China is a country with severe water shortages. Although the total amount of freshwater resources is high, the per capita availability is only 2200 cubic meters, ranking 121st in the world, making it one of the countries with scarce per capita water resources. According to statistics, approximately 360 million rural residents in China drink water that does not meet standards each year, making water resources a major strategic issue for sustainable development and long-term security in China. The vast land area of China, with large spans and significant regional climate differences, leads to uneven distribution of water resources. The basic situation is that there is a high population and low water supply, with more water in the south and less in the north, more along the coast and less in the inland, and more in mountainous areas and less in plains, along with great difficulties in water resource development. The most effective protective measure is to enhance the public’s awareness of water conservation and control water usage from the source.
Historically, there have been many management pain points in China’s water supply industry. Firstly, traditional mechanical water meters rely on manual readings, and with the continuous rise in labor costs, this has significantly increased the costs for water companies. Additionally, manual readings have high error rates and long settlement cycles. Secondly, as the national and public awareness of resource conservation gradually increases, there is a growing emphasis on water resource conservation issues. However, traditional mechanical water meters cannot monitor water usage in real time and cannot detect leakage anomalies, among other problems.
To address these issues, smart water meters have emerged and are gradually being widely applied in people’s daily lives. The biggest difference between smart water meters and traditional mechanical water meters is that smart water meters automatically connect to the network for readings through mobile communication networks, eliminating the need for manual readings. Moreover, this remote reading is more accurate than manual readings and can be complemented by intelligent management systems, facilitating centralized, visualized, and automated monitoring of residents’ water usage, thereby improving the efficiency of management personnel. Smart water meters integrate low-power, multi-channel embedded wireless digital transmission modules that can transmit information via wireless channels. The water meter can form a home water monitoring system with cloud platforms and mobile apps, enabling functions such as remote readings, payments, and real-time monitoring. In the future, with the gradual implementation of relevant policies and the urgent need for resource conservation and the construction of smart cities, smart water meters will gradually replace mechanical water meters, ultimately completing the transition. Narrow Band Internet of Things (NB-IoT) has advantages such as wide coverage, low power consumption, high communication efficiency, and low cost, with network coverage capabilities reaching 164 dB, enabling data communication in underground buildings. At the same time, NB-IoT is based on cellular networks, with a channel bandwidth of 180 kHz, allowing for remote data reading of multiple instruments such as electric meters and water meters. This article focuses on the home water intelligent monitoring system based on NB-IoT smart water meters, addressing the current problems of high costs, high labor intensity, high error rates, and disputes associated with traditional mechanical water meter readings.
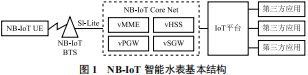
The smart water meter system typically embeds a SIM card, mainly to implement data information storage and user identity recognition functions. The operator provides the mobile user identification code, authentication algorithm, keys, and other necessary information to the SIM card vendor, who writes this information into the card. The operator sells the SIM card to the water department or water meter company, embedding it in the smart water meter. The water company requests the operator to activate the SIM card, power it up, and authenticate it, connecting it to the network to enable data transmission and reception. The NB-IoT protocol introduces two data transmission optimization schemes, CP and UP, to adapt to the characteristics of data transmission.
(1) The CP scheme is characterized by not using wireless data carrying methods but mainly transmitting data through NAS signaling, embedding user data into control plane data for transmission, and processing the signaling through MME before transmitting it to the IoT platform. When the amount of data to be transmitted is small, the transmission speed is relatively fast.
(2) The UP scheme is similar to the LTE system data transmission mode but adds RRC status. When a data transmission request arrives, it automatically establishes the corresponding bearer, allowing data transmission via the user plane. If no data transmission request is received, it temporarily suspends the previous user plane transmission, and during the next transmission, it can quickly restore the suspended user plane connection. Compared to mobile networks, the UP scheme is suitable for infrequent transmissions with substantial content, featuring low power consumption.
NB-IoT is a new generation of wireless communication technology with low power consumption. The NB-IoT operates in licensed frequency bands, offering stronger penetration capabilities and broader coverage. In complex environments, it can ensure effective and reliable transmission of business data. The system significantly improves the serious issue of communication packet loss.
NB-IoT has a very promising development outlook in China, with major operators beginning to build NB-IoT networks, promoting and developing nationwide based on existing narrowband IoT network resources. Operators leverage the existing dedicated IoT network systems to set up dedicated IoT network elements, segregating them from traditional networks to prevent external attacks, effectively controlling access permissions for smart water meter terminals, ensuring secure and stable operation of client networks at all levels.
(1) Remote Meter Reading. The IoT platform can display household water usage data and connect to the payment system, saving the manpower spent on manual billing while reducing errors generated during manual measurements, achieving remote meter reading.
(2) Leakage Monitoring System. The platform can monitor the water meter and pipes; if leakage or pipe bursts occur, the IoT platform can issue an anomaly alert, and the relevant water department will notify the user of their pipe condition in a timely manner, reducing losses.
(3) Real-time Inquiry. Users can query their water usage online; the platform visually displays the household’s water usage hourly, daily, monthly, and yearly, and can graphically analyze this data, allowing users to enhance their water conservation awareness through data comparison. Additionally, the system will provide timely alerts for sudden increases in water usage, helping users check for potential leaks.
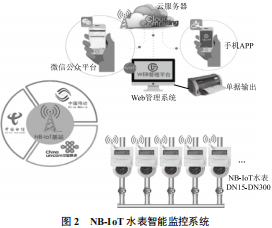
The system is centered around NB-IoT and is based on IoT technology infrastructure. It collects information on the status of water meters and pipes through sensors and chips, then uploads the obtained data to the server via NB-IoT, achieving visualization and automated operation of smart water meters. Users can log into the cloud platform via mobile phones or computers to check their water usage in real time and make timely payments, saving manpower and resources while improving the efficiency of water companies. Water company personnel can also promptly notify users of anomalies detected by the IoT platform regarding water meter monitoring, reducing user losses. This system realizes the monitoring, collection, and processing of water meter information, breaking the isolation of traditional water meters and aligning with the trend of “the Internet of Everything” in intelligentization, promoting the upgrade of smart water meter technology. Additionally, the cloud visualization feature of this system allows users and water companies to visually see water usage, reminding people to conserve water through fluctuations in usage over time, thereby enhancing the public’s awareness of water resource protection. The home water intelligent monitoring system based on NB-IoT smart water meters is of great significance in reducing resource wastage.
References
[1] Shuai Li. Design and Implementation of NB-IoT Smart Water Meter Reading System. Information and Computer (Theoretical Edition), 2021, 33(11): 94-96.
[2] Xinxin Wang, Ling Yao. Exploration and Research on Technologies Related to Automatic Meter Reading Systems for NB-IoT Water Meters. Instrument Technology, 2020, 49(10): 1-4.
[3] Xiang Yu, Lingyou Peng, Wei Xiong, et al. Research on the Application of NB-IoT Smart Water Meters in Smart Water Services. Water Supply and Drainage, 2020, 56(S1): 906-910.
[4] Runhua Xie, Bin Wang, Yunming Zhang, et al. Monitoring and Visualization Applications of IoT Sensors for Smart Cities. IoT Technology, 2018, 8(3): 18-20.
[5] Dan Tan, Zhongping Tian, Wentao Zhang. Analysis of the Application of NB-IoT Technology and LoRa Technology in Intelligent Meter Reading. IoT Technology, 2018, 8(4): 76-78.
[6] Wuzhi Jiang, Nafeng Xu, Weijie Zhong, et al. Research and Design of IoT LoRa Smart Water Meters. IoT Technology, 2018, 8(8): 77-79.
[7] Yaozu Li, Jianhua Pan, Bohao Li, et al. Research on the “Three Meters in One” Collection and Extended Application Based on NB-IoT Technology. Construction Science and Technology, 2017, 16(16): 22-23.
[8] Nuo Li. Research on the Application of NB-IoT Technology in Smart Water Meter Field. China New Communication, 2018, 20(5): 123-125.
[9] Jian Deng, Yanfang Chen. Analysis of IoT Technology and Application Scenarios Based on NB-IoT Networks. Jiangxi Communication Technology, 2017, 38(4): 12-14.
[10] Hualiang Liu, Jian Sun, Tao Zou, et al. Research and Design of Smart Water Meter Terminal Systems Based on NB-IoT. Electronic World, 2020, 42(8): 153-154.
[11] Qi Wu. Application of NB-IoT Technology in the Field of IoT Smart Water Meters. Southern Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(2): 195-196.
[12] Chanye Han, Weiwei Zhang. Design of Smart Home Systems Based on NB-IoT. IoT Technology, 2021, 11(2): 69-71.
[13] Huping Liu. Application of NB-IoT Technology in the Field of IoT Smart Water Meters. China New Technology New Products.