As cars enter the era of electrification and intelligence, the terminology arising from product transformation confuses consumers. For instance, terms related to chips such as CPU, GPU, NPU, SoC, etc. These parameters are particularly important, even rivaling some core component configurations from the era of fuel vehicles.
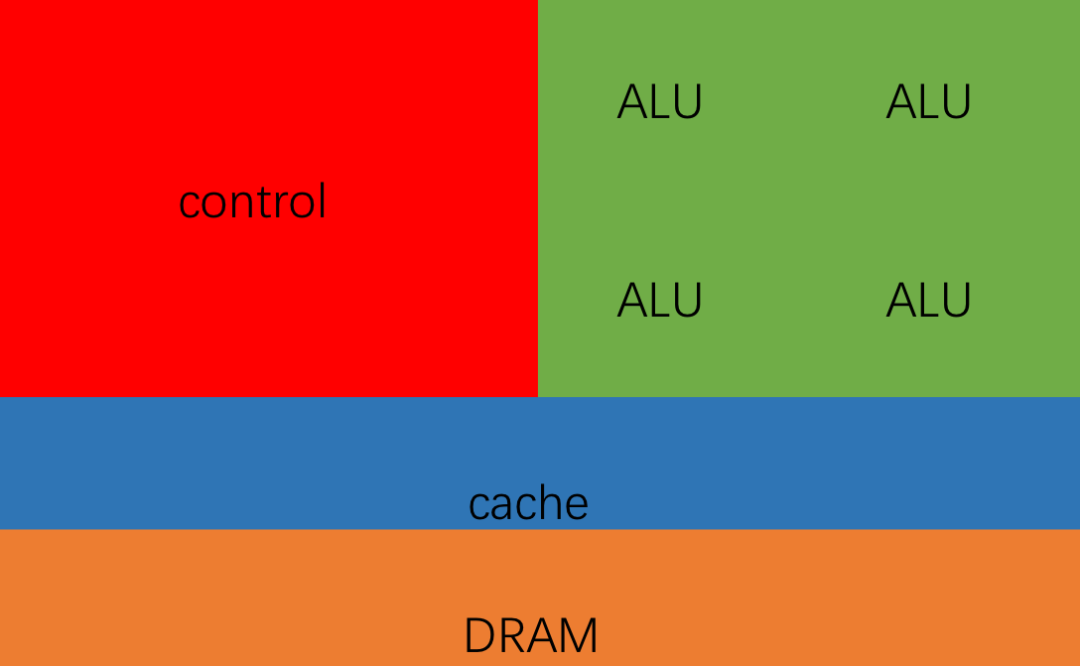


Taking NVIDIA Orin as an example, the CPU core of Orin has 12 Cortex-A78 cores (code-named Hercules), and the GPU is Ampere.
We can take NIO ET7 as an example.
The CUBA unit: NIO ET7 is equipped with four NVIDIA ORIN chips (nearly 1000 TOPS), and its CUBA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) unit reaches 8096, close to the 8704 CUBA cores of the RTX3080 graphics card.
Transistor count: The number of transistors in the NIO ET7 equipped with four NVIDIA ORIN chips is 68 billion, while the transistor count of Apple’s A14 chip, which is known for its high performance, is 11.8 billion.
Data processing capacity: The Tesla FSD chip has an integrated image processor ISP that can process images at a maximum speed of 2.5 billion pixels per second, roughly equivalent to filling 21 1080P HD screens with 60 frames of images.
NPU: The neural processing unit NPU of the Tesla FSD chip has a 32MB cache, comparable to the total cache of 33.75MB of the Intel Core i9-9980XE, which is priced at 16,999 yuan.
2. Intelligent Cockpit Chips
The main chip of the intelligent cockpit is generally referred to as SoC – System on Chip, which includes CPU, GPU, AI engine, as well as ISP for processing various cameras, supporting multiple displays DPU, integrated audio processing, etc. Additionally, the third generation digital cockpit system is equipped with personalized computer vision and machine learning application platforms, including AI accelerators, etc. At the same time, Qualcomm has also integrated advanced Wi-Fi and Bluetooth technologies into the SoC, supporting the hottest Wi-Fi6 and Bluetooth 5.1 technologies.
When it comes to intelligent cockpit chips, one must mention Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8155 chip.
Qualcomm’s 8155 chip is a powerful intelligent cockpit SoC chip, officially named SA8155P. It is manufactured using 7nm technology, has eight CPU cores, and a computing power of 8 TOPS, meaning it can perform 80 trillion operations per second. It can support up to six cameras and connect to four 2K screens or three 4K screens, supporting Wi-Fi6, 5G, and Bluetooth 5.0.
It is worth noting that the 8155 chip does not have a dedicated NPU core; AI calculations are primarily completed through an AI engine composed of DSP, CPU, and GPU. Among them, Hexagon 690 has an AI computing power of 7 TOPS, and the total AI computing power of CPU and GPU combined is 8 TOPS. In terms of manufacturing process, Qualcomm 8155 uses TSMC’s N7 process, which is the first generation of 7nm technology, and belongs to the same generation of products as Snapdragon 855 and 855+.
3. MCU for the Entire Vehicle Domain
Before the widespread adoption of intelligence, early cars were purely mechanical products. At that time, engines did not have electronic controllers, and window controls were purely mechanical, so there was no need for any chips, let alone computing power or image processing.
In the past few decades, mechanical cars have gradually become intelligent. Each time a new function is added, an MCU (Micro Control Unit) is required. This development method has led to a situation where there are too many MCUs, resulting in messy wiring harnesses. This has also contributed to the phenomenon of traditional car manufacturers facing chip shortages.
Of course, don’t underestimate MCUs; the semiconductor companies that support this field are all well-known. If we compare automotive MCU chips, indeed, in terms of performance and manufacturing process, mobile phone chips are much more advanced!
Source: Electric Horse
Scan to join the automotive electronics group and share technical insights in the automotive electronics industry.
