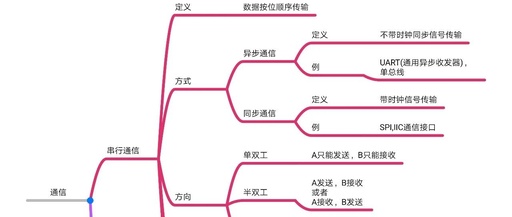
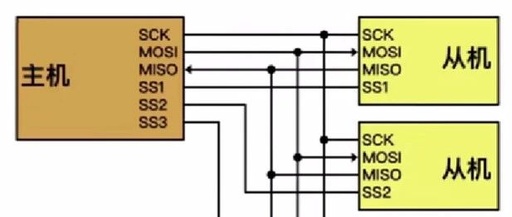
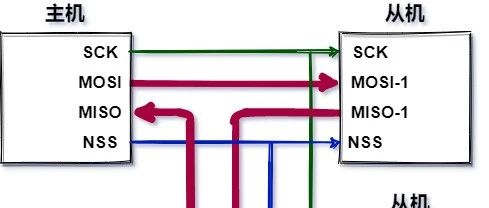
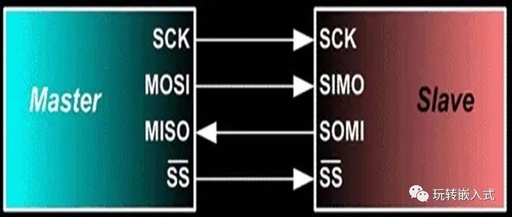
Detailed Explanation of UART Project – 08 Simulation Framework
Click to follow the above “Two Monkey Society“ Set as “Top or Star“, and the valuable content will be delivered first. IC Monkey | Two Monkey Society Introduction The previous articles have covered the design part, and this article will analyze the simulation part of the code. This article mainly explains the overall simulation method … Read more