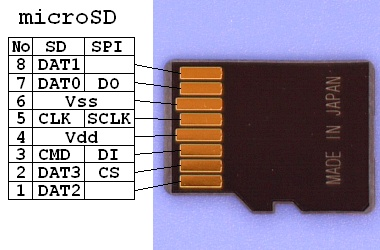
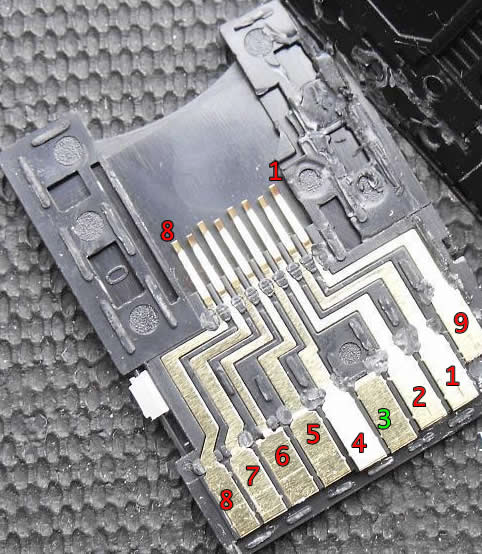
TF Card’s PCB Packaging
From the diagram below, it can be seen that the pin near the circle is not connected to the TF.
Therefore, when making TF packaging and circuits, pin 9 is left floating.
03TF to SD Card
TF cards can be used as SD cards through an SD card converter.

Internal Circuit
04Precautions
TF card + card holder can also be used as an SD card, but a large portion of TF cards do not support SPI access mode. Therefore, when driving an SD card in SPI mode, it is advisable to choose a larger card (SD card) rather than a TF card.
Recommended to follow 👇 the public account below to learn more about electronic technology knowledge!

-
Keil software simulation and hardware simulation
-
This understanding of PWM makes it hard not to comprehend!
-
Huawei comic science popularization | What is DSP?
-
General software and hardware version number naming conventions
-
Divine explanations of the four major communication interfaces: UART/I2C/SPI/1-wire
-
This constant current circuit design scheme, you may not have used before
-
Top 10 microcontrollers favored by engineers in the USA in 2021
-
What are the differences between transistors and MOSFETs? Should I use MOSFETs or transistors?