
When humanoid robots like “Optimus Prime” walk flexibly, when surgical robots precisely suture blood vessels, and when logistics robots shuttle through warehouses 24 hours a day — behind this AI-driven robotic revolution lies a crucial yet often overlooked “invisible champion”: bearings.
Bearings are not only the “joints” of robots but also the core carriers of precision, lifespan, and intelligence. In today’s explosion of AI robots, bearings are transforming from “mechanical supporting roles” into “intelligent cores”, marking the onset of a silent technological revolution.
Extreme Challenges for AI Robot “Joints”
As AI robots gradually penetrate various fields such as industrial production, medical care, household services, and educational entertainment, the demand for bearings is experiencing explosive growth. According to market research institutions, the market size for bearings used in humanoid robots is expected to soar to billions of dollars within the next few years, maintaining a vigorous growth momentum.
However, compared to industrial robots, AI robots (such as humanoid robots and collaborative robots) impose nearly stringent requirements on bearings:
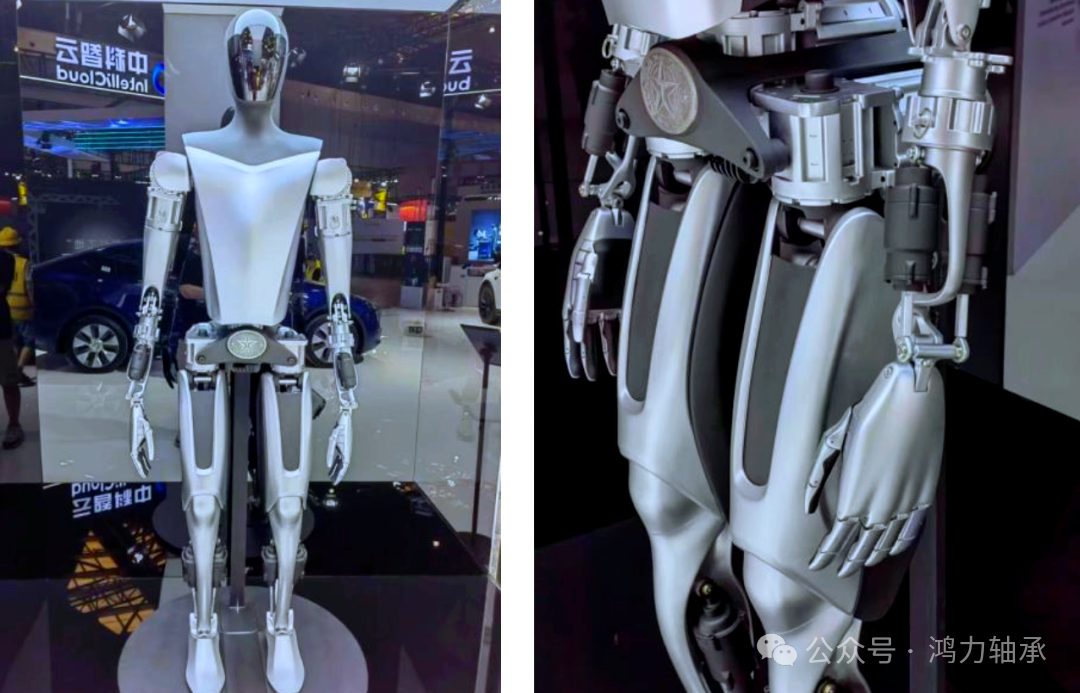
1.Precision: The error of finger joint bearings must be less than 0.001mm (equivalent to 1/80 of a human hair).
2、Lightweight: The leg bearings of Boston Dynamics’ Atlas must withstand 200kg impact force at a weight of 5g.
3、Intelligence: Built-in sensors provide real-time feedback on torque and temperature data, achieving a “perception–decision–execution” closed loop.
4、Long Lifespan: Surgical robot bearings must maintain zero failures over 100,000 surgeries .
Industry Pain Points: The rigid design and high friction loss of traditional industrial bearings can no longer meet the demands of AI robots for flexibility, intelligence, and ultra-precision.
Breakthroughs: Three Major Bearing Technologies
1. Flexible Bearings: Allowing Robots’ “Skeletons” to be as Flexible as Humans
Core Technology: Flexible hinge bearings (such as crossed roller bearings) + superelastic materials (nickel-titanium alloy).
Application Scenarios:
Humanoid Robot Fingers: In Tesla’s Optimus, 19 out of 28 joints use flexible bearings, achieving a gripping precision of 0.1N.
Exoskeleton Robots: The knee joint bearings of Germany’s Ottobock can simulate the stretching of human ligaments, assisting disabled individuals to walk naturally.
2. Smart Bearings: Built-in Sensors as “Nerve Endings”
Core Technology: MEMS sensors embedded in the inner and outer rings of bearings for real-time monitoring of vibration, temperature, and load..
Application Scenarios:
Industrial Collaborative Robots: The joint bearings of ABB’s YuMi predict failures through vibration data, reducing downtime by 90%.
Surgical Robots: The intuitive surgical Da Vinci system’s bearings are equipped with fiber optic sensors, with precision errors less than 0.02mm.
3. Ultra-Precision Micro Bearings: Unlocking Microrobots for “Capillary” Level Operations
Core Technology: Ceramic hybrid bearings with a diameter of less than 1mm (silicon nitride balls + stainless steel cages).
Application Scenarios:
Medical Nanorobots: Micro-robots for targeted drug delivery, with bearing speeds reaching 100,000 revolutions/ minute.
Drone Gimbals: The motor bearings of DJI’s Mavic 3 have a diameter of only 3mm, with stabilization precision of 0.005°.

The Future: The “Symbiotic Evolution” of Bearings and AI
1.Self-Learning Bearings:
AI algorithms analyze bearing wear data to dynamically adjust lubrication cycles (such as Schaeffler’s Smart Bearing).
Boston University laboratories have achieved a bearing lifespan prediction accuracy of 95%.
2、3D Printed Integrated Bearings:
Optisys in the United States has printed RF bearings integrated with antennas, reducing weight by 70%, suitable for space robots.

3.Superconducting Magnetic Levitation Bearings:
Developed by NSK in Japan, magnetic levitation bearings have near-zero friction loss, providing a lifetime maintenance-free solution for rescue robots in nuclear power plants.
