When learning about fire alarm systems, many people encounter the professional terms “Two-Wire Bus”, “Two-Wire System”, and “Four-Wire System”. So, what do they mean? What are the differences and application scenarios? Today, we will quickly clarify these common concepts!

1. Starting from the basics: Where do the Two-Wire Bus, Two-Wire System, and Four-Wire System come from?
To understand these terms, one must first realize that they all relate to connection methods. They describe how devices communicate, receive power, and transmit signals.
For a fire alarm system to operate normally and stably, it must achieve communication + power supply.
The bus is a unique concept in fire alarm systems, connecting the fire control panel to external devices. (Refer to the system diagram)
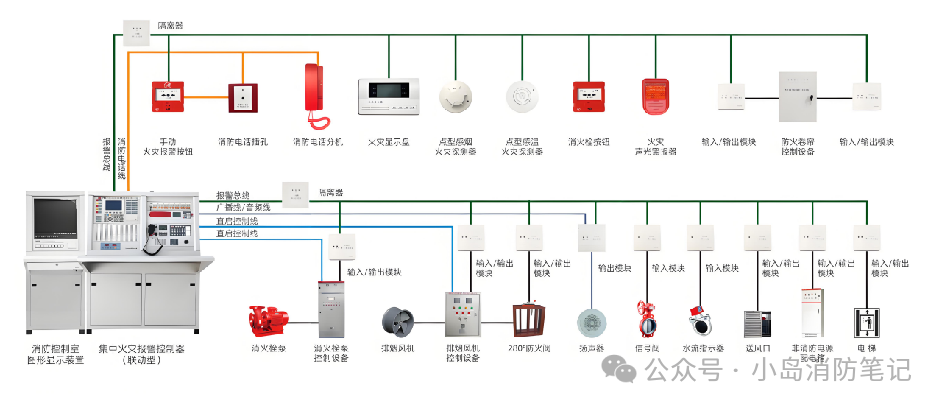
-
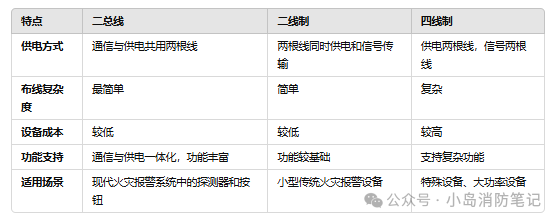
Two-Wire Bus: Refers to a communication method where data and power are transmitted over the same pair of wires.
-
Two-Wire System: A power supply method where devices receive power through two wires to perform basic functions.
-
Four-Wire System: Another power supply method where two wires are used for power and two wires for signal transmission.
1. Two-Wire Bus: One Line for Communication and Power Supply
Definition:
The two-wire bus system is widely used in modern fire automatic alarm systems, and there are five major types of fire-fighting devices that we refer to as two-wire bus type devices, such as smoke detectors, heat detectors, manual alarm buttons, fire hydrant buttons, and input modules. These products do not depend on the manufacturer or type and will always only require two wires (except for fire telephone lines, which are independent systems).
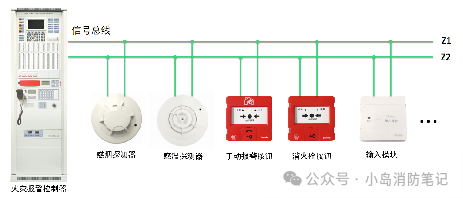
Common Understanding: It’s like a highway where both electric vehicles (power supply) and delivery vehicles (communication) run, achieving “one line for dual use.”
Summary: The above devices share a common trait: low power consumption. Whether in alarm or monitoring state, the two wires can achieve power supply + communication, and these two wires are called the two-wire bus.
2. Two-Wire System: Two Wires for Power Supply and Basic Functions
Definition:
Two-wire systems are different from two-wire buses, which people often confuse. The two wires associated with two-wire bus devices are called the two-wire bus, while the two-wire system mainly refers to devices and systems, particularly high-power devices such as audible-visual alarms, fire display panels, and input-output modules. In this context, both communication and power supply are possible.
Before clarifying the two-wire system, we should first discuss the four-wire system; continue reading:
3. Four-Wire System: Separate Power Supply and Signal Transmission
Definition:
In a four-wire system, devices require two wires for power and another two wires for signal transmission. This is due to high power consumption, where the two-wire bus cannot meet the application needs, and it is mainly applied to control-type devices (such as input-output modules).
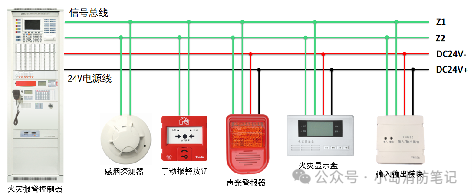
Common Understanding: It’s like having dedicated power supply lines and dedicated communication lines on a road, preventing interference and clearly defining roles.
Summary: Low-power devices do not differentiate between two-wire and four-wire; it is the high-power devices that do. The four-wire system is the traditional wiring method, and before 2020, most were four-wire systems (audible-visual alarms, modules, etc.).
4. Two-Wire System: System Upgrade, Two Wires for Power Supply and Basic Functions
Definition: The two-wire system is in contrast to the four-wire system. After 2020, the domestic market has largely transitioned to a full two-wire system, bringing many benefits to construction and saving a lot on wiring costs. We also refer to 2020 as the year of the two-wire system.
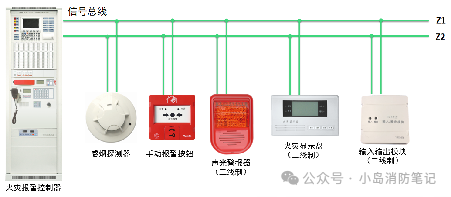
Implementation Method:
With advances in technology, developers have improved the load capacity of the main unit and reduced the power of front-end devices. This balance now allows high-power devices to operate normally with just two wires, which we call two-wire devices, and the system with these devices is called two-wire system.
5. Final Summary
1. Whether in a two-wire system or a four-wire system, we refer to the two signal wires Z1 and Z2 as the two-wire bus; the two-wire bus mainly refers to the wires, and since it consists of two wires, it is also called the two-wire bus.
2. High-power devices (audible-visual alarms, modules, etc.) require a pair of two-wire buses, plus a 24V power line, thus these devices are called four-wire systems.
3. After upgrading four-wire devices to DC24V, they can be eliminated and still function normally; these devices are called two-wire devices, and the system is called the two-wire system.
Through this article, I hope you have a clearer understanding of the “Two-Wire Bus”, “Two-Wire System”, and “Four-Wire System” in fire alarm systems. Mastering these concepts will not only help you understand design blueprints but also assist you in making wiser decisions when selecting and maintaining equipment!
If you find this article helpful, don’t forget to follow us for more fire safety knowledge waiting for you to unlock!
Little Island Fire Notes | Making Fire Safety Easy to Learn