Automobiles are the largest and most promising application scenario in the domestic MCU industry. The MCU is the core chip for automotive control. With the development of smart vehicles, users continually raise new demands for the safety, stability, and intelligence of cars. The realization of each in-car function requires the stable support of complex chipsets and algorithms, and MCUs will play an even greater role. This development trend presents both challenges and opportunities for the domestic automotive-grade MCU industry.
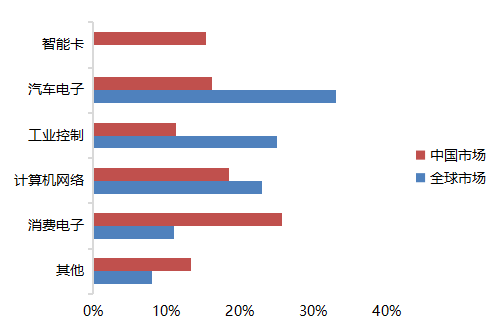
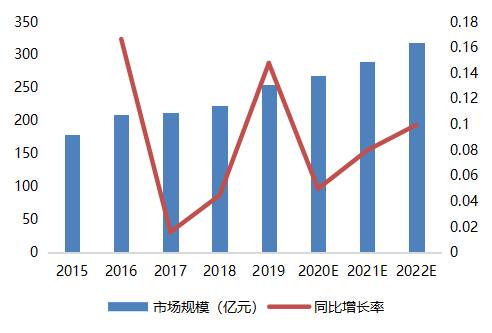
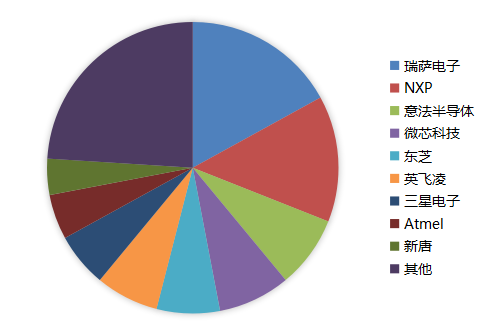
The domestic MCU industry has a market space worth hundreds of billions, but the competitive landscape is highly concentrated, with the top eight manufacturers occupying nearly 90% of the market share, all of which are foreign companies. In terms of automotive applications, the domestic MCU market is still monopolized by foreign brands. Both in terms of market share and technological advancement, overseas leading enterprises currently hold an absolute advantage. Although there are quite a few domestic MCU companies, most focus on consumer-grade markets, and very few can effectively replace imports in industrial control and automotive electronics. Therefore, domestic enterprises urgently need to break through technical barriers, connect the industrial ecosystem, and gradually achieve domestic substitution.
With the joint effects of policy support, supply and demand promotion, technological iteration, and financial support, the domestic substitution of automotive-grade MCUs is imperative. The competition in the domestic automotive-grade MCU market mainly exists between overseas leading enterprises and local companies. Some local companies have launched automotive-grade 32-bit MCUs and are gradually achieving mass production. Domestic companies are expected to continue breaking through technological barriers, aligning with international standards, and connecting the industrial ecosystem, thereby changing the long-standing monopoly of overseas leading enterprises.
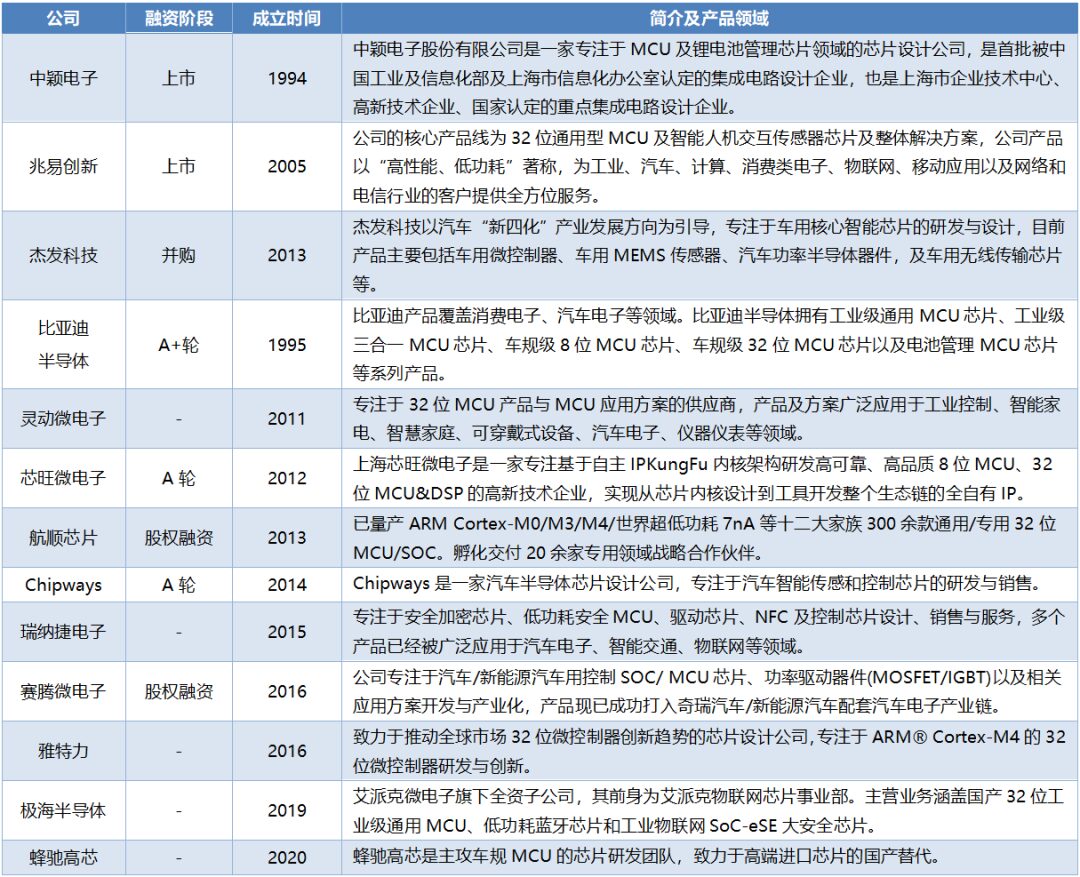
We believe that although domestic companies currently occupy a small market share in the automotive-grade MCU field, the domestic market space and demand for domestic substitution are substantial. Companies that can better leverage their geographical advantages and provide reliable, customized products are expected to continue breaking through and gain larger market shares. We recommend paying attention to primary market investment opportunities in companies such as BYD Semiconductor, Chipway Microelectronics, Chipways, Jihai Semiconductor, and Hangshun Chips.
Contents
1. MCU is the Core Component of Smart Vehicles
2. The Industry is Overall at the End of the Introduction Phase
3. Multiple Factors Drive Domestic Automotive-Grade MCUs into the Growth Stage
4. The Automotive-Grade MCU Industry Chain and Ecosystem Still Need Improvement
5. Accelerated Domestic Substitution Leads to Continuous Changes in Industry Structure
6. Main Conclusions
|
|
1.1
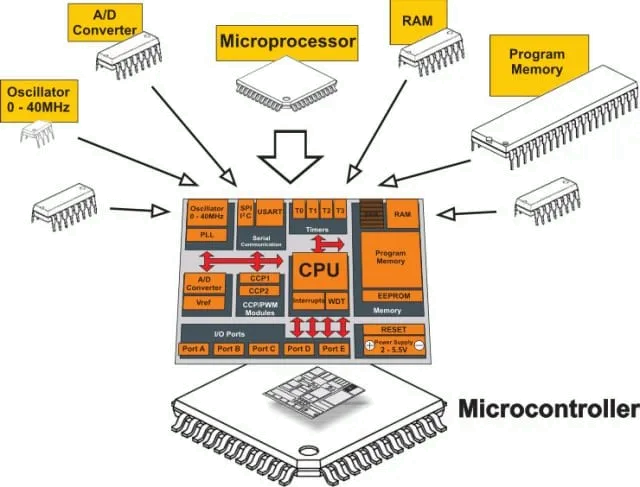
MCUs are Widely Used in Various Industries

1.2
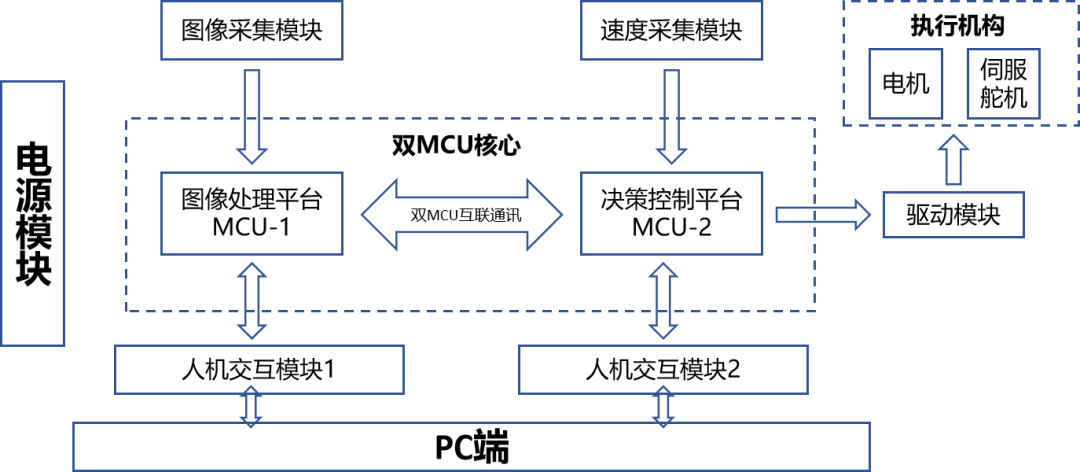
MCUs Will Be an Important Component of the “Brain” of Vehicles

|
|

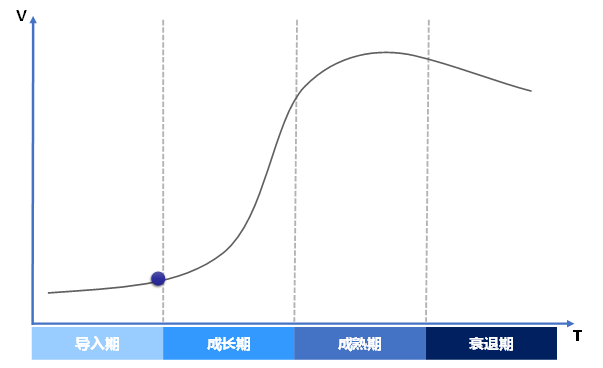
|
|
3.1
Relevant Policies Favor the Integrated Circuit and Automotive-Grade MCU Industry
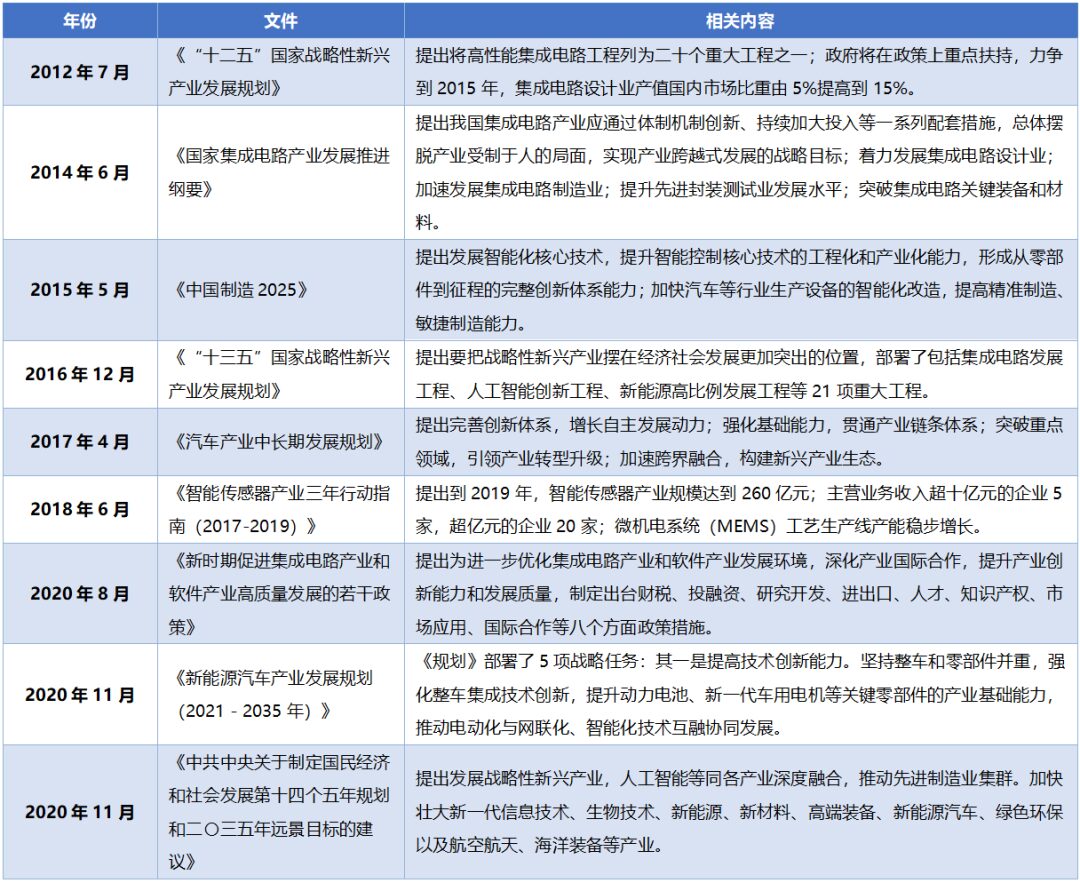
3.2
Domestic Substitution Demand Drives Breakthroughs in Automotive-Grade MCU Bottlenecks
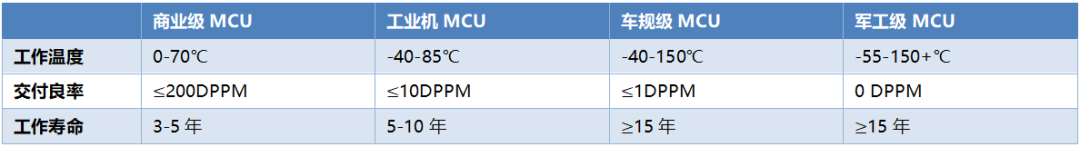

3.3
Smart Connectivity Drives Upgrades of Automotive-Grade MCUs, 32-Bit Becomes the Mainstream Development Direction

3.4
Capital Markets Gradually Enter the Scene, Supporting the Development of Automotive-Grade MCU Industry
|
|

|
|
5.1
External Competitive Environment is Continuously Changing
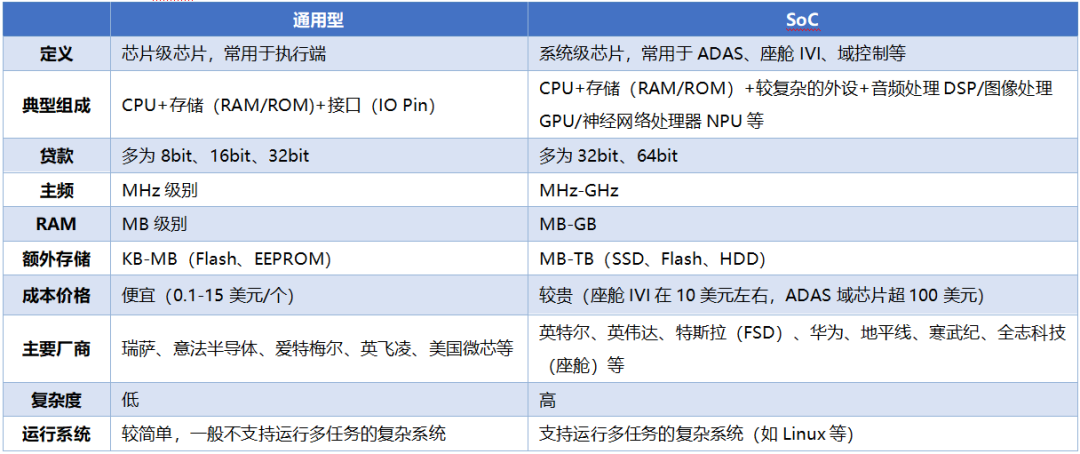
5.2
Domestic Enterprises Achieve Breakthroughs in Automotive-Grade Products
5.3
Domestic Substitution Relies on Continuous Improvement of the Industrial Ecosystem
|
|
Welcome to All Angel Round and Series A Companies in the Automotive Industry Chain (Including the Electrification Industry Chain) (Friendly connections with 700 investment institutions including top-tier organizations; Some quality projects will be selected for thematic roadshows to existing institutions); There are communication groups for leaders of science and technology innovation companies, as well as dozens of groups related to the automotive industry, automotive semiconductors, key components, new energy vehicles, intelligent connected vehicles, aftermarket, automotive investment, autonomous driving, and vehicle networking. Please scan the administrator’s WeChat to join the group (Please indicate your company name)
